The use of wearable technology has steered an increased demand in health industry, thereby generating a more booming market. At MOKOSmart, we have health wearable devices, such as wearable beacons. They are specifically used for management in health sector or information gathering for peoples’ health status.
Developments in and the Future of Health Wearable Devices
Currently, there is a surge in the health wearable technology market. More wearable technology has been put in the hands of businesses and consumers by its maturation. It is predicted that by 2023, the total number of fitness trackers and health-based wearable is likely to surpass 120 million.
This ascendant growth tendency in wearable fitness technology can broadly impact the choice of insurers and health providers to take advantage of all reimbursements of the wearable health devices. The rising cost per patient has been lessened by insurers when they use wearable to increase the lifetime value of customers. Well-managed personal health largely contributes to wearable technology behavior that diminishes hospital visits and readmissions. wearable assist more than 75% of users in engaging appropriately with their health.
Also, companies have significantly benefited from their wearable healthcare technology offers to employees. A healthier corporate culture reduces the turnover of employees. An average turnover of 18% is recorded by all employers who provide more than five wellbeings ‘best practices’ whereas 29% is recorded to those that offer less than three.
Moreover, advanced accurate wearable sensors influence the expansion of device connectivity. This opens room for employers and insurers to impact healthy routines and improved profitability.
Wearable Technology Devices and Applications in the Healthcare Sector
The continuous growth in demand of consumers willing to fully control their health and improvements of wearable technology has impacted the medical industry in developing more wearable devices like wearable monitors, smartwatches and wearable beacons. Some of the wearable technology applications and devices in the healthcare fraternity include;
a) Smart Medical Beacon
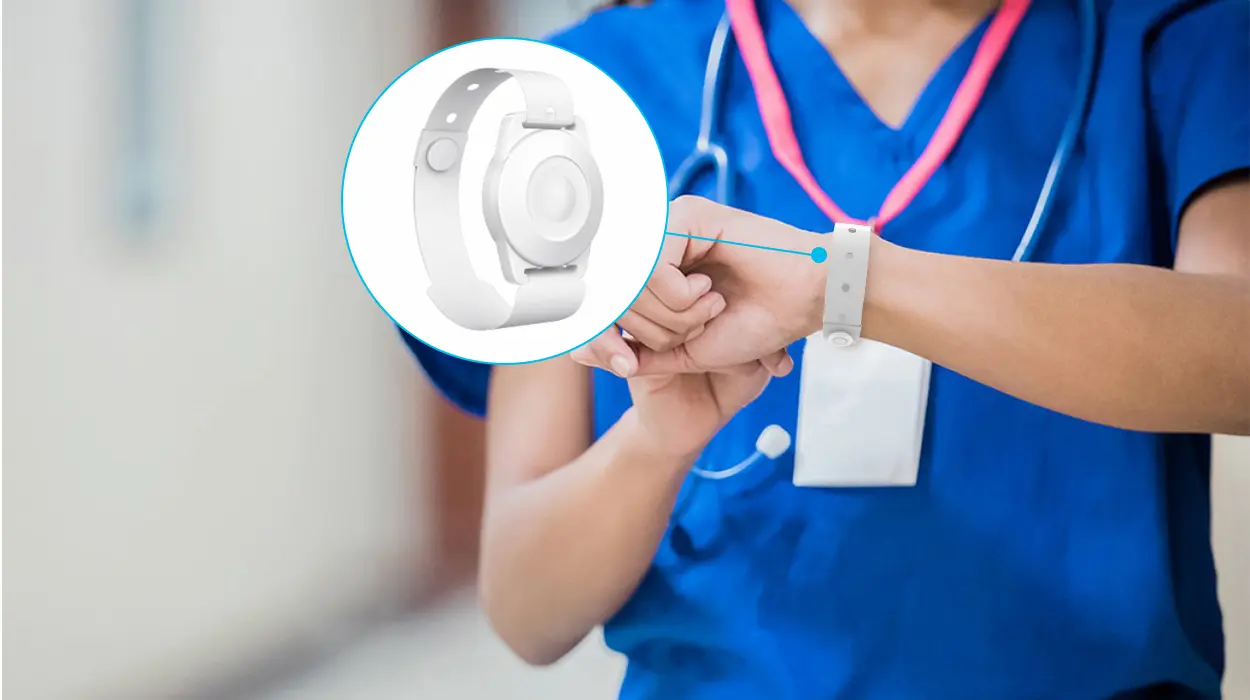
Our wearable health Beacons uses a medical disposable tamper-proof bracelet for unparalleled safety and independence. It is suitable for location tracking in a range of medical situations, such as hospitals and nursing homes. The device applies to all manner of tracking situations, including both people and goods. The W3 Pro Medical Beacon also has an optional button for the SOS function.
