Increasing climate change has led to the extension of wildfire season, which has infinitely expanded the frequency and scope of disasters, causing confusion and certain economic losses to residents and governments. According to the National Interagency Fire Center, twice as much soil was charred by fires in the United States between 2000 and 2020 as in the previous two decades. And there were 58,985 wildfires burning 7,125,643 acres in the US In 2021. California lost the most buildings of any state: 2,031 homes, 196 commercial/mixed homes, and 1,136 small buildings. In response, governments and companies are investing in technology to detect and respond to fires in time. IoT fire detection systems can be deployed to forests and open areas to alert fire authorities. IoT involves a variety of technologies, including LTE/5G, LoRaWAN, GPS, NB-IoT, and so on. So how is the IoT fire detector sensor being applied specifically? Read on to dig out.
How does IoT forest fire detection work?
Sensors are deployed in areas the fire department wants to protect, typically at a height of one meter and 50 meters apart, forming a virtual low-power electronic fence. These sensors picked up the presence of the fire one by one as it spread. When the sensor detects a fire, it sends this information to the gateway, which will send the data back to the cloud. And then the platform alerts local authorities when it detects a potential fire.
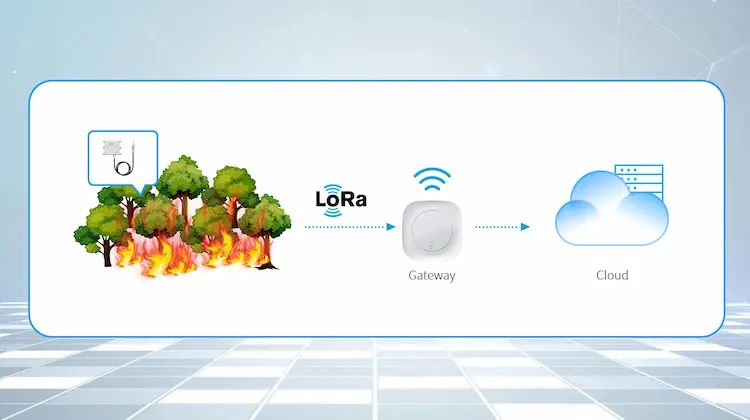
Use IoT fire detector sensor for fire detection in 3 ways
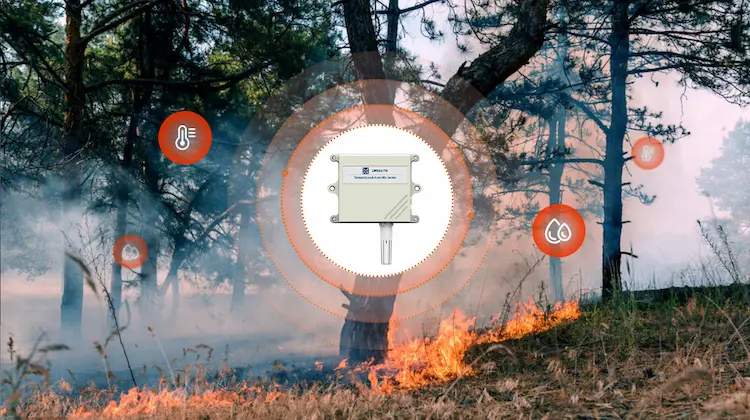
- Identify a forest fire
IoT sensors can help identify and manage wildfires by detecting temperature, humidity levels, and wind direction. In particular, heat insulation sensors can monitor the location, intensity and spread patterns of the initial start of a fire. Remote IoT fire detector sensors collect this data to report fire conditions to first responders and the community. For devices and associated sensors deployed in forests and other distant areas, minimal energy use and long battery life are among the keys to success. Considering that most fires occur in rural and remote areas where the Internet is not readily available, a LoRaWAN mesh network with cellular back transmission and cellular-enabled sensors ensures that sensor data is transferred to the Internet. Data from these sensors help support strategic approaches and key decisions to firefighting efforts.

