Het internet der dingen (IoT) overspoelt talloze gebieden van het moderne leven. Nu, IoT has spread to industrial environments as well – hence the term Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) being used more commonly. But what exactly is the difference between IoT vs IIoT technologies? Both are considered essential for a wide range of IoT market applications. With connected smart devices vastly increasing each year, it is critical to consider the deployment factors of IoT and IIoT. In dit artikel, we’ll compare and contrast IoT and IIoT to clarify when and why enterprises should consider their adoption.
An introduction to IIoT and IoT
The IoT market is projected to reach $805.7 miljard in 2023 and is anticipated to surpass $1 biljoen door 2026, according to IDC. Discrete and Process Manufacturing are set to lead IoT investments, constituting over one-third of global spending throughout the forecast period.
The common ground of IoT and IIoT
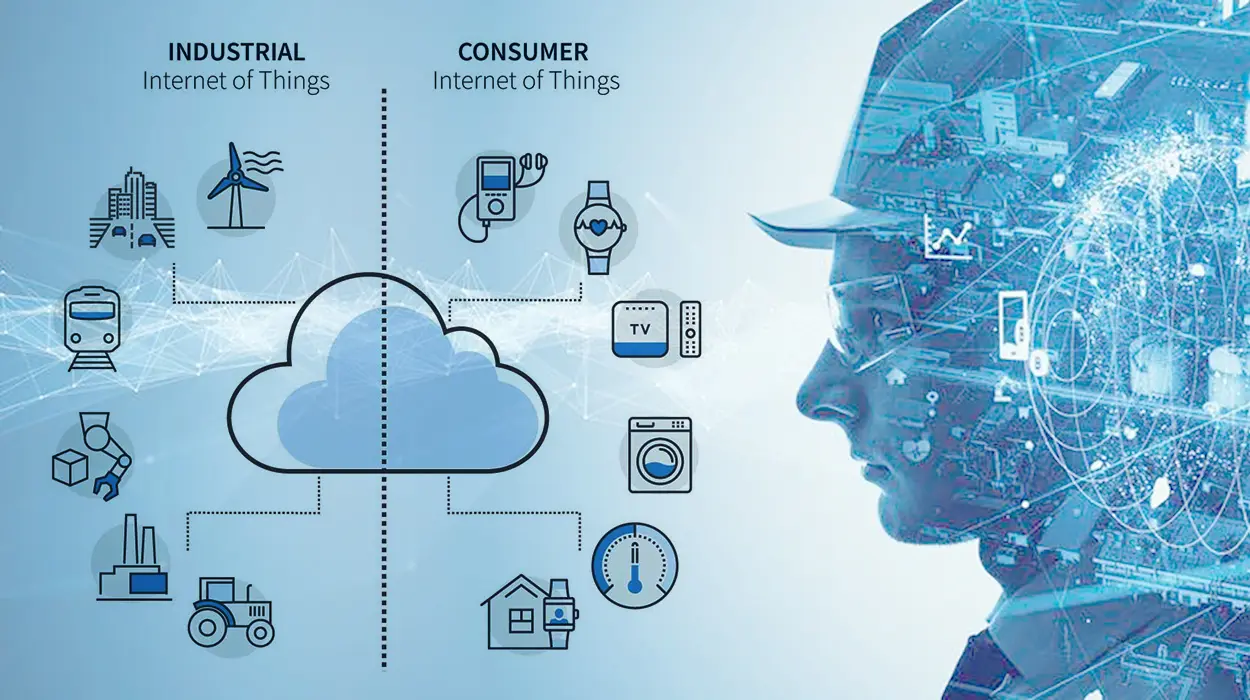
Before delving into IoT and IIoT definitions, it’s crucial to note their shared foundation. Beide, with IIoT being a subset of IoT, utilize common technologies like sensors, cloud platforms, connectiviteit, and analytics. This similarity extends to application domains and adherence to standards and regulations. The universal technology basis for IoT applications, whether consumer-focused or industrial, comprises six domains:
- Device Hardware
- Device Software
- Communications
- Cloud Platform
- Cloud Data
- Cloud Application
What is IoT
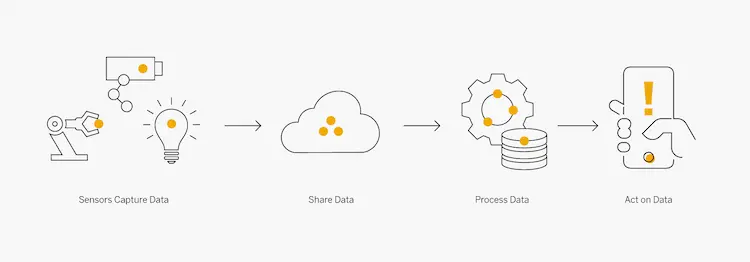
IoT refers to a decentralized network of internet-connected smart devices that can collect and share data via embedded sensors and connectivity. IoT enables devices and electronics we interact with daily – thermostaten, voertuigen, en meer – to be monitored, accessed or controlled remotely. The core components that enable this smart connectivity include:
Embedded Sensors: Collect important data like geolocation, temperatuur, movement and more.
