LoRa (Long Range) sensor wireless technology is creating waves in the Internet of Things (IoT) industry. This wireless technology can deliver reliable connectivity across long distances – stretching as far as 10 km in rural areas and 2km in urban areas. With reliable data transmission penetrating indoor spaces and underground structures, and battery lifetimes crossing several years – all at low operational costs – LoRa promises to eliminate many connectivity and power challenges holding back innovative IoT use cases.
Given its strengths, it’s no surprise industry forecasts expect LoRa to connect the next billion IoT devices. The analyst firm ABI Research predicts LoRa will account for over half of all non-cellular LPWA connections, which may total nearly 1.3 billion by 2026.
What are LoRa sensors
LoRa sensors are wireless sensors that use LoRa communication technology to transmit sensor data to gateways and applications. These sensors use very little power and can operate for multiple years before needing replacement. Common measurements include temperature, humidity, air quality, water flow, soil moisture, vibration, and more.
The sensors contain a microcontroller to take sensor readings, LoRa radio for wireless communication, and a battery power source. Data from the sensors is transmitted periodically over the LoRa network to central applications and analytics platforms. Some common sensors integrated in LoRa sensors include:
- DHT11 – Temperature and humidity sensor
- Ultrasonic – Object detection sensor
- Photosensitive – Ambient light sensor
- Flame Sensor – To detect the presence of fire
- Relays – For controlling device power
- Buzzers – Audible alarms or warnings
- LEDs – Visual indicators
- GPS modules – Location positioning
These sensors can be connected to a LoRa-enabled microcontroller board like an Arduino or Raspberry Pi to collect and transmit sensor data.
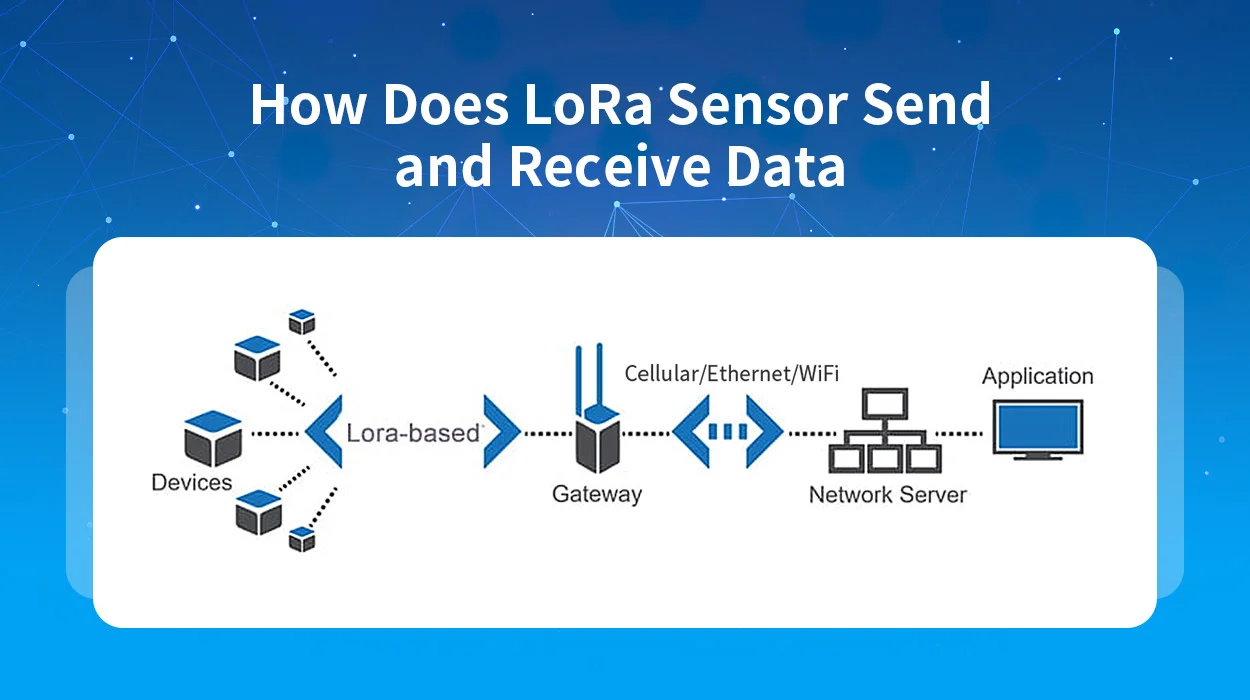
How LoRa sensors transmit and receive data via LoRaWAN
LoRa sensors operate within a LoRa network, utilizing the LoRaWAN protocol for efficient data transmission and reception. The LoRaWAN is a cloud-based media access control (MAC) layer protocol that primarily acts as a network layer protocol. We use LoRaWAN for managing communication between LoRa gateways and LoRa sensors (nodes). It functions as a routing protocol and the LoRa Alliance maintains it. The first version of LoRaWAN was released in the year 2015.