b) Wearable ECG Monitors
Wearable ECG monitors can measure electrocardiograms, and that is what makes them different from smartwatches. After measuring electrocardiograms, these wearable ECG monitors send comparative data to the user’s doctor. Wearable ECG monitors also detect atrial fibrillation and can easily track the user’s pace, elevation, and distance and automatically track the user’s running, walking, running, biking, and swimming speed.
c) Wearable Blood Pressure Monitors
The first-ever wearable blood pressure monitor dabbed the “Heart Guide” was launched by Omron Healthcare in 2019. Although it looks exactly like a typical smartwatch, Heart Guide uses an oscillometer to monitor blood pressure and record daily activities such as distance covered, steps taken, and calories burned.
Wearable blood pressure monitors are built such that they can hold up to 100 readings in their memory. Furthermore, these wearable blood pressure monitors send all readings to a corresponding mobile application. Thus, users who use these wearable blood pressure monitor tracks quickly, and shares data with their physician while also acquiring acumens to how their blood pressure is affected by their habits.
d) Biosensors
Biosensors are the latest imminent wearable medical devices that are drastically different from smartwatches and wrist trackers. They are self-adhesive patches that enable patients to collect data on their heart rate, temperature, and their rate of respiration. As a result, biosensors significantly reduce preventable cardiac or respiratory arrest in patients. This indicates that these wearable devices are beneficial as they can help improve patient outcomes, diminishing the staff workload.
More wearable devices and applications are still in their sample stages. Therefore, to boost these devices’ practical usability and functions, it is appropriate to address user acceptance and security issues as they are significant concerns in wearable health technology.
User Acceptance
It is critical to consider the user’s preference when designing any device that you expect to gain a warm reception in clinical surroundings and home settings. If patients or clinicians stay for a long time without working on sensor systems, they become redundant.
A wearable sensor system should be easy to operate, compact, and embedded with a low maintenance cost. Also, it should not affect the user’s day-to-day activities, nor should it act as if it’s directly replacing a healthcare profession. Unfortunately, this field lacks proficiency and inadequate data despite the benefits of user preferences. Therefore, researchers should focus on the user’s preferences implications when designing these wearable sensor systems.
Security
Before you decide to buy any wearable device, data security and confidentiality are significant apprehensions you should consider. This is necessary as it is at times challenging to always comply with HIPAA regulations. For you to have a comprehensive data-centric system, encryption is essential. When a company uses encryption and encrypted data as its authentication mechanism, its network is more trustable. In addition, a company gains elevated privileges when its data keys and certifications are directly accessible by everyone.
Key management is essential as it strengthens the security of data. This is achieved when the key management increases its dependability on cryptographic schemes. However, designing key management schemes has become challenging due to some risky constrained nature of biosensors.
It is essential to secure your WBAN communications as all the physiological data recorded by biosensors is transmitted over WiFi. This prevents interruption of personal information and snooping. In addition, cryptographic schemes that safeguard essential security services such as privacy, integrity, and validity help achieve a robust security system.
Disadvantages of wearable
All leading wearable devices grounded on IoT platforms should provide powerful applications that can easily access IoT wearable healthcare devices. Even though most of the proposed platforms and structures are already available for measurements in the bio-metric/medical parameters, this way has some serious challenges. However, several disadvantages arise from these IoT wearable healthcare devices. They include;
1. Reliability and legitimacy – At times, there are some variations in wearable devices’ data. There is no evidence data collected by wearable is always correct.