Connectivity Modules: Allow data transmission from device to the cloud servers via WiFi, cellular 4G/5G, Bluetooth and more.
Data Processing Hub: Cloud server that aggregates and processes incoming data from the sensors/devices.
User Interface: Mobile or web dashboards that provide analytics and remote control of IoT ecosystem.
What is IIoT
IIoT stands for Industrial Internet of Things – it refers to IoT technology applied specifically within industrial environments like factories, energy plans, field sites and more. By installing advanced automation and data collection via IIoT, industrial companies gain greater efficiency, control and insights into their operations. Unlike consumer IoT examples like smart homes, IIoT focuses on:
- Connected industrial devices like smart sensors on machinery.
- Optimizing complex operations like manufacturing and supply chains.
- Enabling crucial new technologies like predictive maintenance.
The core components providing connectivity and data exchange in IIoT architecture include:
Industrial Sensors
Wired/Wireless Connectivity
Central Server Hubs
Industrial Network Protocols
Fleet/Asset Management Software
Differences between consumer IoT vs Industrial IIoT
While IoT and IIoT share similarities in connecting devices and leveraging data, there are also clear differences between the technologies:
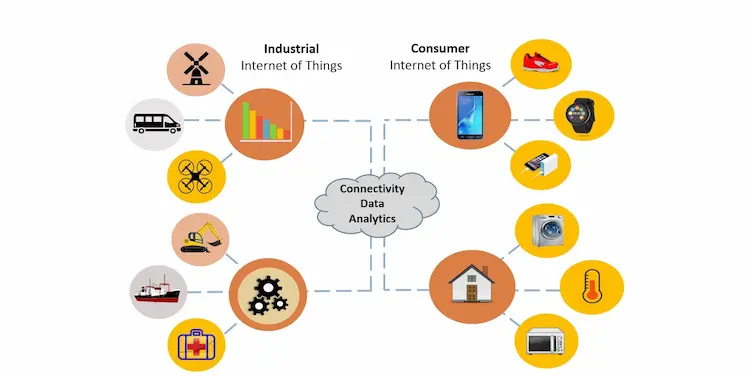
- Market Focus
IoT bestrijkt verschillende sectoren. De IoT-technologie wordt voornamelijk gebruikt door consumenten en experts in zakelijke IoT-achtige ondernemingen, gezondheidszorg, en de publieke sector. Aangezien IoT in verschillende verschillende industrieën wordt toegepast, het heeft de neiging zich meer te concentreren op universele toepassingen. Anderzijds, de IIoT-technologie is gericht op een kleinere markt, aangezien experts deze alleen in industriële omgevingen toepassen. De IIoT-technologie wordt voornamelijk gebruikt in energiecentrales, olie- en gasraffinaderijen, en productiefaciliteiten.
- End Devices
Het IoT en IIoT gebruiken meestal verschillende apparaten, omdat ze allebei verschillende aandachtspunten en doelstellingen hebben. Industriële IoT-apparaten zijn gebouwd om gebruikers gegevens te bieden over apparatuur waar deze apparaten, in plaats van alleen te werken, integreren met bestaande apparatuur. Omgekeerd, IoT-apparaten zijn meestal apparaten die in het dagelijks leven worden gebruikt en die onafhankelijk kunnen worden gebruikt. They include smartphones, smartwatches, slimme thermostaten, en slimme assistenten. Er zijn andere IoT-apparaten zoals slimme sensoren die worden gebruikt om infrastructuren te ontwikkelen.
- Risk of Failing
De kans op uitval bij IoT-apparaten is relatief laag omdat deze apparaten slechts op kleine schaal worden toegepast. Typisch, IoT-apparaten worden niet gebruikt voor herstelpraktijken die een bedreiging vormen wanneer ze falen. alternatief, het falen van IIoT-apparaten en -technologie is gevaarlijker. De IIoT-technologie is gekoppeld aan een systeem; kan daarom levensbedreigende omstandigheden opleveren als een zware machine faalt.
- Environmental Requirements
IoT-apparaten functioneren meestal in dagelijkse omgevingen. Ze zijn ontworpen om standaardtemperaturen en andere ecologische druk te doorstaan. IIoT-apparaten zijn duurzamer en betrouwbaarder omdat ze voornamelijk worden gebruikt in zwaardere omgevingen, zoals fabrieken, energiecentrales, en olieraffinaderijen. Daarom, fabrikanten van IIoT-apparaten maken hun apparaten meestal om extreme temperaturen te verdragen, vochtigheid, en radio-interferentie om ervoor te zorgen dat ze betrouwbare resultaten opleveren.
