Over the past decades, the pace of IoT innovation never ceases to amaze us. We’ve gone from pie-in-the-sky dreams of connected appliances to deployments of massive industrial sensor networks. Market research predicts that over 30 billion IoT devices will be active by 2030 as smart products, wearables, appliances and more become interwoven in our daily lives. The key innovation enabling this change? You guessed it…IoT communication technologies! Notably, that’s also where Bluetooth comes in! In this post, we’ll look at what exactly Bluetooth IoT is and the key reasons it’s an ideal choice for many IoT applications.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things is an exciting concept – connecting smart devices and allowing them to collect and share data. I’d like to use a chessboard as an analogy to describe the IoT. Imagine each piece as a sensor gathering information about its surroundings. Individually they provide situational data. But networked together by IoT technologies, they share a bigger picture allowing them to coordinate and act collectively. This transforms dumb objects into intelligent systems!
We’re seeing this play out through billions of deployed IoT products. Connected sensors embedded into everyday things like appliances, machinery, warehouses and even livestock to monitor, analyze and manage activities. While still early days, it’s predictable that IoT ecosystems are getting larger and more accessible.
Overview of Bluetooth technologies
Most people think of Bluetooth as that wireless standard that connects their headphones to phones. Actually, Bluetooth has evolved over decades of technical innovation while retaining backward compatibility. Classic Bluetooth enables popular uses like wireless headphones and keyboards. And the newer Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) standard optimizes small IoT systems with ultra low power and cost.
And the Bluetooth Special Interest Group hasn’t been resting on their laurels. They continue advancing the standard to keep pace with IoT’s demands. We’re talking major leaps in speed, range, precision and broadcast capacity with each revision. Over several revisions, continuous compatibility improvements have opened huge opportunities in the burgeoning IoT industry including:
- Bluetooth 5– This recent release extends the wireless range up to 800 feet while doubling data throughput. This means whole-home and industrial facilities can be blanketed in a “mesh” of Bluetooth connectivity.
- Bluetooth Direction Finding– By determining the precise direction of signals, new Bluetooth location services bring accurate positioning and navigation to warehouse robots, retail shoppers and more futuristic use cases.
- Bluetooth Low Energy– BLE optimizations allow tiny, streamlined sensors to operate reliably for years instead of days on low-cost coin-cell batteries. This miniaturization and efficiency make embedding connectivity into everyday objects financially viable.
- Bluetooth Security– Layers of encryption, authentication, and verification keep data integrity and user privacy airtight across the exponential growth of connected devices.
But what precisely constitutes Bluetooth IoT, and what can end users expect to gain from this behind-the-scenes connectivity? Let’s break it down!
What is Bluetooth IoT and how does it work
Referring to the broader IoT umbrella term, we essentially have sensors and processors attached to everyday objects that continually talk to the cloud servers. Bluetooth IoT refers specifically to connecting and networking these IoT devices via Bluetooth wireless protocols. Due to its short range limits, Bluetooth only enables this data communications across a massive web of wireless “last several feet” connectivity.
Tiny, energy-efficient Bluetooth radios get embedded directly into connected devices like beacons, sensors and trackers, allowing them to wirelessly network via encrypted peer-to-peer links. These gadgets can auto-discover and exchange data with proximate IoT Bluetooth devices, as well as bridge to broader networks via Bluetooth IoT gateways and Bluetooth mesh networks. This flexible, scalable wireless connectivity framework allows multitudes of machines, appliances, assets and spaces to be linked into smart IoT systems, just the ingenious pragmatism of ubiquitous Bluetooth communication.

Bluetooth IoT devices and applications
With about 5.4 billion Bluetooth enabled devices shipping in small, cost-effective, battery-powered packages already in 2023. The versatility of Bluetooth makes it an ideal fit for the Internet of Things across consumer, commercial and industrial applications. As Bluetooth specs advance, so too do the possibilities.