2. Personal Health Data Privacy and Security – Users are usually concerned with the privacy of the data collected by their wearable devices as they do not own their data. Also, the user sometimes fears losing the data collected as there is always a danger of scams when installing applications.
3. Connectivity and Interoperability – Most health wearable devices lack connectivity and interoperability in their systems. This is because the integration of patient information using wearable technology is relatively new in the healthcare sector.
4. Overload of Data overload – Health wearable monitoring devices record any personal data related to health conditions. This makes some patients feel as if someone is over-monitoring them, thereby causing stress to them. On the other hand, all the data recorded cannot be handled by the health community.
What to Consider When Implementing wearable
At MokoSmart, we focus on implementing all the possible benefits of wearable in workplaces. However, when you decide to purchase some wearable for the office, some of the key considerations to address are;
Employee Privacy
Data privacy is one of the top reasons people take so long to embrace the wearable world. All companies should set an eminent line between ethical and unethical usage. Adequate communication between a company and its employees regarding the anticipated data types to be collected should be carried out. This improves the employee’s satisfaction as it explains how the data recorded is used. Companies, especially those dealing with health metrics, should develop data usage policies to be sent to workers for review and approval before moving forward.
Data Security
Losing wearable, such as mobile devices, is easier than losing a company desktop. However, wearable devices at times can lose some vital company data when they are remotely wiped out. Therefore, before introducing wearable to an office, organizations should develop a management system for wearable devices that protects data from getting into the wrong hands.
User Engagement
For the user engagement initiative to run smoothly, all companies need to embrace an efficient technological system. Most workplaces are introducing wearable in their programs, as they are one of the latest specialized tools available in the market. Frequently, companies succeed in their operations when they combine the user’s engagement with technology. However, when a company thinks that technology is the only solution to its needs, this leads to a fatal error.
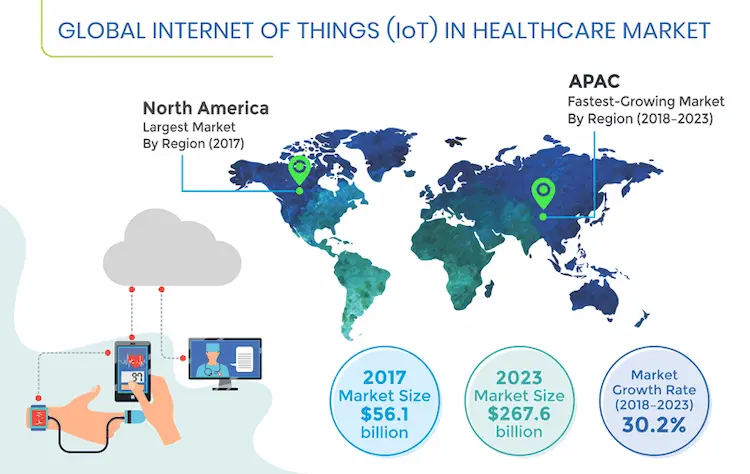
The Global Wearable Healthcare Technology Market
All wearable devices such as activity trackers, medical monitoring devices, and smartwatches make up the global wearable healthcare technology market. They collect the user’s fitness and well being information and creates a custom-made database of health metrics of the user. The user can use the data to track various metrics or can be used for remote monitoring by healthcare professionals.
In the mid-2000s, an interest in the market of wearable devices had hit its peak before settling down when these devices became part of day-to-day life. However, the industry has been boosted by the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic. This is because consumers are investing more in tracking their health. The pandemic has also raised a cognizance of unpredicted health complications and illnesses and how consumers can manage and follow their own needs.