- Bedieningsveiligheid
Bij het omgaan met de meeste IoT-systemen, de veiligheid van operaties is nooit een punt van zorg, aangezien deze systemen gewoonlijk geen geïndustrialiseerde processen aankunnen. Als er een verkeerde beslissing wordt genomen, er zijn geen ernstige beveiligingsincidenten die kunnen optreden om welke reden dan ook, zoals een verkeerde actie of een cyberaanval.
Bij het omgaan met IIoT-systemen, dingen worden heel anders. Het IIoT is een essentieel onderdeel van de controller-loop. Een ongepaste actie van het controleproces kan het netwerk in onstabiele en onveilige situaties brengen. Vandaar, het is zeer belangrijk om PLC's te hebben, sensoren, en een communicatieprotocol of proces in het systeem. Mensen kunnen snel hun leven verliezen in het geval van één onvoorzichtige fout.
- Betrouwbaarheid van de werking:
Bedrijfszekerheid is essentieel, aangezien de beslissingen van mensen volledig afhangen van het resultaat van het IoT-proces. Een IoT-systeem is in staat om opzettelijke of onjuiste handelingen van een goedgekeurd persoon te identificeren en te detecteren. Volgens de exacte toepassing:, het IoT-netwerk moet worden uitgerust met uitzonderlijke maatregelen om elke manipulatie te detecteren en cyberaanvallen te ontwijken die een slecht resultaat kunnen opleveren.
In IIoT, deze beperking is essentieel omdat het systeem een onderdeel is van de ICS-architectuur. Van het grootste belang, betrouwbaarheid is een fragment van de Safety, Betrouwbaarheid, en productiviteit (SIKKEL) triade. Zoals in IoT, IIoT-systemen kunnen ook opzettelijke of onjuiste handelingen van een goedgekeurd persoon detecteren.
- Communication Media
De architectuur van een IoT-ecosysteem moet overeenkomen met de communicatiemedia en het protocol. Aangezien de operaties consumentgericht zijn, het is zeer waarschijnlijk dat het systeem moet bestaan uit Bluetooth, WIFI, en mobiele netwerken. Ook, het maakt gebruik van standaard IT-protocollen. Een uitgebreid IoT-netwerk maakt gebruik van al deze media waar het individueel cyberbeveiligd moet zijn.
Als onderdeel van de ICS-architectuur, het IIoT-netwerk biedt draadloze en bekabelde verbindingen tussen de ICS-server, de sensor, en de PLC. Van die communicatiemedia, informatie wordt doorgegeven aan de provider van het IIoT-netwerk, waar u eenvoudig de aanwezigheid van ICS-georiënteerde protocollen kunt zien. U moet de netwerklatentie verifiëren in de IIoT-ecosystemen die u verwacht om binnen korte tijd feedback te krijgen.
- Cyber Defense
Aangezien de IoT-ecosystemen te maken hebben met consumentgerichte eindapparaten die in winkels zijn gemonteerd, huizen, kantoren, busstations, enzovoort., cyberdefensie betekent een fundamenteel probleem. Deze IoT-apparaten verbeteren de publieke geschiktheid; echter, de technologie wordt geleverd met kostenbeperkingen die de bevestiging van cyberverdedigingsmaatregelen voorkomen. Het is ook altijd belangrijk;
een) Implementeer een verbeterde cyberverdediging voor het systeem dat verbinding maakt met deze apparaten
b) Waar van toepassing, zorg ervoor dat u uw verificatiemaatregelen bijwerkt, such as the device username and password.
c) Voer constant scans uit op uw systemen om vreemde of niet-geautoriseerde apparaten te detecteren
niettemin, met IIoT, dingen zijn heel anders. Het cyberrisico is hier hoger, hoewel de investeringsmiddelen voor retrofits en upgrades gemakkelijk te verkrijgen zijn. Bovendien, naar best practices van het IoT-netwerk dat hierboven al is vermeld, het is ook essentieel om extra maatregelen te overwegen voor uw IIoT-ecosysteem.
een) Voer gevoeligheidsanalyses en aanpassingen uit om de fysieke beveiliging van uw apparaten te verbeteren.
b) Het inbraakdetectiesysteem gebruiken (IDS) om elke afwijking te detecteren
c) Voeg andere speciale verificatiemaatregelen toe die handig zijn voor uw IIoT-ecosystemen
Examples of IoT applications
Here are some of the most common examples of Internet of Things technologies transforming consumer products and experiences:
Connected devices allow homeowners to remotely monitor energy consumption, control lighting/appliances, receive alerts and automate household activities.
