We’re living in radical times where IoT tech is blowing up! Therefore, we come across hip terms like LoRa and LoRaWAN all the time. Most people use these two terms interchangeably because they seem similar. However, this is not perfectly true as there are some key differences we gotta break down. In this guide, we’ll scope the main distinctions between LoRa and LoRaWAN. We’ll also check out some real-world use cases using them and the rad benefits they bring. By the end, you’ll be an expert at telling these wireless IoT techs apart!
Understanding LoRa and LoRaWAN
Before understanding the key differences between LoRa and LoRaWAN, we will have to develop a keen understanding of the definitions and working architecture of LoRa and LoRaWAN.
What is LoRa
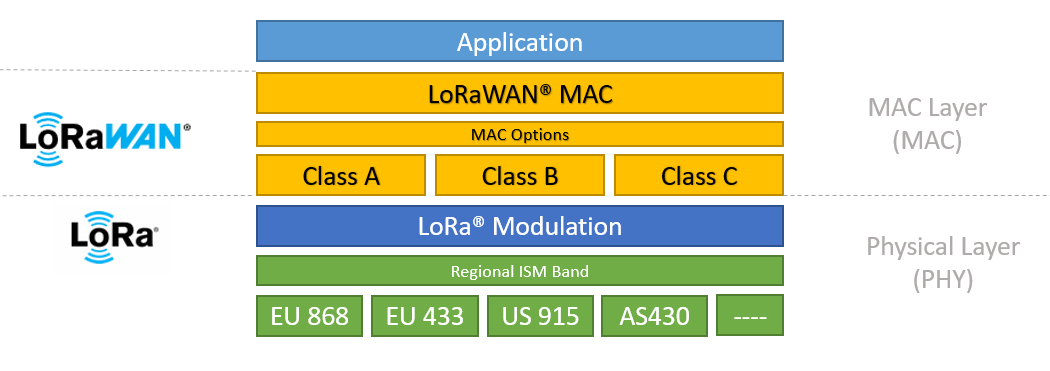
LoRa (Long Range) is a long-range wireless communication technology that operates on radio frequencies to provide IoT connectivity. Developed by Semtech, LoRa acts as the physical layer for transmitting data wirelessly over long distances. You can use a LoRa modem for converting any data set into this radio frequency signal.
At its core, LoRa modulates signals using Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) – a modulation technique making the signal resilient to noise and interference. This helps LoRa effectively harness the full channel bandwidth when transmitting data from IoT devices. Compared to WiFi and Bluetooth, LoRa is famous for its superior communication range, enhanced receiver sensitivity, and large data transmitting capabilities.
LoRa works on license-free sub-GHz frequency bands such as 433MHz and 915MHz. This lets a single LoRa gateway connect thousands of IoT devices spread over several kilometers. Hence, LoRa is ideal for implementing robust IoT applications over wide areas.
What is LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a communication protocol that connects the IoT application with the LoRa signal. LoRaWAN is embedded in the IoT device’s data transfer layer. Operating on the data link layer, LoRaWAN gives you control over the network architecture and communication protocol. Hence, we are better able to determine the service quality, remaining battery span of the connected nodes, capabilities and capacity of the network, and possible security vulnerabilities and the type of applications that are under usage.
Importantly, the LoRaWAN protocol is defined and managed by the LoRa Alliance. LoRaWAN complements the radio frequency signals of LoRa. Therefore, we are able to create economical, bi-directional, low-powered, long-range, IoT solutions that we can deploy in scenarios involving wide ranges. LoRaWAN requires fewer gateways for establishing any network. This is a prominent reason why LoRaWAN is gaining popularity for deployments in applications like Smart cities etc.
LoRa and LoRaWAN network architecture
LoRaWAN networks utilize a star-of-stars topology with gateways relaying data between end nodes (sensors) and a central network server. The wireless connection between end nodes and gateways uses the LoRa physical layer for long range, low power communication. Gateways then forward messages from end nodes to the network server over IP networks.
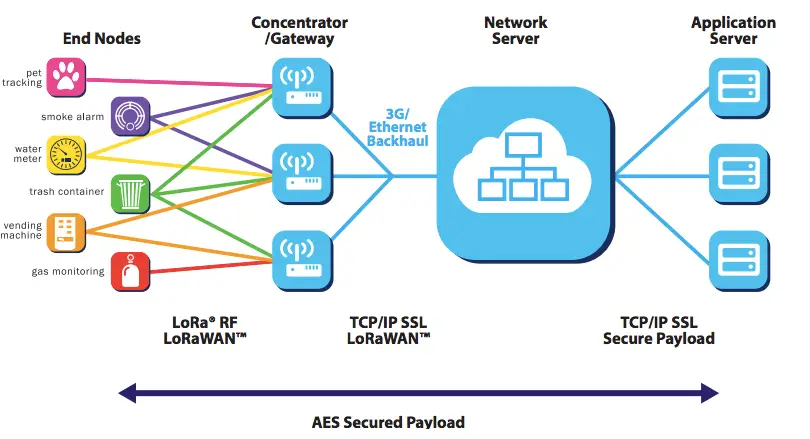
- End nodes: End nodes contain sensors, a LoRa transceiver for wireless communication, and optionally a microcontroller. They transmit directly to gateways in range using LoRa modulation.