In the LoRaWAN architecture, LoRa nodes, which are the sensors equipped with LoRa protocol, initiate asynchronous communication when they have data to transmit. This enables a LoRa network to trade off sensitivity for data rate with a fixed channel bandwidth. It mainly involves selecting the amount of used spread, a selectable parameter between 7 and 12. This spreading factor determines the sensitivity and data rate of a LoRa node.
Data transmitted by a LoRa node is received by multiple LoRa gateways, which forward the received data packets to a centralized network server (IoT server). It filters out duplicate packets, manages the network, and performs security checks. Subsequently, the server sends the processed data to application modules, control panels, or connected smart devices. This way LoRaWAN protocol shows high reliability and accuracy for the moderate load.
Additionally, the LoRaWAN protocol incorporates Forward Error Correction coding to enhance the network’s resilience against interference. With a high wireless link budget around 155 dB to 170 dB, LoRa networks exhibit an extended range, making them suitable for diverse applications.
How to set up a LoRa sensor network
Devices in a LoRa network consist of LoRa nodes (sensor devices), LoRa gateways that relay messages, and a centralized LoRa network server. To use a LoRa sensor, a comprehensive LoRa network setup is essential. Let’s explore the key components in detail:
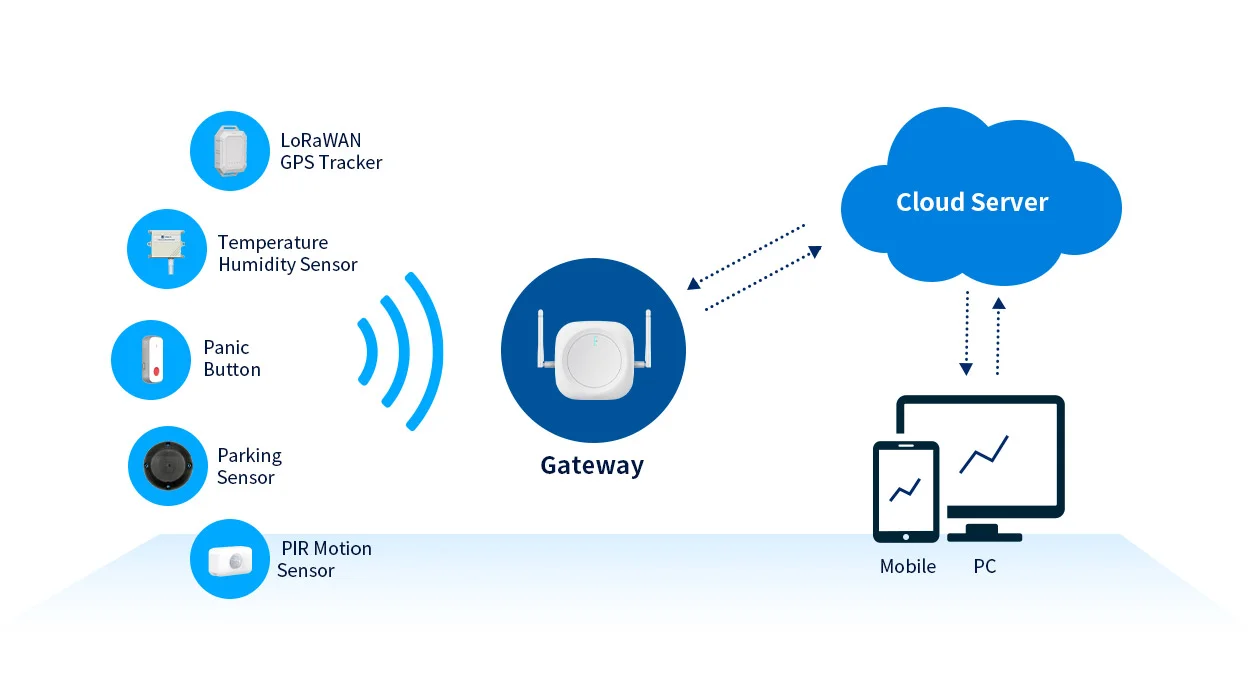
LoRa Node: The sensors embedded with wireless connectivity and LoRa protocol. It collects sensor data and transmits it to the LoRa Gateway.
LoRa Gateway: Acts as the central point for forming the LoRa network. It receives data from LoRa nodes via LoRa wireless and forwards it to the cloud server over IP-based connectivity like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Cellular. Gateways also receive commands from the cloud and send them to LoRa end nodes. Typically multiple gateways will receive the same node transmission – providing redundancy.
Cloud Server: A cloud server that receives and stores data from LoRa gateways. It provides access to the data from multiple platforms, allowing scalability and control over the performance and range of LoRa sensors.