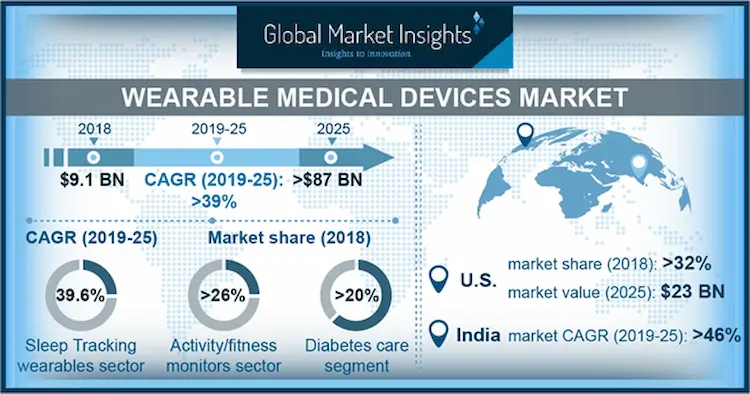
Profit Margins in the Wearable Healthcare Technology Market
The wearable healthcare technology market is categorized into several segments with fluctuating growth potential levels, and now it is worth around $30 billion. Generally, its compound annual growth rate is more than 16%, with several segments having a rapid revenue growth. The Covid-19 pandemic has wedged the evolution of supply chains in businesses. However, the sector is likely to recover soon when the interest in Healthcare heightens.
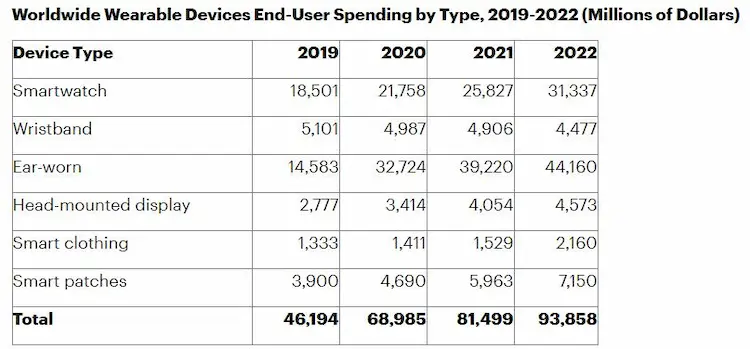
The biggest revenue driver in the wearable healthcare industry is the wristwear section accounts for almost half of the total revenue.
Gartner Global Spending Forecasts on Health Wearable Devices
Cloud-based computing has greatly augmented cloud-delivered SASE offering making digitalization accessible from anywhere and anytime from any device. The Gartner 2021 Strategic Roadmap for SASE Convergence recommends short- and long-term global spending on wearable devices, and they include;
Short term:
1. To replace a legacy VPN for remote users with zero trusted network access (ZTNA), especially in high-risk cases.
2. Develop adequate inventory equipment and contracts on-premises perimeter and branch hardware that favors delivering cloud-based SASE capabilities.
3. Influence a congregated market that develops by combining the available security edge services.
4. Actively engaging in initiatives that focus on transforming and offloading MPLS to integrate cloud-based security edge services into an opportunity of project planning.
Long term:
1. Merging SASE offerings to a sole merchant or two openly partnered merchants.
2. Implementing ZTNA for all users irrespective of the location.
3. Selecting the best SASE offerings that permit all protocols.
4. Creating a devoted security team and networking experts with a joint obligation.
Economic impact
Wearable technology opens a room to numerous stirring applications and can lead to a revolution in technology similar to mobile and internet communication industries. The probable economic impact is enormous. It has developed countless opportunities for both textile and electronics industries, each of which accounts for approximately $ 450 billion in world trade.
The global market volume for smart fabrics and intelligent clothing comprised of wearable devices and photonics is anticipated to exceed $720 million by 2023. It has already shown a remarkable annual growth rate of 18.8% between 2015 and 2020.
Impact of the Wearable technology on Healthcare
Most individuals in society have already adopted the latest technology in their lives. Improved technology is constantly turning dreams into realities as it aims at developing strategies that make life easy by knocking down all the set boundaries.