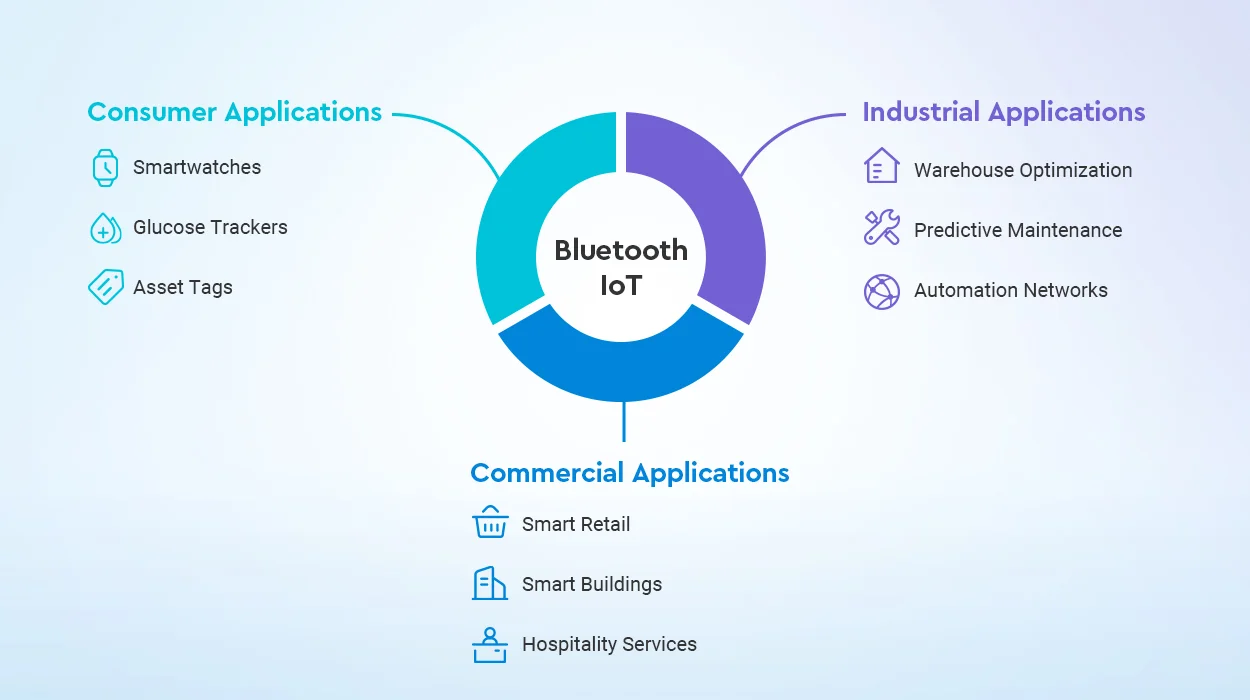
Consumer Applications
- Smartwatches – Monitor health metrics like heart rate, sleep patterns. Some now last up to 6 months on battery.
- Glucose Trackers – Painlessly track blood sugar for diabetics. Alert wearer to dangerous highs/lows.
- Asset Tags – Tiny Bluetooth tags to locate lost items like keys via smartphone app.
Commercial Applications
- Smart Retail – BLE beacons provide indoor positioning to send context-aware promotions to shoppers’
- Smart Buildings – Occupancy sensors optimize lighting, HVAC usage for efficiency based on real-time space utilization.
- Hospitality Services – Guests unlock hotel rooms with their phones for frictionless check-in/out.
Industrial Applications
- Warehouse Optimization – BLE pallets autonomously navigate floor, enable inventory accuracy of +/- 97%.
- Predictive Maintenance – Vibration sensors on machinery detect early signs of failure, enable proactive service.
- Automation Networks – Robots, AGVs and equipment coordinate intelligently with positioning accuracy under 1 meter.
Why choose Bluetooth for IoT connectivity
There are several key reasons why Bluetooth stands out from other wireless protocols for IoT applications:
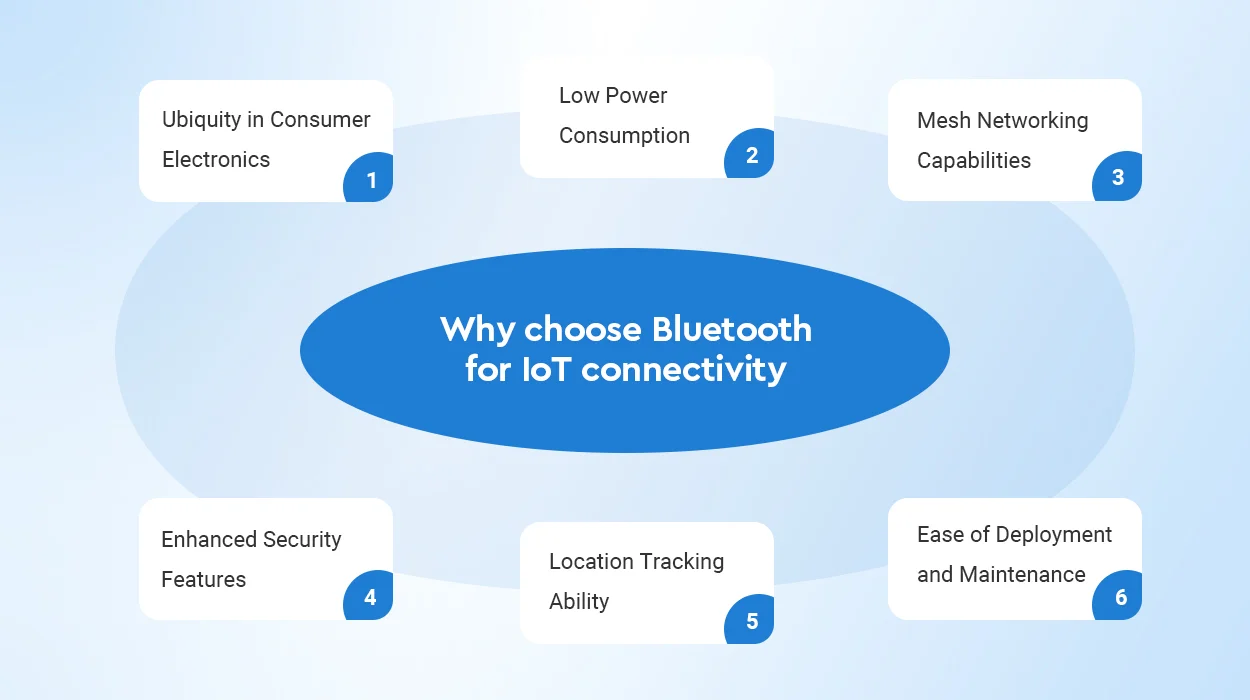
Ubiquity in Consumer Electronics: Bluetooth is ubiquitous – almost every smartphone, tablet, laptop and wearable device comes with native Bluetooth support. This means Bluetooth IoT devices can easily interface with personal gadgets we use every day.
Low Power Consumption: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocol is designed specifically for IoT solutions. It allows devices to run for months or years on tiny, coin-cell batteries by intelligently managing power modes during transmission and sleep cycles. This is vital for distributed sensor networks.
Mesh Networking Capabilities: The latest Bluetooth 5 standard brings mesh networking capabilities – allowing BLE devices to relay data via each other to extend range. Each node only needs to transmit as far as the next node. This builds self-healing networks while minimizing power usage.
Enhanced Security Features: Bluetooth features built-in data encryption to protect against eavesdropping and data manipulation. IoT security is crucial for user privacy and preventing DDoS attacks via hijacked devices. Mandatory encryption prevents MITM attacks.
