Data is the new oil. We’re now entering a new era of innovative modern information technology, in which the Internet of Things is on a rampant march of explosive growth and the importance of information and data is becoming increasingly prominent. Futuristic as IoT technology, you may be wondering who is the game-changer behind the IoT ecosystem that bridges the digital world to the physical one. That’s how IoT sensors(Internet of Things sensors)- the backbone of IoT solutions – are coming into our sights.
Internet of Things Sensors: the backbone of IoT Solutions
Generally speaking, Internet of Things sensors are pieces of hardware that detect changes in an environment and collect data. The sensor itself is useless, but it plays a vital role when we deploy it in an IoT ecosystem. IoT sensors serve to collect data, communicate and share them with the connected devices of the entire network. All of this collected data enables devices to run autonomously, thus making the entire ecosystem “smarter” every day.
Being the foundation of an IoT ecosystem, sensors provide devices with the ability to collect data and make things happen. Without sensors detecting external information, IoT may become a useless heap of technology. Since there is a wide variety of IoT sensors, almost all the physical properties around us can be measured. Pretty much common sensors are now widely adopted in various fields including medical care, logistics, industry, agriculture, transportation, tourism, disaster prevention, education, and many more.

Classification of Internet of Things Sensors
In fact, there are various classifications of Internet of Things sensors depending on different principles. Sensors can be classified according to their detection principle, output signal, energy relationship, and other considerations. Some of the Internet of Things sensors are simple, and some are hard. In the following passage, we’re going to group IoT sensors in a couple of ways.
- Detection (working) principle.
IoT Sensors can vary in their different detection principle, which refers to the varied mechanisms of chemical, biological, and physical effects. There are resistive, inductive, capacitive, magnetoelectric, photoelectric, piezoelectric, magnetoresistive, resonant, photoelectric, thermoelectric, nuclear radiation, and semiconductor sensors.
- Analog sensor and digital sensor.
Depending on the nature of the output signal, the sensor can be divided into two types: analog signal and digital signal. The sensory signal generated by analog sensors is a continuous output signal proportional to the measured results, while the digital sensors produce discrete signals.
- Active and passive sensors.
The division between active sensors and passive sensors depends on the energy relationship between the sensing element and the object being measured. Active sensors can convert the input non-electric energy into electrical energy output and require no external power supply. Passive sensors are on the contrary.
- Contact and Non-Contact Sensors.
The contact sensor regards the sensor itself and the measured object as one body, and there is no need to calibrate the sensors on the site. For non-contact sensors, the non-contact measurement can eliminate the influence of the sensor intervention and cause the measurement not to be affected, thus improving the accuracy of the measurement.
Different types of Internet of Things sensors
Sensor types vary depending on the sensing object they are intended to measure. Though come in different shapes and sizes, smart sensors are essential IoT components capable of converting the real variables they measure into streaming digital data that can be transmitted to gateways. Down below are some of the most widely used sensors in the IoT world.
7 Internet of Things sensors from MOKOSmart
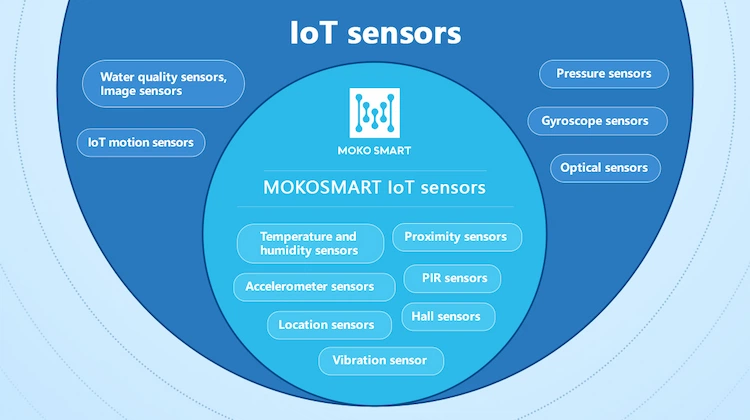
Temperature and humidity sensor: A temperature and humidity sensor, as its name suggests, measures the amount of heat and humidity generated from an area or an object. It detects temperature and humidity changes, enabling us to perform various tasks ranging from manufacturing to agriculture to healthcare.
Proximity sensor: Proximity sensors are widely used in proximity marketing, when passers-by or customers are near the targeted object, a promotion notification will be sent to their phones.
Accelerometer sensor: Such sensors are essential for fleet management, making it possible to monitor and control speed remotely. In addition, 3 axis accelerometer can also be used to monitor whether people or objects fall, and trigger warnings with the panic button integrated.