Various revolutionary innovations erupt every year in the medical industry alone, some of which were seen as impossible to develop a few years before they were created. For example, some of the latest technology equipment in the healthcare sector like MRI’s and CT scans have essentially changed how we scrutinize detailed body parts. Also, research on stem cells has changed the traditional ways of curing illnesses and repairing damaged tissues. When implemented effectively, wearable technology can change how we monitor, gather data, and take care of patients. The quality of life we anticipate life can be achieved if we all increase the quality of care we deliver.
Drivers of a Health Wearable Uptake in Healthcare
Some of the drivers connected to wearable devices in the health care sector that has improved the demand for remote monitoring, diagnostics, and digital management are;
· An aged population
· Supply factors of better quality
· Healthier R&D
· Heightened functionality
· Improved incorporation with solutions and systems of IoT
First Health Wearable Device in the Healthcare Sector
The first wearable device was a pacemaker built-in 1958. It was implanted and worn by patients struggling with arrhythmia. Since then, advancements in technology have contributed to smart wearable devices that operate as mini-computers. These latest wearable devices enable remote monitoring in patients at any place and any time.
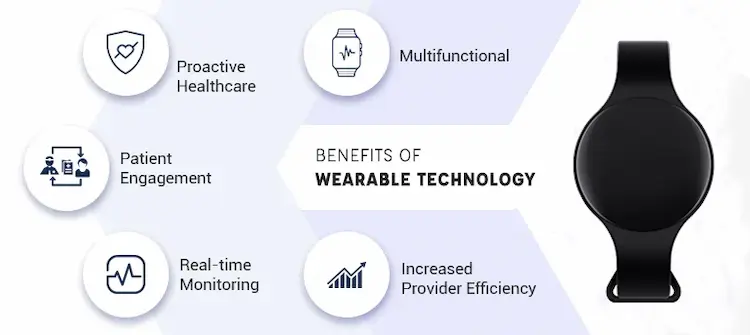
Benefits of a Health Wearable Technology
Although wearable technology has touched numerous areas, the Healthcare sector is the primary beneficiary of this technology. When hospitals and clinicians deploy these wearable technologies in the healthcare sector, they attain multiple benefits at different levels and roles. The benefits of wearable technology in Healthcare include;
a) Heartens Proactive Healthcare
Wearable technology enhances a more proactive healthcare approach. This is because wearable can be used in the early stages to take action rather than responding to healthcare matters when they start causing severe complications. In addition, health wearable devices can detect irregularities by individuals who are prone to health problems.
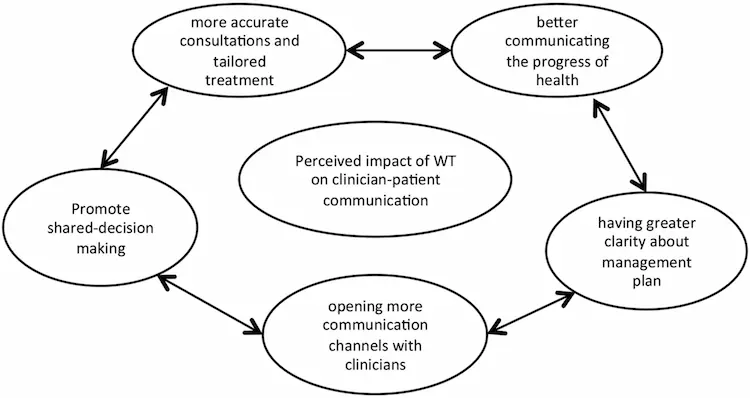
b) Engages Patients
When people start monitoring themselves using wearable technology, they engage more in their health. Access to real-time data gathered from wearable devices gives updates to the users regarding their health conditions.
c) Accomplishes Multiple Functions
Currently, the market has numerous types of IoT wearable healthcare, each with a different use case. There are many wearable devices in the medical field, although the most common devices are consumer-focused. MOKOBeacon can track the patients’ locations for convenient management for the healthcare agency.
d) Monitors Patients
Healthcare providers can also use wearable technology to monitor patients who are disposed to health issues. Patients can be monitored using wearable technology when at home if they are at risk that is not severe. This ensures no problems arise.
e) Improves the Satisfaction and Care of Patients
Wearable devices provide surgeons and physicians with accurate data used to increase patient connection opportunities while at the same time improving the decision-making process. For instance, surgeons use smart glasses to access the patient’s vital organs during surgeries.
f) Strengthens Functioning End Result
Wearable devices increase productivity as when they are installed on custodial staff, they simplify cost savings.
