The onset of Industry 4.0 and exponential growth of connected devices has led to the advent of remote IoT device management solutions. IoT can be regarded as an ecosystem, it can connect multiple smart devices through wireless networks such as Bluetooth, WiFi, and LoRa. Smart devices like beacons, sensors, and trackers are common, each assigned a unique IP address for identification. After connecting to device management, a large amount of data is automatically collected and transmitted without human intervention, aiding in monitoring and troubleshooting. In this article, we will get deeply into the definition and other topics regarding remote IoT device management.
What is remote IoT device management?
Remote IoT device management refers to monitoring, managing, and controlling internet-connected devices from a central location or platform. Instead of having to be physically next to devices to configure settings or troubleshoot issues, remote management allows administrators to securely manage entire fleets of distributed IoT assets through cloud-based tools.
Remote IoT device management is indispensable for operating scattered connected devices efficiently at scale. Basic systems provide monitoring and remote control while advanced platforms utilize telemetry data analytics for insightful oversight. In all, the ability to diagnose impending issues preemptively is highly valuable.
How to manage IoT devices remotely
There are several key steps to implement a remote IoT device management solution:
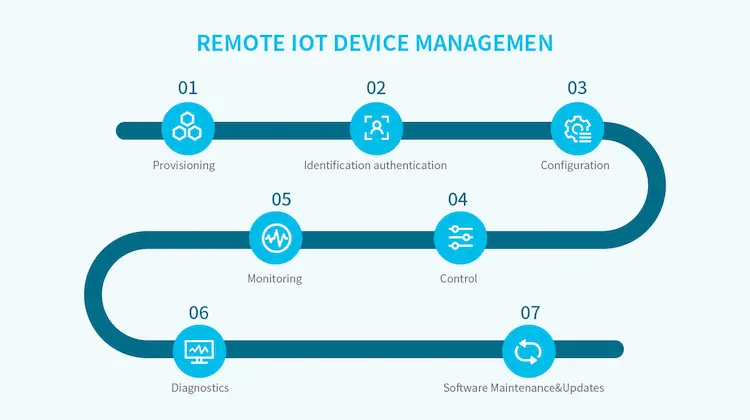
Step 1 – Provisioning: Onboarding Devices
Provisioning is the first step in IoT remote device management, where a smart device needs to be connected to the Internet in order to work properly. Provisioning brings new IoT devices onto the network. It involves:
- Complete the first connection between the IoT solution and device by registering the device.
You can register a single device or multiple devices at once. Devices are commonly grouped for efficient control, and then you can send commands to different devices at the same time. For instance, a fleet of delivery robots could be registered together under one group.
- Configure the device according to the requirements of the specific solution.
This may involve connecting to specified cloud platforms, gateways, setting communication protocols, etc. Initial configuration establishes a baseline to build on.
Step 2 – Authentication: Verifying Identities
Authentication confirms device identities before allowing IoT remote access, effectively preventing intrusions and keeping proprietary information confidential. To enable authentication, administrators should set up device and network security settings to authorize or block access attempts.
Although the authentication process for devices is different, each device has a different certificate or key to verify the authenticity of the identity. The model number and serial number are some of the credentials used to verify identity.
Step 3 – Configuration: Customizing Functionality
As we mentioned above, IoT configuration management is a way to customize the functionality of IoT devices. After the new device is installed, further configuration tailors connected devices to their required functions by:
– Integrating customized logic and behaviors through coding
– Fine-tuning settings to optimize performance
– Modifying configurations to support new use cases
For example, a building HVAC system could be reconfigured to self-adjust set temperatures.
Step 4 – Control: Operating Devices Remotely
You should be able to control devices after they are provisioned, authenticated, configured, and connected to the network through devices. Remotely manage IoT device behaviors after configuration involves:
– Setting automated actions to happen upon certain triggers
– Tracking device statuses and operating states
– Issue commands to groups of devices from the management dashboard
This allows administrators to coordinate devices without physical access.
Step 5 – Monitoring: Generating Insights
Another key goal of remote IoT device management is remote manage IoT over Internet. Monitoring IoT devices generates valuable insights like:
– Uptime analytics from system dashboards
– Predefined performance reports (e.g. temperature data)
– Alerts & notifications for critical issues needing timely intervention
These help administrators optimize and troubleshoot the network.