It provides access to the data across various platforms, offering the flexibility to scale and manage the performance and range of LoRa sensors.
The cloud server also serves as a conduit for sending commands from a control panel (smart device) to the LoRa nodes. In this case, you can make adjustments in the performance, range, or other parameters of the LoRa sensors in the LoRa network.
So, this is how we set up LoRa sensors within a LoRa network. A LoRa network can accommodate as many LoRa sensors as required.
Benefits of using LoRa sensors
LoRa technology, standing out among disruptive technologies, is not a vision for the future but a present-day reality with a global footprint. Billions of LoRa and LoRaWAN sensors are already deployed worldwide in various IoT implementations, and this number is steadily on the rise. Leveraging the LoRaWAN protocol, LoRa sensors contribute significantly to the evolution of a smarter world. Here are some key benefits of LoRa sensors:
Long range connectivity
LoRa technology is distinguished by its low-power consumption and long-range data communication capabilities. It provides reliable wireless connectivity for up to 10 km in rural areas and 2 km in urban locations for underground and indoor sensors. This is critical for agricultural or water metering uses.
Low power operation
LoRa sensor nodes can operate for up to 10 years on a single battery by optimizing sensor measurement frequency, sleep cycles, and LoRa link data rate. Low power is essential for remote agriculture, utility infrastructure, or tracking use cases. This also reduces maintenance overhead.
Interference resilience
LoRa uses chirp spread spectrum modulation which provides resilience against radio noise and interference. Forward error correction schemes provide signal robustness.
Global ecosystem
The LoRaWAN specification and associated alliances offer an interoperable framework usable by diverse public and private LoRa network providers. With over 500 members, including 100 public network operators in more than 58 countries, the LoRa Alliance’s ecosystem ensures global accessibility. With networks in 100+ countries, it enables swift deployment of LoRa solutions worldwide.
Versatile applications
LoRa complements technologies like Cellular, WiFi, Sigfox for cost and power sensitive applications. This drives adoption for smart cities, buildings, agriculture, logistics and industrial scenarios.
Prospective applications of LoRa sensors
LoRa Sensors offer a wide range of possibilities that we can use for applications across multiple sectors. Some of the prospective applications of LoRa sensors are:

Smart Agriculture
LoRa soil moisture sensors, light sensors, humidity monitors help optimize water usage and growing conditions to improve crop yields. Location tracking of livestock health is enabled.
Smart Cities
LoRa sensors relay data on the availability of parking spots, environmental monitoring parameters, and even waste bin status. City services around lighting, traffic monitoring leverage the technology. LoRa is also employed in leakage and structural health monitoring applications.
Smart Healthcare
LoRa networks enable low cost, reliable connectivity for medical asset tracking, temperature monitoring of drugs/blood samples, elderly patient health monitoring. IoT solutions based on LoRa sensors and gateways can help monitor high-risk patients around the clock.
Smart Industrial Monitoring
Operations in the industry can benefit from the LoRa sensors, which have continuous monitoring functions. LoRa wireless sensors for temperature, vibration, pressure, power consumption help analyze factory equipment health without costly cabling. GPS-free location services track high-value assets and containers across industrial parks leveraging the extended range.
Smart Utilities
Since meters are often located indoors, underground, or in dense urban environments. This makes it difficult for most wireless technologies to reach them. Cities are rolling out smart meters for gas, electricity, and water supplies based on LoRa radio connectivity to relay consumption data remotely instead of manual in-person inspection.
Smart Supply Chain & Logistics
LoRa sensors make it affordable and easier for logistics and supply chains to track high-value assets in transit. The long-range and low power consumption of LoRa sensors makes it easier for the geolocation of vehicles and cargo. Pallets fitted with shock or temperature sensors help determine mishandling and insurance claim validity.
Alzheimer Patient Tracking
LoRa technology wearable tracking devices can alert caregivers when an Alzheimer patient leaves a designated safe zone. This will help in ensuring round-the-clock safety in the absence of physical supervision. Longer battery lifetime compared to BLE tags keep maintenance effort low.
Smart Homes & Buildings
LoRa sensors seamlessly transmit information regarding home and building dynamics. They keep tabs on energy usage, HVAC functionality, and security measures such as smart door and window sensors. Beyond that, LoRa extends to creating intelligent and interconnected living and working spaces.
Conclusion
If you are working on an IoT-based solution and want to use LoRa technology but are worried about the complexity of the process, then you can rely on MOKOSmart. We offer a variety of robust LoRaWAN sensors, which you can use as per your needs. Additionally, we provide hardware designing, prototyping, product assembling, RF debugging, and LoRaWAN embedding services. So, you will get professional-grade LoRa modules for your IoT-based solution. Feel free to contact us if you want to inquire about a quote or ask any questions.
READ MORE ABOUT LORA