Wondering what this whole “RTLS” thing is about before adding real-time location tracking to your application or business? Make sense – it’s a big investment. And if you’re reading here, chances are you know that real-time tracking can optimize operations and reduce costs. Indeed, many companies are setting their sights on RTLS: in fact, the global real time location system market is expected to hit $31.09 million by 2030, growing from $4.91 billion in 2022, indicating a widespread adoption of this solution. If you’re thinking of jumping on the RTLS train, this post will break it all down for you – how it works exactly, typical uses, leading vendors, and some differences.
What is RTLS (Real-Time Location System)
Real-time location systems, or RTLS, are technologies that automatically track and locate assets or personnel in real time, usually within defined spaces like buildings. In short, RTLS tech tells you the current spot of a given item or person – not necessarily everywhere they’ve been or how they got there, but exactly where they are right now.
Accordingly, wireless RTLS tags attach to things or people. Fixed reference points then pick up wireless signals from the tags to determine their precise location. RTLS is an end-to-end system, including tags, anchor sensors, reader hardware, software, integration and analytics capabilities. Unlike GPS that works outdoors using satellites, real time location system RTLS leverages signals and algorithms optimized for indoor areas. As a result, this provides super precise location data within just centimeters or feet.
How does real time location system work
There are several key components that make up an RTLS system and enable its location tracking capabilities. With the exception of some GPS tags that transmit data directly via cellular networks, most RTLS technologies include at least these three components:
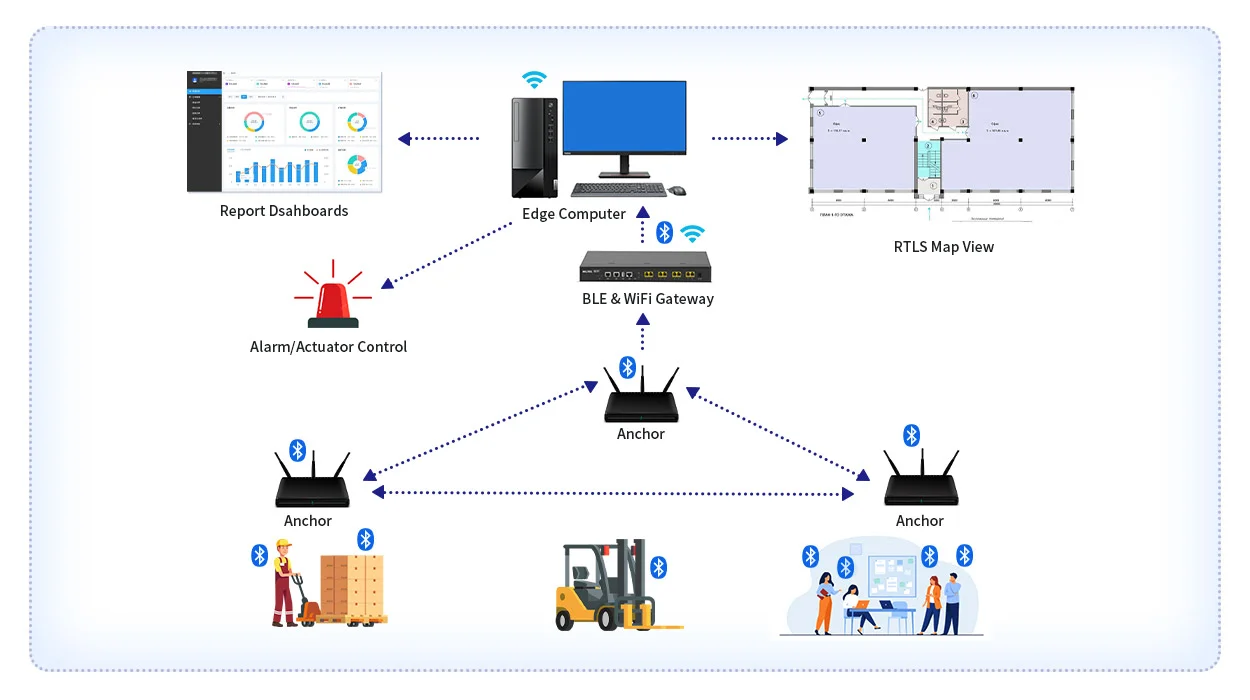
Location Tags – Battery-powered wireless tags attach to assets and people to track. The tags periodically transmit radio signals to receivers in the environment. Key specs are battery life, size, attachment methods, and transmission frequency. All RTLS solutions need tags affixed on each asset being monitored, with substantial technology differences depending on the system.
Receivers – For WiFi-based systems, standard WiFi access points act as the receivers. For other RTLS solutions like infrared or radio frequency, dedicated receivers are needed. Receivers collect signals from the tags and relay them to software via WiFi, cellular, Bluetooth or wired networks. Their form depends on the technology used.
Software – This includes online tools, on-site server software, and any features enabled in receivers to retrieve location data. Back-end software analyzes the signal data to accurately calculate locations. RTLS software also provides workflows, dashboards and analytics around the location data.