Step 6 – Diagnostics: Identifying Issues
After completing the process, the administrator can diagnose the entire device network and device health status. These processes enable administrators to perform diagnostics from the management platform without having to physically visit each device installation point, effectively and quickly troubleshooting and fixing problems.
Step 7 – Software Maintenance & Updates: Enhancing Functionality
IoT devices require complex software-defined attributes to manage their security and functionality. IIoT devices can last a decade or more. Therefore, to manage remote IoT devices, administrators should be able to send firmware updates to enhance functionality to any devices across the network at any time. Several examples of software updates are listed below:
– Installing new firmware updates to fix bugs and enhance features
– Delivering security patches to make sure security protection is up to date
– Using Python to update the code for device functionality to adapt to changing business requirements
– Tuning configurations like status reporting frequencies
Benefits of remote IoT device management solutions
There are a multitude of benefits driving the adoption of dedicated remote IoT device management platforms including:
Automatic locate: You can quickly search an entire fleet of devices or find any IoT device you want to use a combination of attributes such as device status, device ID, and type to take action or troubleshoot.
Remote management: The Internet of Things connects multiple devices, sometimes hundreds or thousands of them. Remote IoT device management enables you to manage or update devices remotely and maintain the health of your device cluster. You can also remotely perform fleet wide operations such as restarts, security patches, and factory reboots.
Improved security: Internet of Things devices such as routers and base stations risk being hacked. Therefore, security updates are critical in protecting networks. With continuous monitoring, abnormal behavior in data traffic and any attempts to change the configuration are detected and an alarm device is triggered.
Scalability: The ability to scale up a deployment depends on an organization’s ability to monitor and manage IoT devices remotely through a central management interface or on-site mobile devices.
Network optimization: Organizations need tools to deploy software changes for optimizing data usage, battery life, and functionality for devices at the network’s edge.
Faster time-to-market: The IoT device management platform helps developers minimize the time required for development and testing efforts
Lower cost: IoT device management detects device failures, which helps predict maintenance. This prevents minor incidents from becoming larger and requiring less maintenance time, which in turn leads to lower operating costs.
When do you need remote IoT device management
There are a few situations that demand the implementation of a dedicated remote IoT management platform including:
- Managing large volume of distributed IoT assets – Allows efficiently managing thousands of devices deployed across multiple sites.
- Devices in hazardous/hard to access locations such as mines, bridges and dams- Provides safe, online access to assets in dangerous places employees should not manually enter.
- Business-critical assets demanding high availability – Supports quick failure identification and resolution to minimize costly downtime.
- Frequent software/firmware updates required – Simplifies large-scale over-the-air update deployments.
- Regulatory compliance requirements – Built-in controls aid compliance with regulations mandating access controls, activity records, and remote wipes.
Types of commonly used IoT devices
Common IoT devices include Bluetooth beacons, sensors, and various smart connected objects. A connected entity can have dozens of sensors built into it to identify and react to the environment. A connected entity may have dozens of sensors built into it to identify and react to the environment. The sensor outputs information and exchanges data with other connected systems before sending a report back to the cloud.

- Temperature sensor
The industrial healthcare sector and cold-chain transport are particularly in need of such sensors to keep goods at a specific temperature.
- Humidity sensor
Humidity sensors can be used to calculate the amount of water vapor and water level in the atmosphere and are commonly deployed in heating systems, kitchen sewers, dams, and air conditioning.
- Accelerometer
Accelerometer is used to detect the rate of change in speed of objects relative to time. They are often used in intelligent pedometers and fleet monitoring. In addition, they are widely used in anti-theft protection systems, which notify when a stationary object or person enters a room
- Energy monitoring sensor
Energy tracking sensors are mostly used in smart water meters, which save the time and effort of manual meter reading and improve accuracy.
- Location tracker
Our daily life is now inseparable from location tracking solutions. There are a variety of IoT-enabled location sensors on the market that you can apply to your cargo or the person you want to track. When multiple trackers are deployed, real-time visibility of all devices becomes particularly important.
Features of remote IoT device management
IoT remote monitoring systems require some features to provide you with a higher level of control over remote devices.