Wearables
Internet-connected exercise trackers, smartwatches, medical monitors and more are shaping the wearables market.
Slimme steden
IoT technology underpins smart city infrastructure. Sensors can monitor traffic congestion, alert authorities about needed road maintenance or send real-time public transit updates to waiting commuters.
Slimme gebouwen
IoT stelt steden in staat om de productiviteit en werking van openbare gebouwen te verhogen. Slimme technologie kan in steden worden gebruikt om informatie uit verschillende systemen in het gebouw te verzamelen, zoals lichten, liften, en airconditioning.
Slimme hulpprogramma's
Sensors are integrated into smart cities’ infrastructure to improve productivity, onderhoudsprogramma's uitbreiden, bediening op afstand toestaan, en andere voordelen behalen. Sensors can be mounted in street lights, wegen, watersystemen, transportation networks, enzovoort.
Connected Vehicles
Automakers are getting onboard with IoT too! Modern vehicles collect telematics data to relay nearby traffic conditions. Consumers also leverage IoT for tracking drivers, fuel efficiency and automating maintenance updates.
Examples of IIoT applications
Meanwhile in industrial environments, IIoT is proving equally transformative by optimizing complex operations, improving uptime and avoiding equipment failures. Common IIoT factory and enterprise use cases include:
Connected Robotics & Assembly Lines
Factories link robots, conveyors and assembly line components to collect production metrics. Insights improve manufacturing efficiency, output quality control and speed of design iterations.
Voorspellend onderhoud
Instead of reacting to equipment breakdowns, IIoT sensors detect early warning signs of wear and tear. This allows manufacturers to schedule predictive maintenance saving an estimated 12-18% over routine upkeep.
Supply Chain/Logistics
IIoT tracking devices allow enterprises to monitor product handling temperature, trailer refrigeration, location and more. This ensures timely handling and adherence to safety policies from factory to end customer.
Energiebeheer
Within offices or production environments, IIoT-connected HVAC, lighting sensors and other building systems reduce wasted electricity – targeting 10-15% lower energy consumption.
Advantages of leveraging IoT and IIoT
Implementing IoT or IIoT delivers quantifiable technology advantages plus harder-to-measure benefits related to customer/employee experiences, sustainability and future competitiveness.
For consumer IoT, advantages include:
– Gemak: Controls that automate our environment and daily tasks or summon services/content on-demand.
– Veiligheid & Security Monitoring: Real-time home security alerts and entry access controls for peace of mind.
– Gezondheid & Wellness Tracking: IoT wearables provide vitals monitoring and help individuals set and achieve fitness goals.
Industrial IIoT advantages for operations and the bottom line include:
– Time and Cost Savings: Optimized processes mean faster production cycles and less waste.
– Minimized Equipment Downtime: Data insights enable predictive maintenance and near-zero loss of productivity.
– Enhanced Workplace Safety: Wearables that monitor employee biometrics plus environmental anomaly alerts.
– Duurzaamheid: Reduced energy consumption and material waste.
Why IIoT is the backbone of Industry 4.0 transformation
IIoT stands as a core enabling technology for the digitization of manufacturing happening under the banner of Industry 4.0. By providing equipment interconnectivity and data exchange, IIoT empowers the information-driven and hyper-connected factory.
Additional Industry 4.0 technologies like industrial big data analytics, kunstmatige intelligentie, digital twin simulations and cloud-based industrial software platforms integrate directly with IIoT sensors and infrastructure. Samen, these innovations enable entirely new capabilities like:
– Decentralized Production Decisions: IIoT machinery self-modifies based on operating data instead of centralized control.
– Intelligent Supply Chain Adaption: Inventory levels automatically shift based on real-time order data.
– Rapid Design Iterations: Simulated digital twin tests of new products replace physical prototypes and trial runs.
A McKinsey survey on Industry 4.0 indicates manufacturing companies are ramping up IIoT adoption to drive efficiency, expecting 15-30% improvements in labor productivity and 30-50% reductions in machine downtime. But cost optimization tells only part of the story – IIoT also unlocks game-changing innovations to serve customers better and pivot strategically.
MOKOSmart’s IoT and IIoT hardware solutions
Trusted by over 7,132+ customers globally, MOKOSmart offers a versatile lineup of IoT hardware perfectly suited for various applications. Our product portfolio includes IoT-sensoren, spoorzoekers, connectivity modules, gateways, en slimme stekkers.
MOKOSmart’s sensor offerings detect crucial environmental metrics like temperature, vochtigheid, water leaks, en beweging. Connectivity options range from WiFi, Bluetooth to Cellular and LoRa ensuring reliable transmission.
Whether you are an engineer exploring IoT solutions or software managers needing IoT end devices, MOKOSmart delivers proven IoT hardware engineered for various demands. Learn more about realizing the IoT solutions today.