Location Tracking Ability: Bluetooth beacons and tags transmit identifiable signals that nearby devices can detect and use to pinpoint their position. This allows for indoor location tracking without needing expensive WiFi/cellular triangulation hardware.
Ease of Deployment and Maintenance: Bluetooth devices can rapidly self-organize into networks rather than rely on technical staff for deployment. Combined with long battery life and small form factors, its easy to install BLE devices in hard-to-reach places.
The future of Bluetooth technology for IoT
Far exceeding classic “pair and play” functions, Bluetooth now achieves wonders of performance once solely associated with far more expensive or power-hungry communication platforms. Yet the underlying technology retains a simplicity and cost-effectiveness easing integration into almost any space, appliance or activity within people’s daily lives. In the unfolding Internet of Everything landscape, Bluetooth standards offer perhaps the magic glue connecting this new world.
Bluetooth technology sits poised to enable the next generation of wirelessly connected realities. Future Bluetooth versions will bring greater speeds, stronger authentication and enhanced proximity detection features. Anyway, Bluetooth powered IoT ecosystems promise to drive the next technology revolution – get ready for this exciting new hyperconnected world!
FAQs about Bluetooth IoT
How far can Bluetooth IoT devices communicate?
Bluetooth 5+ standards allow for ~800 feet (240 m) communication ranges outdoors and even farther with specialized antennas. This is suitable for most smart home and commercial spaces.
Which devices work with Bluetooth IoT?
Most modern smartphones, tablets, computers, and IoT hubs contain Bluetooth radios compatible with BLE devices. Bluetooth SIG also ensures consistent interoperability across over 34,000 certified device types.
What’s the benefit of IoT Bluetooth vs WiFi?
Bluetooth achieves far lower energy usage and cost at short ranges. This allows for years of runtime on tiny batteries ideal for dispersed sensor networks.
Can Bluetooth IoT scale to very large deployments?
Bluetooth mesh networks can smoothly bridge thousands of devices across large facilities. New capabilities like direction finding also improve location services.
CONTINUE READING ABOUT BLUETOOTH