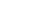Battle of the Beacon Technology:
Google continues to work on the all-encompassing networking and has now introduced an equivalent to Apple’s iBeacon. The open beacon format Eddystone offers a range of tools and interfaces with which developers can control the communication and data exchange between different devices. The platform supports both Android and iOS devices and is a holistic beacon technology concept with extensions for UriBeacon / Physical Web, telemetry and sensor data and a central beacon registration for open beacon platforms.
Specifications were uploaded to the Github developer portal. Google relies on the Bluetooth Low Energy transmission standard and small radio transmitters – so-called beacons. With the help of the radio transmitter, it is possible to connect the offline with the online world. Traders can send product offers to the smartphone of customers and passers-by or use beacon technology for indoor navigation. So far, the installation of a corresponding app and the activation of Bluetooth was a prerequisite for using beacons.
Google Beacon Technology
You are a retailer and have ideas but not an app? Do you have an app but no iBeacon infrastructure? Contact MOKOSmart and we will show you how you can profitably use the beacon technology.
Google has released two interfaces as part of its beacon initiative: the Nearby API and the Proximity Beacon API. Nearby is intended to help locate, connect and exchange various devices in the area. Google relies on a combination of Bluetooth, WiFi, and audio signals that are inaudible to the human ear. The Proximity Beacon API can be used to control and manage the data exchanged between the device and the beacons. These are stored in the cloud. With the Places API, location-based actions can be controlled. Google is not only targeting the connection of smartphones but is also looking toward the smart home. Google works with various beacon manufacturers, including MOKOSmart, Estimote, Kontakt.io and Radius Networks. MOKOSmart sees Eddystone as “an important step for all providers of proximity applications and beacon solutions” and expects Google’s beacon initiative to boost the beacon market and thus also location-based services and apps.
How do Beacon devices work?
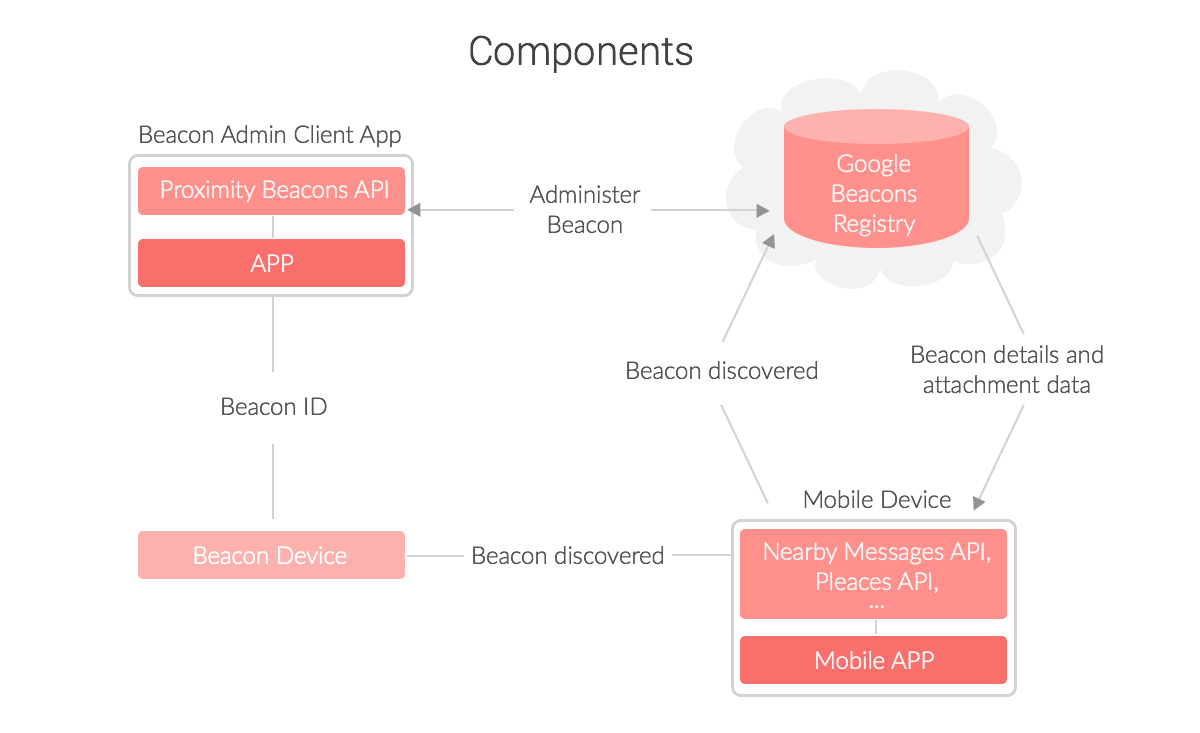
The Beacon technology is based on BLE – Bluetooth Low Energy. This enables a BLE-capable device to initiate a so-called broadcasting process. It always sends the same values at a fixed interval, similar to a beacon. With an iBeacon, the message sent, the so-called standard advertisement, consists of UUID, major and minor. The smartphone receives this unique combination and can evaluate it without the need for pairing or data exchange.
