Technology is the greatest achievement of extraordinary human imagination. In terms of location and navigation technology, GPS (Global Positioning System), which delivers precise position outdoors based on satellite signals, was a major leap forward in the 20th century, while IPS (Indoor Positioning System) opened up a whole new world within indoor environments where GPS doesn’t work properly. In this article, we’ll introduce you to indoor positioning system and outline the different technologies available.
What is an IPS?
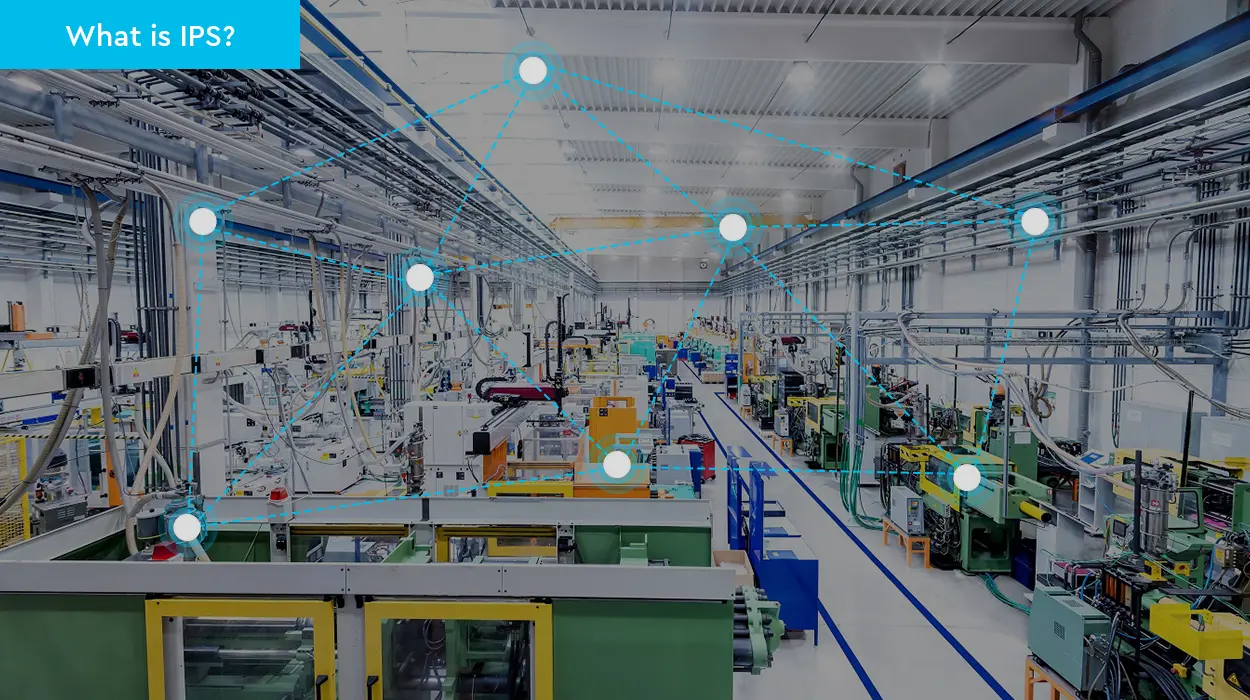
Indoor positioning, also referred to as indoor location tracking, is a network of devices used to locate people or objects within an enclosed space where GPS signals are not strong enough. Simply put, it can be explained as ‘Indoor GPS’. Just like GPS helps people locate objects anywhere on the earth, IPS does the same but in large indoor spaces like train stations, shopping malls, hospitals, and underground locations. An indoor positioning system gives you the ability to accurately pinpoint the location of objects inside a building, typically via a mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet.
IPS can be essential to enhance your indoor positioning experience. It is estimated that more than 70% of a person’s time is spent indoors, so there remains a strong demand for technologies to deliver indoor location services, and this is as well as a big market opportunity for IPS technology vendors. IPS may not be a necessity for daily routines, but it’s absolutely necessary when accessing environments that you’re unfamiliar with, especially in emergency cases where the GPS signals are very weak, such as disaster management in a multi-storied building, coal mine, etc.
Why is indoor positioning necessary
Pretty much people are wondering why GPS cannot be used indoors. If you have the same confusion, just read on and find out why indoor positioning systems are all the rage these days.
Inaccuracy of GPS signals when used indoors
The success of GPS has shifted the way we related to technology. However, the efficiency of it only works well outdoors and fails to meet the expectations for sophisticated indoor environments. Since GPS technology uses the signals of satellites in orbit, these signals are seriously degraded by roofs and walls as soon as the satellite waves try to penetrate the barriers and enter the buildings. Typically, GPS can achieve an accuracy of 5m-10m in an open area where there are no adjacent tall buildings that can block signals.