- Gateways: Gateways act as a bridge between end nodes and the network server, converting RF LoRa packets to IP packets. They are powered and connected to the network server via IP.
- Network Servers: The network server receives data from gateways, handles de-duplication and routing to application servers. It enables bidirectional communication – both uplink from nodes and downlink from the application.
- Application Servers: Application servers build end-user applications and integrate with other cloud services. They interface with the network server to communicate with the LoRaWAN network.
LoRa vs LoRaWAN: a comparative analysis
Here is a table summarizing the main differences between the physical layer LoRa and the networking layer LoRaWAN:
| LoRa | LoRaWAN | |
| Technology type | Physical layer modulation technique (CSS) | Network layer communication protocol |
| Modulation | Chirp Spread Spectrum | Builds on LoRa PHY |
| Frequency Bands | 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz | 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz |
| Developer | Developed by Semtech | Managed by LoRa Alliance |
| Power Consumption | Low power wireless connectivity | Low power optimized for IoT devices |
| Range | Long range wireless modulation | Long range leveraging LoRa |
| Data Rates | Low Data Rates | Low Data Rates |
| Bi-directional communications | No | Yes |
| Application | Robust signal modulation | LPWAN for IoT/M2M |
LoRa and LoRaWAN – The backbone of LPWAN
With the growing trend of IoT, we are seeing more and more LPWAN deployments. Many tech giants and IoT companies are relying heavily on LPWAN for various applications. In fact, LoRa and LoRaWAN are becoming the de facto standard for large-scale and wide area IoT deployments. It is interesting to see that LoRa and NB-IoT will dominate the LPWAN market with over 85% of the connections worldwide in 2028.
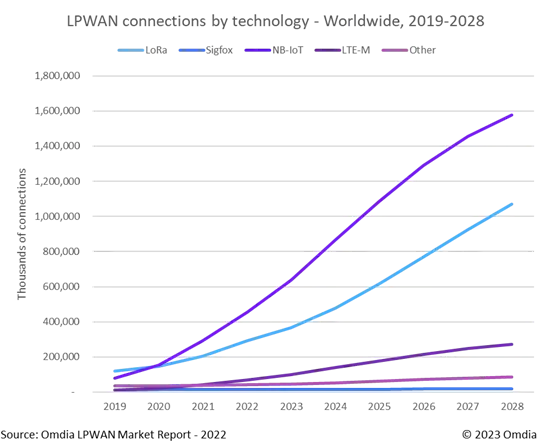
This growing community ensures an ecosystem of innovation that encourages everyone to switch to a more trustworthy solution. There are many reasons for this rapid growth and we will take a look at some of them.
- Lower costs: LoRa and LoRaWAN operate on free bandwidths. Therefore, they are more accessible. Moreover, LoRaWAN network components like gateways and devices are more economical compared to cellular or WiFi.
- Simpler deployment: LoRaWAN networks are easier to deploy than traditional cellular, requiring just endpoints and gateways.
- Long range connectivity: A single LoRa gateway can connect thousands of endpoints over several kms.
- Security: Encrypted data transmission end-to-end.
- Standardized protocol: Being an open standard enables interoperability.
- Bi-directional capabilities: LoRaWAN’s bidirectional communication enables downlink control messages.
- Rapidly growing ecosystem: The LoRa Alliance has over 500 partners worldwide.
Groundbreaking benefits of LoRa and LoRaWAN
There are many groundbreaking benefits of LoRa and LoRaWAN. However, here we will take a look at only a few of them.
- Long-range capabilities make it possible to implement innovative solutions like smart city applications.
- They require low power hence it ensures that the connected IoT devices will have longer battery life.
- Their low bandwidth makes it perfect for IoT deployments which are practical. This is because such deployments require fewer data transmissions or the data transfer isn’t constant.
- They are easier to set up as compared to other technologies. Additionally, they are faster to deploy as well.
- These have two security layers. One layer is dedicated to the network and the other is dedicated to the application. Both feature AES encryption hence you will have the assurance that you won’t have any security vulnerabilities.
- They allow for complete bi-directional transmission and communication.
- These operate on an open standard that is protected under and open LoRa alliance.
Real-world use cases of LoRaWAN and LoRa
There are numerous possibilities for using LoRa and LoRaWAN solutions. However, key players are only interested in certain sectors and they are only investigating the most promising probabilities. Some of these involve the development of smart parking lots, smart traffic and waste management, remote metering, safer homes and buildings, better supply chain and logistics, convenient and productive farming, efficient mining, and automated manufacturing. Simply put, LoRaWAN is ideal for many industrial IoT applications involving the interest of private corporations and government entities. In this section, we will take a brief look at some of the unique and prominent use cases.