The range of the BLE signal is up to 50m and thus closes a gap between NFC (Near Field Communication), which sends data very precisely but only up to a few centimeters, and Wi-Fi, which can cover a much longer range, and thus again is too imprecise for a position determination.
In the meantime, Google has followed up and published its own protocol with Eddystone, which can contain even more information, such as a direct URL to enable the use of mobile web applications.
The basis of the beacons is the transmitter-receiver principle. For this purpose, transmitters (the beacons) are placed in the room that acts as signaling devices. These beacons send signals in a certain time interval that the receivers (e.g. smartphones) can understand and process. This makes it easy to determine the location of the recipient, which also enables indoor navigation.
Categories of the measured distance
![]()
Depending on the signal strength, the measured distance between transmitter and receiver is divided into one of the following categories:
The immediate distance: A few centimeters
Near distance: A few meters
Far distance: Up to 70 meters
A beacon can send a broadcast to the receiver if the receiver either enters the region, “exited”, or stays in the region (“lingered”) – depending on how the beacon was configured. These beacons can be configured via a management platform from the manufacturer. The device is registered using the unique identification number (UUID), major and minor of the beacon. Events can also be assigned to the beacon.
Management platforms of beacons
The beacons only send their “identity” (UUID, Major, Minor). The associated app – if the receiver is a smartphone – has to interpret this signal and know what to do with it. However, the smartphone only receives this signal when Bluetooth is activated. How the app deals with the information depend on the implementation. The desired action (e.g. displaying a push notification) is either implemented in the app itself or additional information is requested from a server. However, the information does not always have to be displayed on the smartphone, but movement patterns can also be recorded and later analyzed. An example of this is the recording of walkways in stores, which can help optimize store layouts.
What are the advantages of Beacon Technology?
- High precision
The technology explained and the associated options make beacons particularly exciting in location-based service: BLE can be used wherever you cannot reach a sufficiently precise position because GPS or Wi-Fi is not available with the accuracy you need. The technology can also be used where the distance from NFC would not be sufficient. WiFi has a range of about 46 meters indoors, while the beacons have an accuracy of up to 150 meters.
- The signal is sent automatically
In addition, beacons send signals to the user’s device without any action being required as is the case with QR or AR codes, for example, which the user must capture with the camera. In the indoor area, floors are no longer obstacles.
- The different range for different actions
This peculiarity uses the iBeacon protocol and gives a “ranging”, relative distance measurement with “Immediate” says that you are only a few centimeters away, “Near” means a few meters, and “Far” means more than 10 m away from the beacon, The applications of this technology seem almost endless: you can use relative and absolute positions to the beacons and thus revolutionize entire branches of industry.
- Affordable cost
Compared to other technologies, Beacons is much more affordable due to the easy deployment, making it low-risk and potentially high return on investment.