Widespread application of precise positioning
The widespread applications of precise positioning have strengthened the demand for indoor positioning system services. While the need was there, indoor positioning systems are becoming more and more important in various sectors by virtue of their advantages of improving service efficiency. Beyond the reach of GPS signals, IPS services are leveraged by industries including commercial, healthcare, military, or inventory tracking in warehouses. Currently, there is no standard for an IPS system, and companies including the top name Google and Nokia are fighting to bring these solutions to customers.
![]()
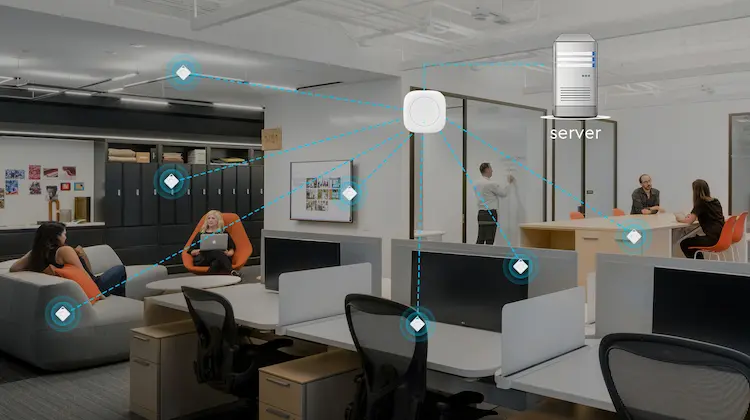
How do indoor positioning systems work
Before we dive into IPS technologies, it’s important to see how it works. Similar to the transmitter-receiver principle of GPS, IPS works as the same principle. Using a variety of beacons and tags, an IPS estimates the target object’s location from the collected observation data. To tracks objects within a building, stationary beacons (anchors) are deployed to receive the signals transmitted from the mobile beacons (tags) attached to the tracked objects. Anchors receive the signals from the tags and forward them to a server, which then calculates the real-time location of the object.

Types of indoor positioning technologies
Contrary to satellite-based GPS, IPS is a melting pot of multiple different technologies, including radio-based, optical, acoustic, and magnetic technologies, while each comes with its own advantages and limitations. The different IPS technologies and techniques walk hand in hand toward integration for better accuracy. The following part will show you the classification using various types of signals.
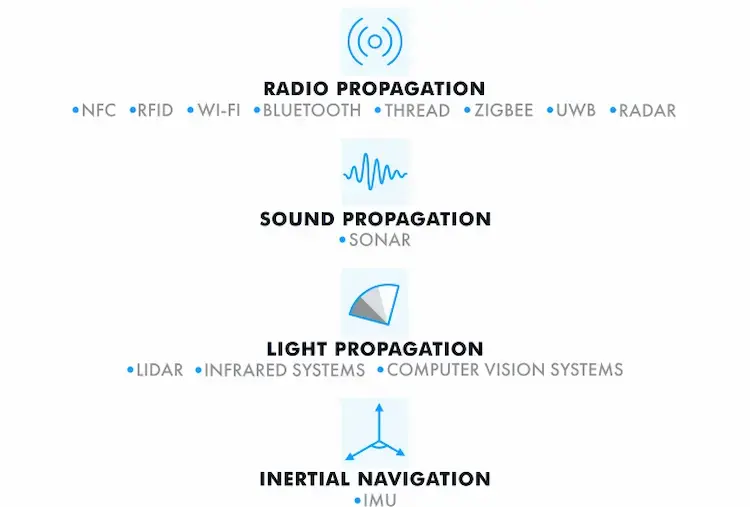
IPS using radio signals
Radio-based technologies are widely used in indoor positioning systems because these signals can pass through many materials commonly found at worksites, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Radio Frequency Identification(RFID), Ultrawideband(UWB), Radio Detection and Ranging (RADAR). Such systems could detect object positions with radio signals propagating from transmitters to receivers.
IPS using optical signals
Although optical signals is some kind of electromagnetic radiation, they are quite different from radio waves. Comprising light-emitting and light-reflecting objects, this indoor positioning system type includes infrared systems, Visible Light Communication(VLC), Light Detection, and Ranging (LiDAR).
IPS using acoustic signals
Acoustic signals consist of pressure waves traveling through the air. Due to the fact that sound travels much more slowly than electromagnetic signals, it becomes much easier to measure the time period. These systems can be highly accurate, but as solid surfaces block signals, they are usually viable only in larger, open facilities, including Ultrasound and Audible Sound.
IPS using magnetic field
To determine the location of a person or object, indoor positioning systems based on the Earth’s magnetic filed uses magnetometers to measure magnetic field variations. No wireless network signals will be required, and location estimation is commonly achieved by methods such as fingerprinting.