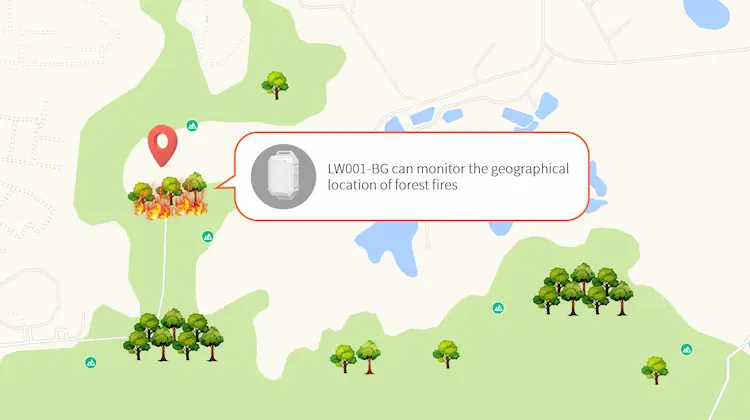
- Report the location of the disaster area
In addition to determining the likelihood of a fire breaking out in a particular area, an IoT fire detector sensor can also report the precise geographic location of the fire. The most widely used positioning technology in the early days was GPS. With the rapid development of LoRa and NB-IoT, fire departments have more options to choose from, and solution providers can provide a hybrid solution for different needs, allowing firefighters to get to the front line in the fastest time.
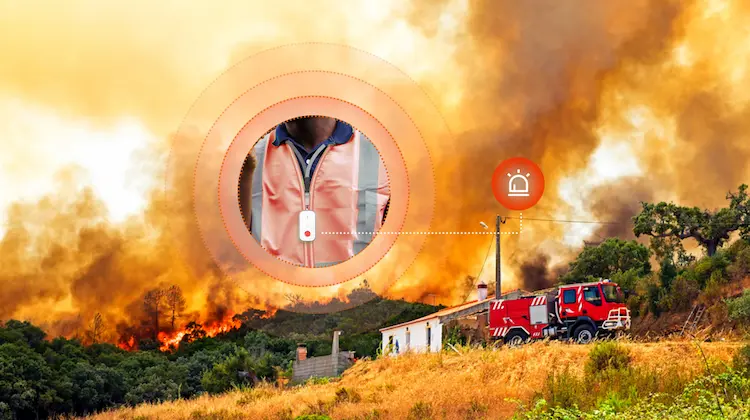
- Send out an alarming alert
In the event of a fire or other accident in the wilderness, it is difficult to be detected, so it’s necessary to deploy a fire detector sensor that can detect the disaster and then automatically report a warning for help.

The challenges of detecting wildfires using the Internet of Things
Early experiments with field-deployed sensors and digital fire detector sensors were established, but large-scale use was impractical. In many remote areas where wildfires are burning, Internet access is severely limited. From a cost and implementation standpoint, a sensor mesh network covering hundreds of thousands of acres is nearly impossible, especially when you consider that these sensor networks are regularly disrupted by what they’re supposed to detect. But the Internet of Things and sensors still have an important role to play in fire detection and prevention. Infrared sensors installed on the drone can automatically scan the forest floor to know the time and temperature of ignition and ignition in advance. The incident response app can send alerts to first responders and lead them to aimed locations via GPS sensors on smartphones.
These smaller, more manageable networks of field-deployed temperature sensors make a great difference in simulating fire behavior through controlled combustion. Mapping the movement of heat and how it is affected by vegetation, wind, and other environmental factors plays an important role in many coping and evacuation strategies. There are countless other digital signals like, traffic from navigation apps, social media posts and smart home smoke detectors that should be harnessed.
Solve problems with MOKOSmart
Forest wildfires are a growing threat to forested areas with prolonged dry seasons. As their frequency and severity continue to increase, innovative and adaptive solutions are needed to detect, contain, and ultimately eliminate them before they spread to endanger communities and habitats.
Because forest wildfires occur in places where traditional cellphone service is inadequate, MOKOSmart developed an infrastructure that uses LoRa connections to be more adaptable and flexible in remote areas. Forest fire detector sensors are deployed in fields or forests 15 kilometers apart and collect values every few minutes that might indicate the presence of a fire. These sensors send data to the LoRa gateway, which is processed by an artificial intelligence platform, providing a detailed, comprehensive view of conditions in the monitored area. If a fire (or the possibility of fire) is detected, emergency control personnel will be on standby.
MOKOSmart offers a scalable, cost-effective, secure and unmatched IoT solution for any application. From global cellular data connectivity to IoT infrastructure platforms and industry-leading device management, MOKOSmart sets the standard for future enterprise IoT deployments. MOKOSmart customers can count on future-proven, always-on connectivity anywhere in the world, benefiting from industry-leading experience in the most unique deployments.
In nutshell
Firefighters and first responders can use the information to limit the impact of environmental disasters However, communities and government businesses must invest in these technologies to predict and prevent wildfires from becoming uncontrollable anyone living on the West Coast knows how devastating wildfire season can be, so via LoRaWAN, LTE/5G, AI, and other IoT technologies are needed to slow and prevent the damage of future wildfire seasons