- Adaptable and flexible
Bluetooth beacon technology is easy to use with multiple usages to extend to many industries such as offices, factories, airports, hotels, retail, education, and other public places.
- Personalized marketing
Gain deeper insight into customers and make personalized marketing and customer segmentation based on proximity marketing technology.
- Enhance customer experience
According to the research, about 14 percent of standard push notifications are turned on by people, but more than 50 percent of the messages sent by beacons are turned on because they seem more relevant.
- Stimulate local sales
People will be enticed by Beacon-based proximity trigger notifications to install the enterprise mobile app and eventually be directed to a specific location in the store.
Disadvantages of beacon technology
- Information bombing
As long as the message being pushed is valuable to the user, it is successful marketing. However, if the beacon is sent to the wrong audience, it is a poor experience for the user. They will feel bombarded with information, so they will get angry about receiving too many push notifications and even stop using the app
- Short battery life
Most beacons are powered by a coin-sized battery, and battery life is mainly based on the application, so some users may find this inconvenient. However, you can also use USB beacons instead or check with the supplier when you place your order.
- A limited audience
Beacon Technology is limited to BLE(Bluetooth) signals, so there is no way for Beacon technology to detect the user’s device without Bluetooth enabled. This has limited the company’s access to data, and only users with Bluetooth can be targeted to the target audience, which is mainly young people. In addition, some brands rely on apps to interact with customers. If customers enter the store without installing their app, there is no way to receive offers and other notifications.
- Cost consideration
Though beacon technology can win much more profits for business, it’s still an expensive expenditure for small enterprises to deploy many beacons as there are costs of deploying, testing, and maintaining.
How beacon technology can be used?
Beacon technology has already arrived in offline trade and is hotly traded as a wonder weapon for the RoPo (research online – purchase offline) case. With the appropriate app, the smartphone can use a beacon signal to identify whether the user is in the vicinity of shops and products that are of interest to him. Here is a small example:
Google ads
Max sits on the couch in the evening and looks at a new collection of winter coats, consults with friends on social channels, and states which products he likes.
Proximity marketing
A short time later he is in a shopping street with a shop that offers this collection. The app registers the radio signals of the proximity beacons in the background and evaluates them: a push message informs Max that a coat can be bought nearby and sends him a discount voucher. Max then opens the app.
Navigation
Through other beacons installed in his area, Max can see his position on a map, and the navigation path to the corresponding store is displayed.
Proficient customer insight
In the store, another push is triggered on the employee’s tablet that a potential customer is on the way. She also informs him of the approximate time until it arrives. If Max already has a customer account, the employee also learns Max’s first name and what product he is looking for – the winter coat. When Max arrives, the seller can approach him and speak to him personally, with the desired product in hand.
Asset tracking
And as the location of each product item can be monitored, the seller can locate the product instantly and see if there are more alternative options in the warehouse for Max. If this seems familiar to you: that’s state-of-the-art in e-commerce.
Pleasant condition monitoring
Max must feel good about this experience as he not only finds valuable information and choices for his purchase need but also feel comfortable as the environmental condition such as temperature status is being monitored and the beacon deployed can operate with the appliances as per the need.
Automatic payment
Different from the previous shopping experience, Max doesn’t have to line up for payment as once he had downloaded the mobile app of the store, then the payment can be finished online or made automatically.
Alarm button
More interesting is that the beacon devices are alarming settings, once there’s an emergency in the store, the seller can push the beacon button and ask for help.
What are the areas of application?
IoT Beacon technology can easily be integrated into everyday life.
![]()
Retail store
The first shopping centers in America are already equipped with retail beacons. If a customer enters the store equipped with proximity beacons, he will be informed about special offers, discounts, and vouchers from advertising beacons, or he will be reminded of his birthday voucher that has not yet been redeemed. If the customer has saved the store’s customer card in the associated app, it can already be opened at the checkout.