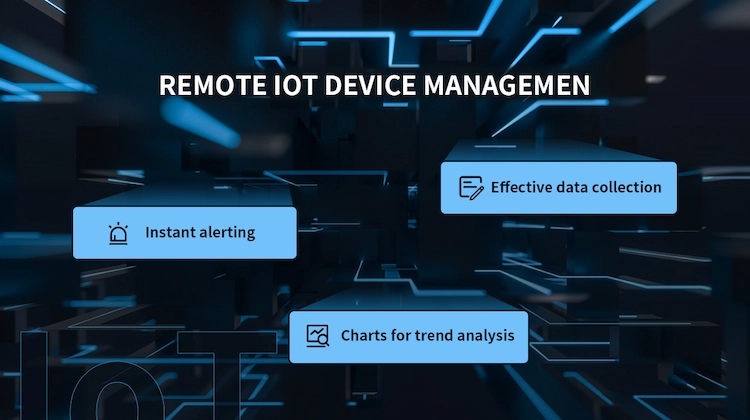
Instant alerting
Instant alerts enable you to receive important changes about the state in time. Your alerts are only meaningful if they can be properly deactivated or responded. If the notification reports a problem that cannot be resolved remotely, it should provide enough information so that you know what to do next. These pop-ups need to be delivered to people who can take action. Another approach is to perform event management. When you look at the root cause of critical failure alerts, you can know what other notifications can be set to help prevent the same problem from happening again.
Effective data collection
Your IoT devices may be deployed in remote locations, so you need to have an efficient method of data collection. There are two important methods to gain data: notification push or polling. For IoT monitoring systems, a push-based approach may be more convenient, but trade-offs should be considered. These trade-offs usually include appropriate communication protocols. It is important to ensure that the protocols supported by your device have an efficient way to collect data. But it’s also necessary to use open protocols for ensuring interoperability across multiple devices.
Charts for trend analysis
The remote IoT monitoring system can provide data for any defined period. However, the raw information itself is not directly usable but can help us grasp the information. However, the raw information itself is not directly usable, but can help us grasp the information. It’s best to have a monitoring system that enable you to execute some type of query across a database and then visually display the data. There are many other types of visual representations of data while line graph is the best way to achieve what you want.
Wireless technologies to manage IoT devices remotely
IoT is managed by connecting devices to a network and exchanging information and transmitting data. Therefore, appropriate IoT communication methods should be selected when starting the remote management IoT strategy. The following are some communication methods used for Internet of Things data transmission.
WiFi
WiFi is a local area network that exchanges data with connected electronic devices. Its fast data transfer makes it suitable for file transfers but also consumes much power. WiFi technology is based on the IEEE 802.11n standard and is mainly used in homes and enterprises, providing a range of hundreds of Megabits per second.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology is an important IoT protocol that is very suitable for mobile devices and is widely used for short range communication. It is suitable for sending small pieces of data to personal products such as smartwatches or sensors. It consumes relatively little power and has the potential to be scaled up to all markets for innovation.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWan, short for Long Range Wide Area Network, is an Internet of Things device used for remote wireless batteries and one of the most popular Internet of Things communication methods, known for long distance interaction with very low power consumption. In addition, it can also detect signals below the noise level. It’s common in smart cities that connect millions of devices.
NFC
NFC is a wireless technology designed for short distances, up to 10 centimeters. It works by using electromagnetic induction between two coil antennas near an electromagnetic field. Customers can use NFC for instant file transfer and non-contact payments. As a short distance communication protocol, the power consumption is low.
ZigBee
ZigBee is also a short-range wireless Internet of Things device communication protocol based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. The operating frequency is 2.4GHz and the data rate is 250kbps. The advantages are low power consumption, security, persistence, scalability and high number of nodes. ZigBee can transmit data over distances of up to 200 meters and has up to 1024 nodes in a network.
RFID
RFID utilizes electromagnetic fields for identifying and tracking tags attached to objects. The device captures data from the tag and sends it to the database.
z-wave
Z-wave is a wireless low power RF communication technology. Suitable for home automation products such as lamp controllers and sensors. With mesh network topology, up to 232 devices can be controlled and communication distance can reach 40 meters.
SigFox
SigFox aims to reduce the cost of wide-area coverage in application domains. It allows any communication requiring minimal power consumption, based on two-way functionality, for consumer goods, retail, transportation, and energy related communications.
