With people spending over 80-90% of their time indoors, precise indoor positioning has become a need for businesses and consumers alike. While GPS provides great outdoor coverage, technologies like Bluetooth are filling the indoor positioning gap. Especially the Bluetooth 5.1 introduced new direction finding capabilities through Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) to enable precise indoor localization. This guide will explore how to use Bluetooth AoA and AoD for precise location across various spaces.
Bluetooth AoA and AoD for direction finding
What is Bluetooth AoA and how does it work
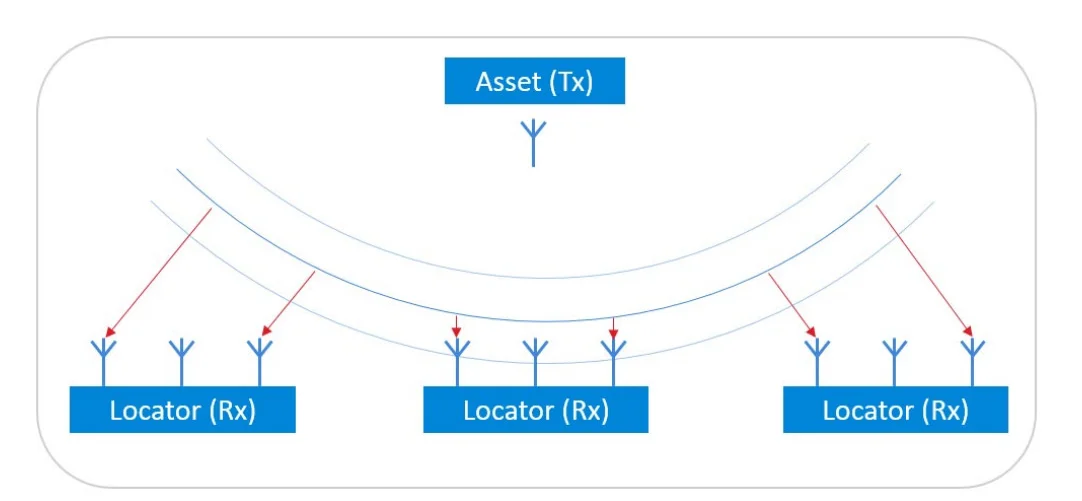
Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) is a method for estimating the direction of an incoming Bluetooth signal using antenna arrays and phase differences. The device sending the Bluetooth LE direction finding signal uses a single antenna, while the receiving device (called the locator) has an antenna array with at least two antennas.
The locator performs IQ sampling on the received signal as it switches between antennas in the array. This results in phase differences between the signals received at each antenna due to the different line-of-sight distances from the transmitter.
By analyzing these phase differences, the locator can calculate the angle of arrival – the direction the Bluetooth signal arrived from. More antennas in the array allow for more accurate angle estimates.
As the transmitting device moves, the locator can track the changing angle of arrival over time. This allows the system to estimate the position and movement of the transmitter based on the changing directions of the incoming Bluetooth signals.
What is Bluetooth AoD and how does it work
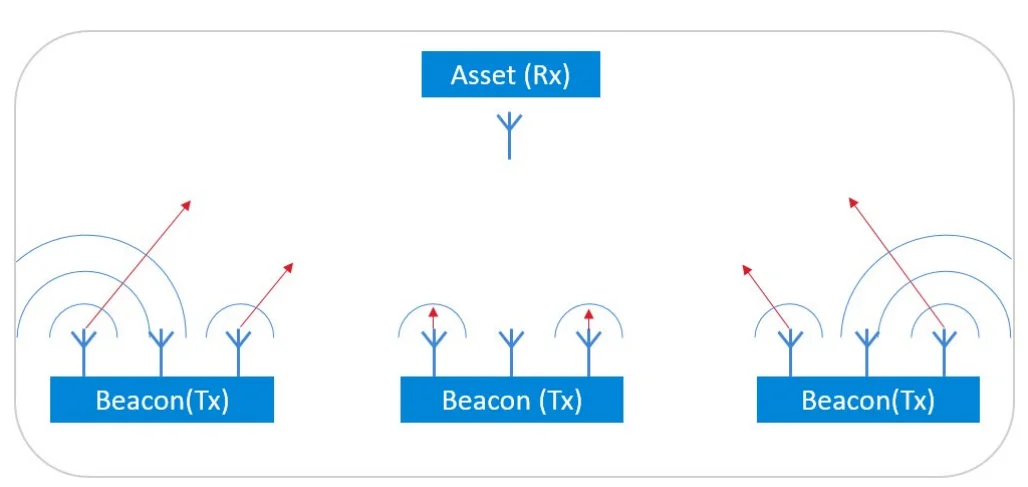
The basic principle of using phase differences of signals to calculate angle is the same, but AoD and AoA reverse the roles of the transmitting and receiving devices. In AoD, the transmitter has multiple antennas and the receiver has a single antenna. Devices with multiple antennas use multiple antennas to send signals, while receiving devices receive all these individual signals through a single antenna.