Supermarket
Additional product information, for example, the ingredients of food in a supermarket, can also be displayed. What’s more,with the temperature and humidity beacon, the managers can monitor the food condition and ensure food safety.
Mobile payment
Another futuristic use case would be that in the future payment for the purchase will be made automatically when you leave the store. For example, beacons could be used as a good alternative to NFC in the mobile payment segment.
Education
Another area of application can be found in the field of education. For example, beacons can block certain students’ apps – such as WhatsApp or Facebook – or immediately block Internet access on their smartphones. Furthermore, the presence of the students in the classroom could be checked using beacons.
Household
Beacons can also be used to support the household. For example, if you approach the stove, the cookbook app opens. If you approach the refrigerator, the shopping list opens.
Sport
Many stadiums are equipped with beacons that send notifications, broadcast updates on events and discounts in real-time, and allow users to navigate to their reservations.
Public transport
One of the common use cases of beacons is notification messages on public transportation platforms, where users can know when a vehicle will arrive, students can also use beacons as evidence of identity, and parents can learn their children’s real-time location based on the beacons they wear and come out to greet their children almost at the front door.
Airport
You may have been lost in an airport or other large public place, but with beacons, you can confidently navigate to your desired location and be informed of the latest notification posted by the airport through beacon marketing. All the promotion information and your luggage location can be updated in real-time.
Factory
Social distancing is one of the anti-epidemic measures that many companies have adopted since the outbreak of Covid-19. The wearable beacon can trigger an alarm when a safe social distance between the two is exceeded, and its movements can be monitored as well. In addition, there are great crowds coming and going in factories and construction sites. Beacons, as an identity authentication method for employees, optimize the intelligent attendance system, effectively check the intrusion of foreign personnel, and the background can also timely be notified when employees enter dangerous areas. Important assets and tools can also be attached with beacons to facilitate asset management and maintenance.
There are already many areas of application for beacons that should make our daily lives easier and support standard processes through automation. The use of beacons is particularly interesting in the areas of marketing, advertising, indoor navigation, and mobile payment. Although this technology is still in its infancy and will continue to develop in the coming years, some applications have already been implemented. It remains to be seen to what extent the trend with the beacons will develop and prove useful.
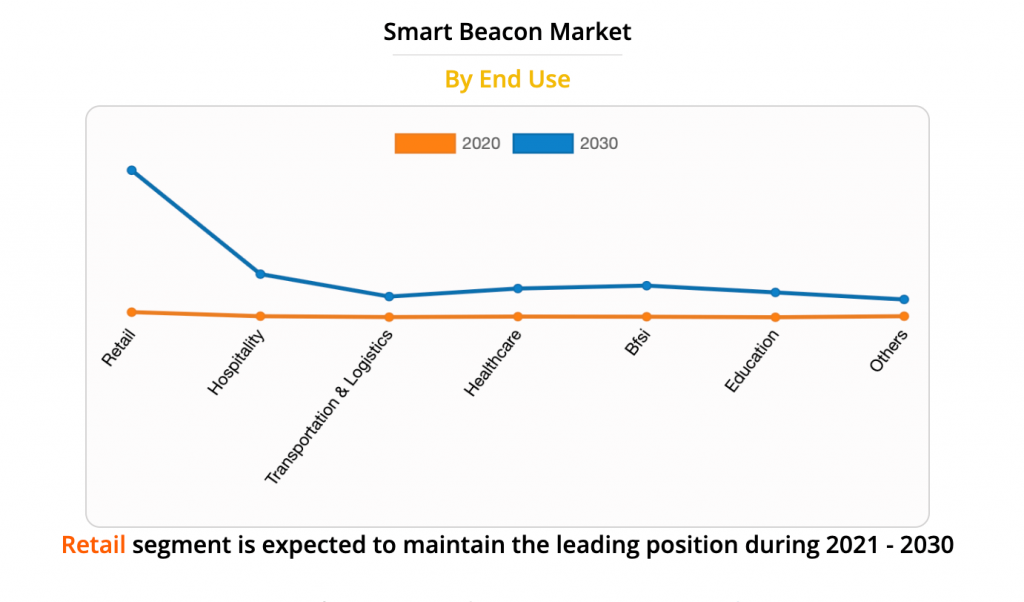
The market outlook of beacon technology from 2021 to 2030
According to the report, the global smart beacon market has been expanding and growing and will reach the US $103.94 billion by 2030.