Minol Zenner uses LoRaWAN in the housing and utility industries in Germany
This is a sub-application of smart and innovative metering. They have developed a solution based on LoRaWAN which can make it easier to perform remote metering. They are currently working on making it compliant with legal standards. Talks are underway to deploy this smart metering system. It will considerably reduce the metering cost and turn the metering process into an automatic one.
Apana’s smart water management system
Before the deployment of this system, they had no way of knowing their current water usage. Apana’s Smart Water Management System not only detects water usage and remaining water levels but also detects and monitors any possible water leakages. Hence, it is capable of preventing any major water loss and therefore it allows for considerable cost reduction. This system is so efficient because it is based on LoRaWAN.
MOKOSmart’s GPS tracker for real-time location monitoring
MOKOSmart is a well-known name in the market for LoRaWAN devices. Our LoRaWAN GPS tracker provides accurate and precise GPS tracking of any shipment or package. The real-time tracking can be easy for customers even if they have no prior experience with IoT. Our GPS tracker is developed by using LoRa and it transmits and processes data through the use of LoRaWAN protocols. It deploys quickly and notifies the customers about the location of their package at all times. Hence, it helps in fighting against asset thefts and combats supply chain disruptions.
ComplianceMate for food monitoring
Laird Connectivity and CM Systems are independent IoT firms that are working on coming up with unique and sustainable IoT solutions. They have developed a product known as ComplianceMate. Its primary purpose is to monitor the nutritious content of food and notify the concerned people if it is unhealthy to eat. Food retailers can integrate ComplianceMate in their refrigerators, food containers, or storage units. It can eliminate contamination by suggesting effective temperatures for food storage and by notifying the retailer if there is any risk.
KotahiNet connects the Cook Islands in New Zealand
KotahiNet has developed a LoRaWAN-based network which is providing a smart sensing infrastructure to the Cook Islands. Private businesses and government entities are able to analyze and collect data from the environment. Therefore, they can make smarter decisions about their limited island resources and extensive business operations. KotahiNet also provides related services and products which are operational on their network.
LoRa and LoRaWAN vs other LPWAN technologies
LoRa and LoRaWAN are leading technologies in the LPWAN space for IoT. How do they compare with other competing LPWAN technologies?
LoRa/LoRaWAN vs NB-IoT
NarrowBand IoT (NB-IoT) is an LPWAN standard developed by 3GPP for cellular IoT connectivity. NB-IoT leverages existing LTE infrastructure but operates in licensed spectrum, so there are costs associated with using NB-IoT networks. NB-IoT offers good indoor penetration and low power operation. However, network deployment flexibility is lower compared to LoRaWAN.
LoRa/LoRaWAN vs Sigfox
Sigfox is a proprietary LPWAN technology using ultra narrow band modulation to enable low-cost, low power connectivity. As it is proprietary, Sigfox offers less flexibility but can provide very low costs at scale. Sigfox has limitations like low uplink messages per day and no downlink capability.
LoRa/LoRaWAN vs Zigbee
Zigbee is based on the 802.15.4 protocol and enables mesh networks for IoT. As Zigbee operates at 2.4GHz, range is lower compared to sub-GHz technologies like LoRa. Zigbee offers interoperability but can have complex network set-up and synchronization requirements. Power usage is higher than LPWAN tech.
The role of LoRa and LoRaWAN in the IoT sector
Many renowned telecom companies rely on LoRa. These are ideal for communications between several data gathering systems involving IoT devices. Such communications involve large data transmissions which happen frequently after set intervals. These have much more to offer them their competitor technologies that is why they are gaining popularity.
Most of the other technologies such as Sigfox operate on ultranarrow bandwidths that is why they are much more expensive and inaccessible. Therefore, it is not practical to deploy these other technologies for large-scale wide area IoT applications. On top of that, other technologies are much more prone to noise and frequency fluctuations. However, LoRa and LoRaWAN are relatively immune to these.
Most key players in the IoT industry are looking to develop products and solutions for IoT applications involving large distances, low power consumption, and large data transfers. Therefore, more and more prototypes based on LoRa and LoRaWAN are in the design phase. With its continued expansion, it will meet our future demands and offer more applicable LoRa and LoRaWAN solutions.
Getting started with LoRa and LoRaWAN
MOKOSmart is a renowned name in the IoT industry. We have years of experience in designing and manufacturing IoT products. MOKOSmart has a dedicated R&D team and we specialize in LoRaWAN-based products. We have mass production capabilities and we can help you with all of your LoRa-related needs. Superior Quality is our hallmark and we always deliver on time. Feel free to contact us if you have any further questions or if you would like to get a quote for LoRaWAN products.
READ MORE ABOUT LORA AND LORAWAN