PIR sensor: The PIR sensor monitors the movement of people and objects, allowing you to see if there are people in your home or other important spaces. On the one hand, it avoids significant property damage caused by the invasion, and on the other hand, it helps maximize space management.
Location sensor: Almost all industries have positioning requirements. Location sensor is often used for warehouse management, smart attendance management, asset tracking, and personnel tracking.
Hall sensors: Hall Sensor is used for automatic switches, the direction of motion, and speed, and is commonly used for automated management of vehicles and various appliances.
IoT vibration sensor: The IoT Vibration Sensor on a vehicle can trigger an alarm in the event of abnormal vibration, preventing the vehicle from being abandoned, or allowing administrators to take timely action.
Other 6 types of Internet of Things sensors trending in the market
Optical sensor: Optical sensors can measure and convert physical quantities of light rays into electrical signals that can be easily read by users or electronic instruments/equipment. Optical sensors are applicable in environment monitoring, healthcare, aerospace, energy, and many more industries. Some of the main uses include ambient light detection, optical fiber communications, and digital optical switches.
Water quality sensor: Water is as essential as air for the smooth going of life, so water quality sensors are widely put in use for checking water quality. Water quality sensors can measure different values such as PH value, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, clarity, and more to ensure that the water is pure enough for daily consumption. There are different kinds of water sensors, including residual chlorine sensors, turbidity sensors, pH sensors, and total organic carbon sensors.
Image sensor: Converting optical data into electronic signals for displaying or storing files electronically, image sensors have found deployment in digital cameras, medical imaging systems, media houses, smart vehicles, night-vision equipment, thermal imaging devices, sonars, radars, and security systems. Image sensors can be found whenever a smart device is required to ‘see’ its surroundings.
Pressure sensor: The task of pressure sensors is to detect pressure changes in gases and liquids. If there is any deviation from the standard pressure range, notification of any problems that need to be fixed can be sent to the monitoring administrator. One application is in medical devices, such as blood pressure cuffs, to make sure the patient’s blood pressure matches the number displayed.
Gyroscope sensor: Gyroscope sensors are capable of detecting rotation and measuring angular velocity, making them ideal for navigation systems, robotics control, consumer electronics, cellular & camera devices, and manufacturing processes involving rotation. Due to its ability to detect rotation or twists, its application can be found in sports activities to help athletes measure body movements and improve their performance after analysis.
IoT motion sensor: Motion sensors help detect physical movement within a given area. Apart from the primary application of security monitoring, motion sensors have been extended to automatic door controls, automated sinks, toilet flushers, hand dryers, automatic parking systems, energy management systems, etc. As technologies advance, opportunities for motion sensors will continue to grow.
Considerations when choosing Internet of Things sensors
More and more businesses are realizing that IoT devices or sensors can bring greater efficiency and increased profitability, but many struggle to choose the right Internet of Things sensors to meet their specific needs. Let’s take a look at some of the most important factors that you can take into consideration when choosing IoT sensors.
• Accuracy: Accuracy of the Internet of Things sensors can be utilized to ensure efficient usage of the device in a specific location, especially when precise information tracking or measurement is required.
• Cost: Budget comes next. The cost of the sensors should be as low as possible so that the implementation of a use case can be feasible.
• Connectivity: Due to the diversity of communication protocols in IoT networks, connectivity is a key component in the IoT ecosystem. Sensors should be compatible with more communication protocols.
• Longevity: IoT devices can take a long time to deploy and maintain remotely, so it’s important to consider their longevity. The stronger the battery, the better the performance of IoT sensors.
• Security: In terms of sensors and security, attention must be paid to sensor vendors whether they can handle security issues properly and avoid any data disclosure.
How much did the COVID-19 outbreak affect IoT sensors’ market progress
With the sudden outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an unexpected domino effect in industries around the world, and the IoT sensor market is no exception. The sensor market was severely impacted by the COVID-19 virus, resulting in a sales decline of more than 10%. Both supply and demand for IoT sensors have been affected, with production facilities shutting down and the supply chain disrupted leading to a decline in IoT sensor production, and social distancing reducing the number of Internet of Things sensors used in business applications.