An increase in organized retail, such as hypermarkets and shopping malls, will get the biggest slice of the pie. This was followed by services, banking, healthcare, education and transport, and logistics.
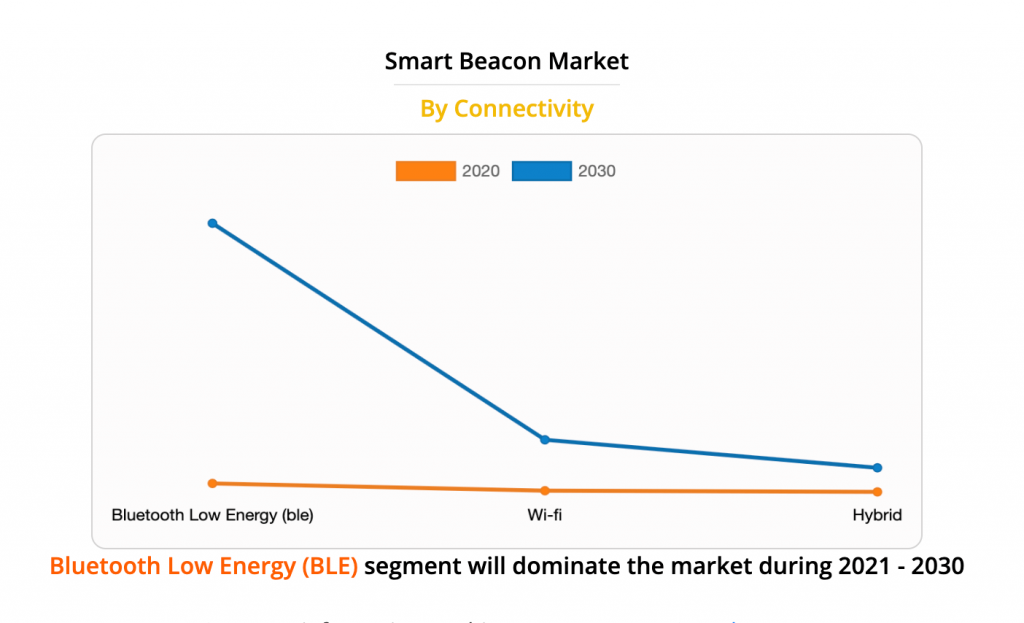
Overall, the market is dominated by North America, followed by Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Europe. The reason for this is the massive adoption of beacon technology in North America and the high penetration of mobile devices.
In addition, low-energy Bluetooth hardware is expected to dominate, and the standard type is represented by iBeacon. But there are also issues of lack of technical resources and privacy concerns.
To allay privacy concerns when implementing location-based technologies such as beacon technology, It’s necessary for companies to look for providers that focus on protecting user privacy, especially when it comes to location data. MOKOSmart’s beacons are encrypted, so users can rest assured of their privacy.