5 types of different RTLS technologies
Choosing the right real-time location system (RTLS) is critical – the tech varies widely. In fact, every solution out there has different trade-offs, suited to different use cases at different price points and complexity. To find the best RTLS for your needs, focus on your actual application.
| Technology | How it Works | Cost | Typical Usage |
| RFID | Uses passive RFID tags and RFID readers | $ (inexpensive passive tags) | Mostly indoors for high volume, low cost asset tracking |
| WiFi | Leverages existing WiFi network and connected devices | $$ (uses existing network) | Indoors and outdoors where there is WiFi coverage |
| Bluetooth LE | Uses BLE beacons and gateways/mobile devices | $ (low cost beacons) | Indoors and outdoors within short range of beacons |
| UWB | Uses UWB tags and UWB anchors | $$$ (expensive tags) | Indoors where high accuracy is critical |
| Infrared | Use infrared tags and infrared receivers | $$ (low cost compared to active RFID/UWB) | Indoors for room-level accuracy tracking |
RFID
RFID relies on tags emitting radio waves which are picked up by readers. It’s widely used for large-scale, low-cost tracking thanks to inexpensive passive tags (around $0.10 each). But RFID has limited accuracy and range. RFID is a cost-effective option best suited for tracking high volumes of lower-cost items that just need basic real-time location capabilities.
WiFi-based systems leverage existing WiFi network infrastructure for indoor tracking. Tags are not required – the WiFi-enabled devices like smartphones and laptops that connect to the network can be tracked. WiFi RTLS is most accurate when there is a dense layout of WiFi access points. It scales well since it utilizes hardware already in place and is easy to set up.
BLE
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a short-range wireless tracking technology that is highly power-efficient, with small battery-powered beacons lasting years. BLE location tracking uses inexpensive, battery-powered beacons ($5-$30) for simple deployment of real-time tracking across smaller areas. But BLE has lower location accuracy between 1-5 meters. It’s a lower-cost option for basic tracking that doesn’t require high precision.
UWB
Ultra-wideband (UWB) RTLS transmits across a very wide radio frequency band up to 500 MHz, allowing for precise localization of tags and immunity to multipath interference. However, UWB infrastructure and tags remain expensive at $10-$100 per tag. But for applications where high real-time location accuracy is critical, UWB is worth the premium. In particular, the ultra-precise tracking capabilities justify the higher costs of UWB for missions requiring real-time location data.
Infrared
Infrared RTLS works like a TV remote, using infrared signals between battery-powered tags and fixed receivers. Tags emit unique IDs at set intervals. Nearby infrared readers detect these ID signals and forward the data to track asset locations at room-level accuracy. Infrared provides a low-cost real-time visibility option when pinpoint precision isn’t needed – just identifying the room containing each tagged asset.
Common use cases for RTLS IoT solutions
RTLS delivers benefits across many industries, from healthcare to manufacturing to logistics. Furthermore, the technology integrates with existing systems to provide enhanced visibility, automation, and data. RTLS tracking brings transformational real-time location intelligence for a variety of use cases:
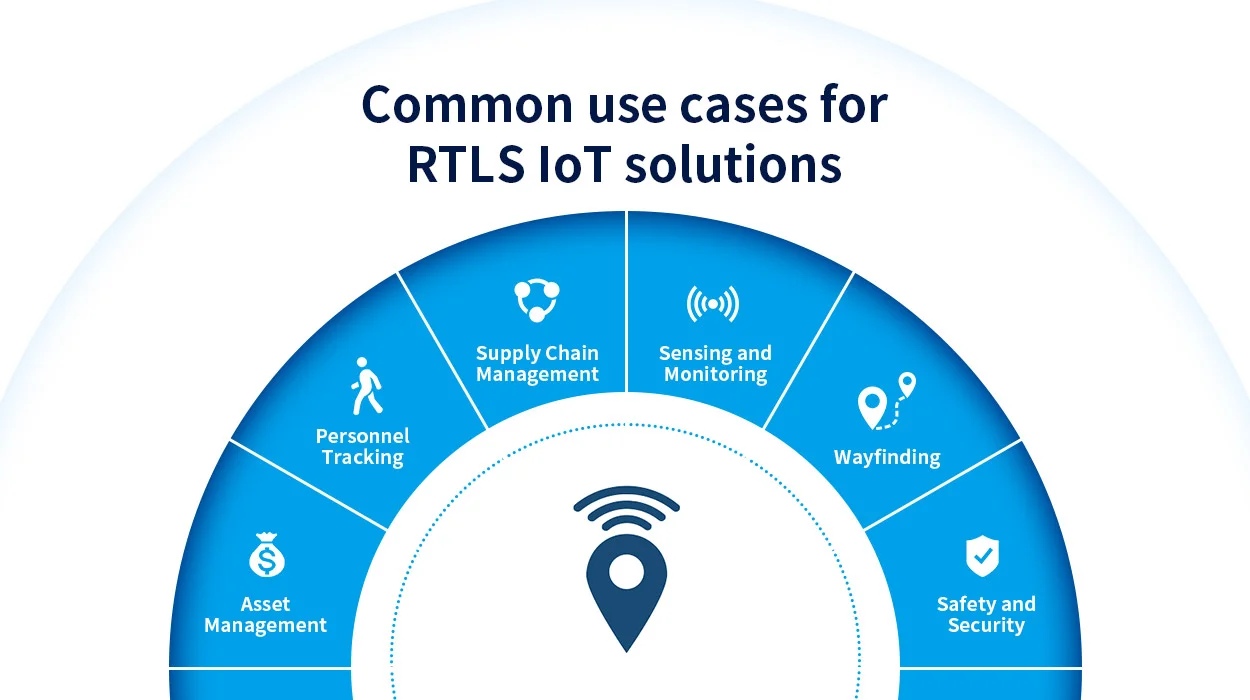
Asset Management
RTLS tags can be affixed to high-value enterprise assets like medical equipment, laptops, servers, and tools for precise real-time tracking of location and utilization.