Common use cases for IPS
The term IPS is broad and can be implemented in pretty much industries where the accurate position of animate or inanimate objects within indoor space is indispensable. Whether in shopping malls, amusement parks, transportation hubs, hospitals, universities, or even large corporate offices, IPS will make your track location and navigation an enjoyable journey with an application on your smartphone. Below, we’ve selected some of the common use cases of IPS.
Airports & Railway Stations
In transportation hubs, whether in large airports, railway stations, or bus stations, an indoor positioning system is of great help to passengers. People can locate themselves within the station and find a less crowded way to their vehicles with the help of indoor maps. Transportation hubs can also apply indoor positioning technologies to provide a better experience for travelers.
Industry and Manufacturing
The use of indoor positioning systems in industry and manufacturing sectors has been increasing in recent years, with the purpose of increasing labor safety, reducing cost, and saving time in processes. Especially in large factories, indoor positioning system helps a lot in assets control, logistics, and emergency response.
Shopping Malls
IPS can be used not only to enhance the shopping experience for consumers, but also for location-based marketing campaigns held by vendors. Normally, these shopping malls are large and often accompanied by complex infrastructures. Based on shared guide assets, visitors could spend less time finding their desired products and get relevant information about what is easily accessible to them within the mall.
Hospitals
Hospitals have been trying to tackle the problem of indoor wayfinding for decades. An indoor positioning system can help visitors navigate their ways easily, thus lowering the stress and late arrivals. Besides, doctors and other staff can also benefit a lot, which allows them to find the medical equipment quickly, locate the patients within a certain range, and avoid delays in emergencies.
Multi-story car parks
Multi-story car parks are usually built under shopping centers and large office buildings where GPS signals are not available. A smart parking system using indoor positioning technologies can track the occupancy of parking lots and assist drivers to establish routes to the nearest free space. In addition, digital maps based on IPS can be created to ensure navigation and convenient access to vehicles.

How do IPS and GPS differ
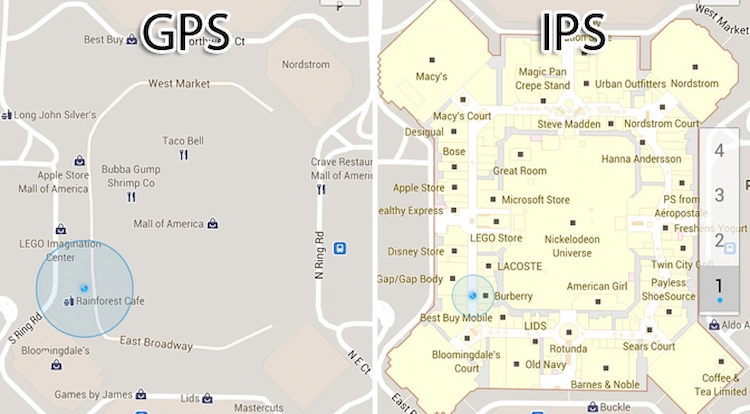
Pretty much people can be confused when it comes to the difference between GPS and IPS, as they perform similar tasks and have similar acronyms. In fact, IPS can be regarded as further development and extension of GPS. As we mentioned earlier, the biggest difference between IPS and GPS lies in the field of application. One is accurately for indoor environments, and the other is practically designed for outdoor spaces.
Due to the huge difference between the outdoor and indoor space, technology adoption of IPS and GPS is totally different. A GPS receiver has to lock on signals from three or more satellites to determine a location and track the movement, while IPS applies diverse technologies to make more precise measurements. What is worth noticing is that indoor GPS is an ongoing area of research, and new options may emerge in the future.
Is indoor navigation the same as indoor positioning
Indoor navigation and indoor positioning are actually two separate applications that combine together to serve an enhanced wayfinding experience for users. Indoor positioning allows users to pinpoint their location inside a building and indoor navigation will suggest a path to their desired destination. To simply put the difference, indoor positioning or tracking is passively recording the data, whereas indoor navigation is actively suggesting the users follow a path.
Indoor navigation combines indoor positioning technology with wayfinding to show a blue dot on an indoor map that moves with the user in real-time. Without an indoor navigation system, your current location will be displayed but there are no directions, and if there is no indoor positioning system, users of indoor maps have to choose the starting and ending coordinates on the map. It is with the help of indoor positioning systems that you can create effective interactive indoor navigation.
Learn about MOKOSmart IPS hardwares
MOKOSmart is a trusted partner for outstanding Internet of Things hardware and software. Our team delivers a wide range of reliable and efficient beacons for indoor positioning system. Whether your goal is to increase productivity, enhance customer engagement, or mitigate risks, if you have any confusion about accurate indoor positioning and tracking technology, you can send information to our technical team for some consultation.