The transmitting device sends signals from each antenna. By analyzing the phase differences between these signals, the single antenna receiver estimates the angle of departure – the direction the signals were transmitted from. This enables indoor positioning, with a fixed AoD transmitter sending directional signals to AoD receivers like phones. The receiver uses the angle to locate itself relative to the transmitter. Like AoA, AoD uses phase differences between multiple antenna signals to calculate the angle.
By analyzing the difference between these signals to estimate the relative signal direction in which they leave.
Benefits of Bluetooth AoA/AoD direction finding
The direction finding capabilities introduced in Bluetooth 5.1 provide both consumers and businesses with powerful new benefits:
- Accurate indoor positioning and navigation
Direction finding allows for accuracy down to 0.5-1 meter for tracking locations of Bluetooth devices indoors where GPS struggles. This facilitates detailed indoor mapping and navigation.
- Real-time location tracking
Since Bluetooth signals are available continuously, it enables real-time location tracking of assets, inventory, and even people for applications like proximity marketing.
- Enhanced location-based experiences
Precise positioning opens up opportunities for businesses to send geo-contextual offers, enable indoor turn-by-turn navigation, or help visually impaired individuals navigate safely.
- Versatile use cases
Bluetooth direction finding applies to a wide range of uses like asset tracking, point-of-interest identification, proximity sensing, spatial analytics and more. The possibilities are unlimited and we’ll explore later.
Real-world use cases of Bluetooth AoA
As more devices integrate Bluetooth tech, Bluetooth AoA/AoD location will enable more frictionless interactions between the physical and digital. Here are just a few real-world use cases unlocked by Bluetooth AoA and AoD direction finding:
– Finding misplaced devices like Bluetooth trackers or headphones using proximity and direction.
– Navigation and wayfinding in airports, museums and other indoor spaces.
– Location-based gaming, delivering experiences that adapt as you move through physical space.
– Proximity-based marketing and analytics in retail stores.
– Robotics navigation and collision avoidance using spatial intelligence.
– Logistics tracking and inventory management in warehouses.
– Fixed asset management and electronic fences for enterprises
– Safety applications like socially distanced meeting alerts based on real-time location data.
– Improved connectivity experiences as devices interact intelligently using positioning context.
Challenges of adopting Bluetooth AoA direction finding
While Bluetooth AoA and AoD direction finding represent a major advancement, certain challenges need addressing as the technology evolves. Some key issues to overcome include:
- Interference from reflected signals: Smooth reflective surfaces like metal and glass can reflect BLE AoA signals, causing interference and inaccurate angle measurements.
- Deviation of antenna array: Lower cost RF switching antenna arrays and mutual coupling, phase center errors, and orientation errors can introduce positioning errors that need to be compensated for.
- Complex floor or area environment: Hollow floors, multiple rooms, and physical separations between areas make high-precision positioning challenging.
- Perturbation of antenna directionality: Different device positions and orientations perturb the antenna directionality, affecting angle detection. Antennas need to adapt to different device placements.
AoA vs AoD: the differences, strengths, and synergies
Bluetooth AoA and Bluetooth AoD both facilitate direction finding, but there are notable distinctions. Presently, Bluetooth AoA is the predominant solution in the market, while the AoD solution is still in its developmental stages.
| Transmitter | Receiver | |
| Bluetooth AoA | Positioning terminal, single antenna, simple processing | Positioning base stations, IQ sampling, complex processing |
| Bluetooth AoD | Positioning base station, antenna array, simple processing | Positioning terminal, IQ sampling, complex processing |
Measuring approach: Bluetooth AoA measures the arriving signal angle while AoD measures the departing signal angle. One tracks receivers, the other tracks transmitters.
Hardware: Bluetooth AoA requires an antenna array on the receiver while AoD needs it on the transmitter. Ideally, both devices would have arrays.
Strengths: Bluetooth AoA is better for tracking mobile devices while AoD excels at covering fixed transmitters spread out across a space.
Their synergistic use improves accuracy and reliability of direction finding. AoA and AoD complement each other well rather than compete.
Bluetooth AoA vs UWB for indoor positioning
Ultra-wideband (UWB) is another technology gaining traction for high-precision indoor positioning. How does it compare to Bluetooth AoA direction finding? UWB offers very high accuracy, down to 10-30 cm, compared to about 0.5-1 meter for Bluetooth. However, UWB has higher power consumption and hardware costs.