Personnel Tracking
Personnel tracking with RTLS improves safety and security by monitoring staff and employee locations within a building. It also optimizes location-based workflows.
Wayfinding
Indoor wayfinding powered by RTLS provides navigation and directions for employees, patients, and customers in offices, healthcare facilities, and retail stores. Personalized experiences can be delivered.
Supply Chain Management
RTLS tracks raw materials, inventory, parts, products, and workforce efficiency throughout warehousing and logistics. It also enables real-time shipment and vehicle tracking for inbound/outbound supply chain visibility.
Sensing and Monitoring
The monitoring of the ambient environment around assets. Combining RTLS with sensors and beacons can get remote monitoring of temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, and more. As a result, this prevents spoilage and waste for temperature-sensitive storage area.
Safety and Security
Pinpoint location of all staff, assets, and products ensures immediate response to safety and security incidents. RTLS also tracks personnel entering hazardous zones and aids in evacuations.
Top RTLS solution vendors to watch out for
With RTLS momentum growing, notable vendors lead the market in enterprise-grade real time location tracking solutions:
Zebra Technologies – An RTLS powerhouse, Zebra offers RFID, UWB, and BLE solutions tailored to key verticals like retail and healthcare. Their MotionWorks RTLS solutions provide robust location tracking capabilities for assets, inventory, staff – everything that moves in these environments.
Aruba – This Hewlett Packard Enterprise company brings savvy WiFi RTLS solutions. They integrate location services right into enterprise wireless gear, so assets and people are fully visible across facilities. With advanced BLE and WiFi, plus new analytics, Aruba has the wireless RTLS chops to deliver scalable location intelligence.
Cisco – This networking tech titan enables RTLS through wireless infrastructure and an ecosystem of partners. Cisco builds location services into WiFi, BLE, UWB and other tracking tech. Moreover, leveraging Cisco’s widespread wireless presence, Cisco can take real time location services across industries.
Securitas Healthcare – This RTLS specialist excels at tracking healthcare environments. Their AeroScout platform leads for WiFi-based locating of patients, staff and assets. Advanced room-level tracking boosts hospital workflows. So for healthcare sites seeking location visibility, Securitas brings RTLS expertise tailored to this demanding vertical.
How do GPS and RTLS differ
When it comes to location tracking, GPS and RTLS have some major differences to understand. GPS uses satellites for outdoors positioning. But those signals can’t penetrate indoor spaces – it’s a no-go for within buildings.
In contrast, RTLS takes location tech inside using tags, sensors, WiFi and other signals optimized for indoor accuracy down to centimeters. No line of sight needed either – RTLS provides true enterprise-wide coverage.
GPS gives you outdoor location checks. But RTLS delivers 24/7 real-time visibility across indoor facilities. It enables asset management, workflow optimization, inventory control and other precision tracking use cases indoors.
So for comprehensive location intelligence, RTLS complements GPS to handle the indoor space. While GPS covers you outside, RTLS becomes your location oracle within buildings and facilities. It takes visibility to the next level where GPS falls short indoors.
Differences between Asset tracking and RTLS
It’s key to understanding the differences between asset tracking and RTLS for location visibility. Asset tracking checks asset locations at set spots. You get periodic checkpoints but no real-time, organization-wide awareness.
On the other hand, RTLS, real time location tracking system is a whole different ballgame. It actively tracks all assets enterprise-wide without line-of-sight needed. You get precise positioning in real-time plus predictive movement analytics – true 24/7 location intelligence. RTLS requires planning and infrastructure to sync tags, networks, sensors to provide robust workflows, security, inventory tracking and more.
The bottom line? Asset tracking provides location glimpses. Real time tracking system delivers constant visibility with the power to digitally transform operations. For ultimate location capabilities, RTLS is the strategic choice.
MOKOSmart BLE-based RTLS tags and sensors
Accurate indoor positioning is crucial but challenging. MOKOSmart solves this through innovative BLE tags and sensors for real-time location tracking. Whether you need precise asset tracking or cost-effective whole facility monitoring, MOKOSmart has reliable BLE tags to meet your needs. Therefore, partner with MOKOSmart to implement the right RTLS solution and take your indoor positioning capabilities to the next level. Our experts are ready to help you maximize the value of accurate indoor tracking.
CONTINUE READING ABOUT RTLS