What We Know About Health Wearable and Corporate Health Programs
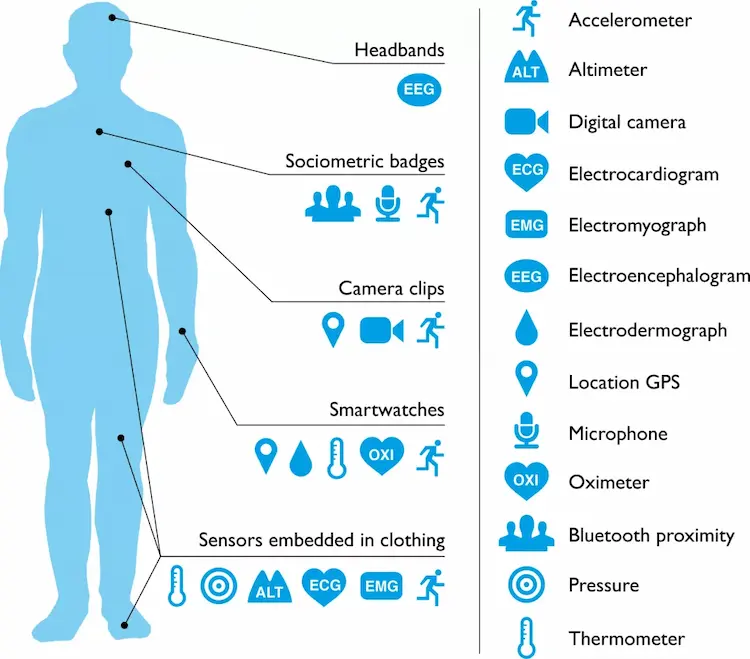
Presently, wearable devices are being used to monitor heart rate, sleep, oxygen in the blood, body temperature, brain waves, and other human constraints. The diagram below shows how various data tracking is at present done with wearable devices.
Those who manufacture wearable devices endorse them as proficient in monitoring everything from detecting moles to menstrual cycles. Health wearable devices are great at monitoring movements, assessing calories used, measuring heartbeat, temperature, and blood oxygen. Wearable devices are becoming better with time as they gain more effective and reliable measures of therapeutic information. This is why they are so common amongst people who are physically full of life. The strength of wearable devices is that they can easily monitor and report data, while their inability to change human behavior is their main weakness.
The majority of those who use healthy wearable devices are below 44 years of age; hence this is more problematic. This indicates that most of those who use these devices are “already fit.” They use it to track and monitor their activities. As a result, these people gain more benefits when it comes to an active lifestyle.
How Health Wearable Can be Used to Address Covid-19 in the Healthcare Sector
Most startup companies that deal with manufacturing wearable look at different uses for their devices and develop strategies to help support consumers during the pandemic. Several startups have developed in the last few months, especially in the sports, wellbeing, and fitness fields, establishing devices that can pivot the Covid-19 pandemic fight.
This has enabled wearable devices to be a key enabler that enhances the experience of clinical mobility and bedside care. For instance, patients using wearable devices, whether in their hospital room or at home, can now, in real-time, inevitably alert the healthcare staff. In the Covid-19 context, this has become progressively significant as every second matter when saving a patient’s life.
Moreover, different wearable form factors that address the Covid-19 pandemic are consistently being accessed by the healthcare industry. Some of the devices used for contact tracing on medical personnel and patients,some of them used to measure a patient’s body temperature, breathing rate, and other essentials at home and in hospitals are smartwatches, rings, stamps, badgets and patches. These devices can also monitor coughing, which is one of the Covid-19 early key indicators. For example, the latest innovative wireless wearable device attached below a patient’s throat has a postage stamp size. Northwestern University researchers built this device. It monitors coughing and all the movements in the chest, body temperature, heart rate, and respiratory sounds.