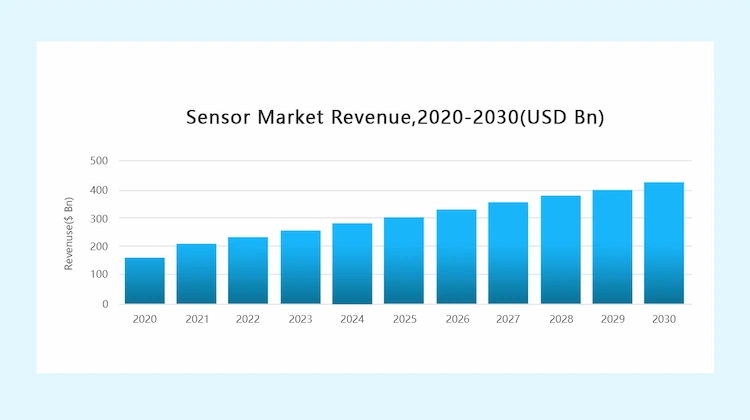
According to Next Move Strategy Consulting, the global sensor market is projected to more than double in size from 151.40 billion in 2020 to 431.21 billion dollars in 2030. While the growth of the IoT market is hampered by COVID-19 in the short term, the trend is toward smart sensors in the coming years. This is due to the numerous advantages of sensors such as increased productivity, high current capability, ease of installation, and reduced overall cost, as well as other factors such as the explosion in IoT technologies, development of smart cities, rising usage of smartphones, and other technological advancements.
FAQs about IoT Sensors
1. What is the Internet of Things sensor data?
IoT sensor data refers to the data collected by smart sensors and devices in any Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. These sensors and devices can range from large objects like a car to small gadgets like a thermostat. Once collected, data can be transmitted to the networks for further analysis and instructions.
2. What data do IoT sensors collect?
Due to the wide variety of IoT sensors, the same is true of the data collected by sensors. Sensors can collect an immense amount of information about their surroundings including temperature, humidity, light, location position, activity level, movement tracking, attendance of students, and many more.
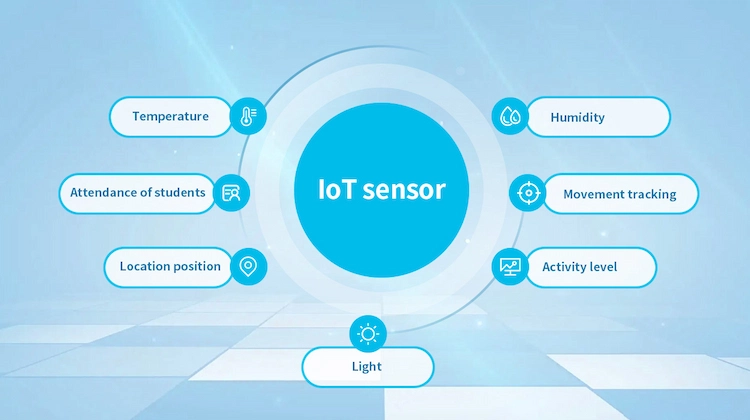
3. What are the advantages of IoT sensors?
The advantages of IoT sensors are numerous, including:
- Collect data on processes and assets in real-time
- High current capability
- Monitor processes and assets accurately, continuously, and reliably
- Increased productivity and reduced total cost
- Lower energy wastage
4. How do sensors work in general?
By changing its electrical properties, the sensor can respond to changes in physical conditions. In simple terms, sensors convert stimuli such as heat, light, sound, and motion into electrical signals, which are converted into binary code by an electronic system and passed on to a computer for processing.
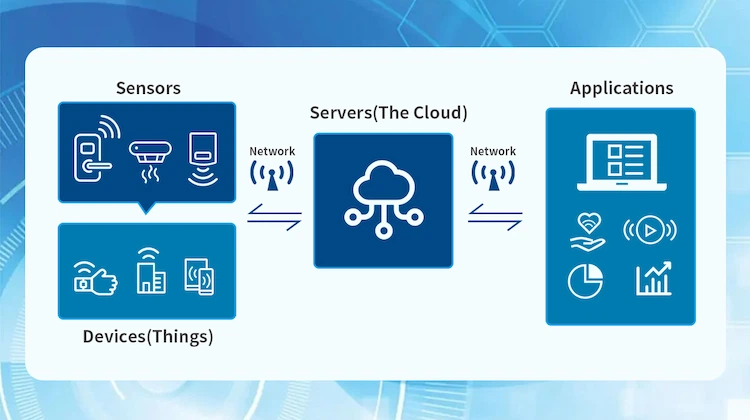
Bottom line
As we continue to step into a more connected world, IoT devices and sensors are increasingly finding their way into our day-to-day lives. Whether in our homes or industries, IoT applications are no longer out of reach. If you would like to learn more about IoT sensors and other topics related to IoT technology, we encourage you to request a consultation today.