Difference between beacon technology, Geofencing, NFC, and WiFi
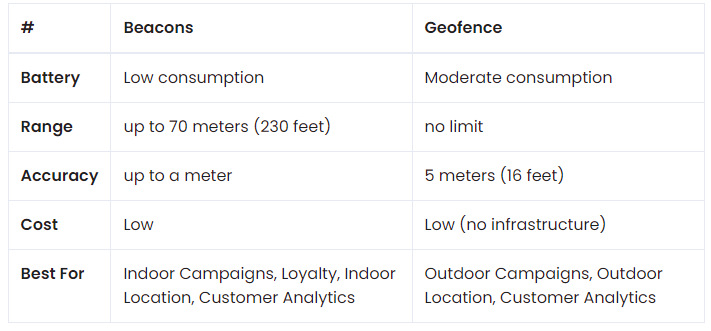
Beacon vs. Geofencing
Unlike geofencing, which uses GPS signals, beacons communicate with smartphones via Bluetooth. GPS is a bigger drain on the battery life of a customer’s mobile device than beacons because it requires satellites and cell towers to pinpoint the location. In addition, beacons capture more accurate data than geofencing and work much better indoors. Geo-fencing is more suitable for outdoor proximity marketing because its signal is greatly affected due to physical obstruction.
Beacons vs. WiFi
Beacons and WiFi work in much the same way — beacons and WiFi routers send radio signals that are detected by mobile devices to locate or relay proximity activity. However, beacons are significantly cheaper than WiFi routers (ranging from $1.00 to $15.00 per unit). On the other hand, most places such as shopping malls already have at least one WiFi router, so there is no installation cost involved.

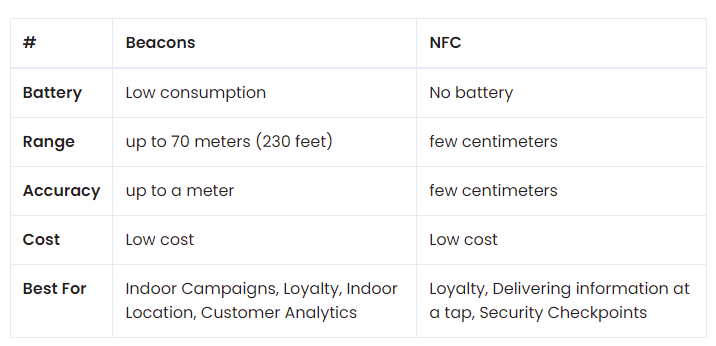
Beacon vs. NFC
NFC does not require batteries to operate, which is the main factor that distinguishes NFC from beacons. NFC tags are also much cheaper than beacon devices, but the downside is that NFC provides only limited information about a customer’s behavior and is only effective when clicked.
Types of beacon devices
Beacons on the market require different sensors depending on their size, battery performance, resistance to exogenous factors, and use cases. The most common types of beacons are:
Standard beacon: Suitable for indoor tracking.
Small beacons: Ideal for asset tracking and proximity solutions.
USB Beacon: Its appearance looks like a flash drive.
Video beacon: A small device used to transmit background video and digital signage.
AI beacons: Use machine learning algorithms to detect movements and gestures.
Sticker beacons: Being widely used for asset tracking.
Parent beacon: manages the ble beacon network, collects data from other beacons, and sends it to the cloud storage.
Dedicated beacons: It’s been regarded as the most preferable solution for tracking indoor activities and working in tough environments.
Beacon sensor
When choosing your Beacon Solution, you need to be aware of the environmental conditions to which you are deploying, and then decide which sensor is more appropriate for your application. Here are some of the most common Bluetooth sensors and tags:
Temperature and humidity sensor: Collects temperature and humidity data from the device
Accelerometer: Collects data on device acceleration. In a tag-based deployment, the accelerometer can detect whether an asset has moved or vibrated abnormally to determine whether the machine has been stolen or if there is an operational failure.
Light: Measures the level of light hitting the device
Button: Press the button to send any predefined real-time feedback and alerts to the cloud. This can be used for incident reporting, internal communication, or task completion reporting, among others.
Others: Vibration, air quality, etc
About MOKOSMART
MOKOSMART is the industry leader in Beacon Technology. We help customers of all sizes and industries accelerate digital transformation through open, and standard API. Industries we’re serving include healthcare, manufacturing, airports, government, etc. Beacons, gateways, modules, and other application services we provide all pass global certifications such as ISO9001 and CE, etc. We are committed to reducing time-to-market and costs for them and making a real difference wherever we can in the world.