MQTT
MQTT is a lightweight protocol for delivering data flows from sensors to applications and middleware. It sits at the top of the TCP/IP layer and consists of 3 components: broker, subscriber and publisher. Publishers collect data and transmit it to subscribers. The broker tests publishers and subscribers to check their authorization.
MQTT provides three patterns for achieving quality of service:
- QoS0 sends at most once: the least reliable, but fastest mode. Publications were sent but no confirmation was received
- QoS1 send at least once: A message may be sent at least once, but duplicate messages may still be received
- QoS2 sends exactly once: it is the most reliable pattern, but it is also the most bandwidth intensive pattern requiring a control copy to make sure that the message is sent only once.
AMQP
AMQP is an open standard subscription and publishing protocol from the financial industry. It provides asynchronous subscription or publication communication through messaging. The storage and forwarding function ensures reliability even when the network is interrupted. AMQP is probably the only viable protocol for end-to-end applications in the Internet of Things, often used in heavy industrial machinery or SCADA systems.
DDS
The Data Distribution Service protocol is designed specifically for real-time communication, reliable, scalable and high-performance data exchange between connected devices independent of software and hardware platforms. It supports architectures with fewer multicast and agents to ensure high-quality QoS and interoperability. It can be used for industrial IoT deployment, including high-tech services such as self-driving cars, smart grid management, air traffic control and robotics.
LwM2M
LwM2M is a lightweight M2M designed to meet the needs of processing resource-constrained devices. It defines many IoT device management functions, such as remote device operation connection management and monitoring, as well as firmware and software updates.
OCPP
OCPP is a protocol that enables EV charging systems to communicate with a central management system. It is used to transmit a 24-hour forecast of local available capacity to the charging point operator.
Challenges of managing distributed IoT devices
While delivering immense value, remote IoT device deployments also pose challenges – especially when dealing with thousands of distributed assets as opposed to a fixed set of equipment at a single site. Common pain points and challenges faced when managing remote IoT device networks and equipment include:
- Fragmented Industry, Emerging Standards
IoT remains an emerging, quickly-evolving industry without universal standards across connectivity protocols, data formats etc. Successfully managing different hardware, models, and connectivity types is essential.
- Battery Constraints
Supporting low-power operation to maximize battery life of assets while still collecting and transmitting adequate data requires careful balancing. Frequent over-the-air updates can also quickly drain connected batteries.
- Network Coverage & Bandwidth Limitations
Assets in remote locations often have spotty cellular or WiFi availability. Even in connected areas, transmitting lots of sensor telemetry can strain available bandwidth. Carefully assessing available connectivity and setting data transmission frequency thresholds is key.
- Increasing Scale & Complexity
As more assets get connected and deployed, the headaches of managing thousands of heterogeneous devices and increasing data volumes can accumulate quickly. Choosing solutions specifically designed to easily scale is critical.
Remote IoT device management platforms
You can find cloud platforms for various IoT solutions in the market. Below are three of the leading remote IoT device management platforms targeting business applications:
AWS IoT
Cloud services and device software are provided by AWS IoT for connecting your IoT devices to other devices and integrating them into AWS IoT solutions. Protocols as below can be provided:
LoRaWAN
MQTT
MQTT over WSS
HTTP
Azure IoT
AWS IoT is a cloud platform that provides services for multiple security mechanisms, for example, encryption and access control of data collected by devices, as well as services for configuration monitoring and auditing, through open edge and scalable security to cloud IoT solutions.
Google Cloud IoT
Google Cloud IoT platform lets you unlock insights into the global network of devices. Its fully managed interactions enable you to connect, analyze, and store data in the cloud or edge. You can leverage the strengths of Google’s Cloud IoT building blocks to get value from device data from data ingestion to intelligence. With this platform, the need of maintenance and optimization of its performance can be detected in real time.
Conclusion
If you’re planning the IoT project or would like to upgrade the deployed equipment network, remote IoT device management is essential for your solution. The platform serves as a key to keeping your device online updated and optimized to meet your specific application needs. All of these benefits will give you the best ROI on your investment.
To learn more about adding medium to large scale remote monitoring and management capabilities leveraging modern IoT innovations, visit MOKOSMART to explore our end-to-end IoT hardware solutions including Bluetooth and LoRaWAN devices.