Given the distinct technological demands in various scenarios, Bluetooth AoA and UWB find their own niche applications. For instance, UWB technology is better suited for open environments, whereas AoA technology excels in dense rooms. In areas with sizable pillars, the AoA solution proves more fitting, while in long-distance one-dimensional settings, UWB technology prevails. Consequently, the idea of merging and integrating the strengths of these two technologies has gained traction.
The approach to technology integration is also contingent on the specific application needs. Industries such as industrial production processes, smart medical care, smart prisons, and chemical plants necessitate the amalgamation of UWB, Bluetooth AoA, and even other technologies like Zigbee, WiFi, LoRa, among others.
MOKOSmart Bluetooth AoA Kit for indoor location
MOKOSmart offers a quick, affordable way to add Bluetooth direction finding capabilities to location services. Our Bluetooth AoA Product Location Kit integrates various Bluetooth beacons and AoA locators to simplify indoor positioning and navigation.
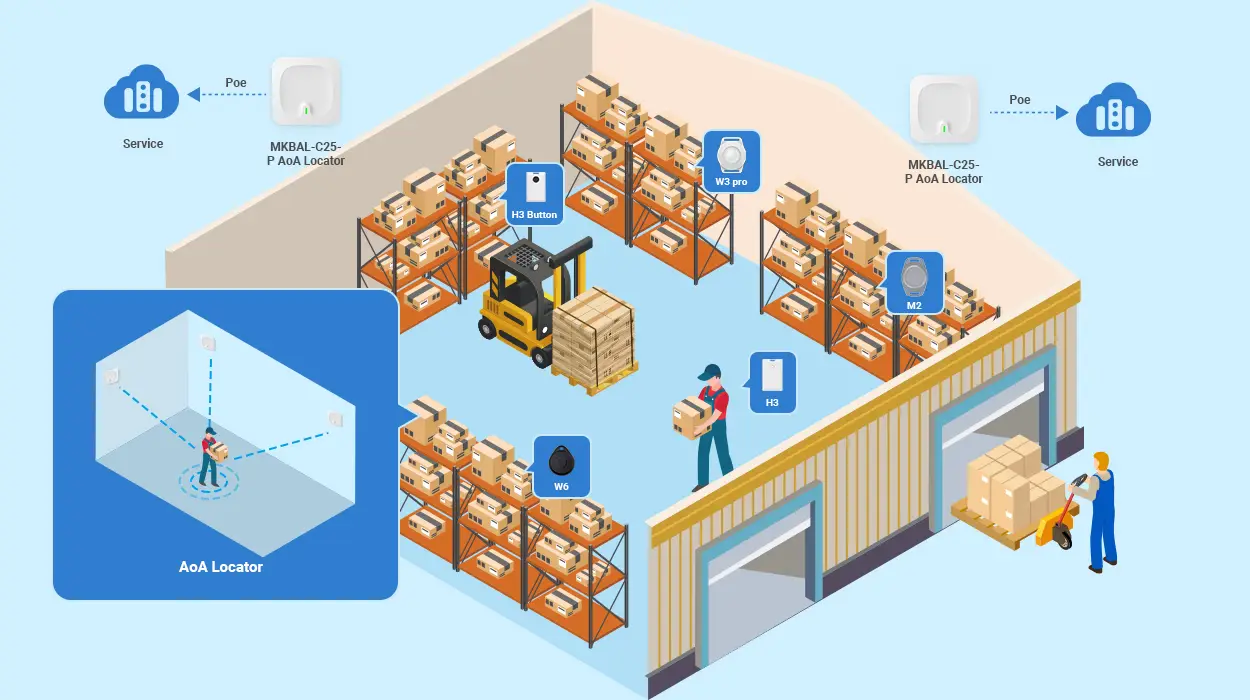
Key features of the AoA kit include:
- Provides a series of Bluetooth AoA tags for tracking personnel, assets, and equipment
- Compact multi-antenna Bluetooth gateway with Bluetooth 5.1 AoA support can cover areas up to 500 m2
- Connect to cloud services via WiFi or Ethernet for data analytics and visualization
- Provide iOS and Android SDKs for easy integration
- Achieve positioning accuracy up to 0.1~1m for precise locating
With success stories across industries, MOKOSmart is devoted to Bluetooth AoA technology innovation for advanced indoor tracking applications. Our AoA kit enables rapid development for accurate location services.
The future is exciting for Bluetooth location
Bluetooth direction finding via AoA and AoD provides precise real-time indoor tracking. This precision creates opportunities for seamless spatial experiences indoors. With meter-level accuracy, Bluetooth direction finding propels the next generation of smart, contextual indoor connectivity. While RSSI has driven location services so far, Bluetooth 5.1 AoA brings more precise positioning. As companies like MOKOSmart advance hardware and standards progress, Bluetooth direction finding will continue advancing – driving the future of seamless indoor localization.