In today’s technology-driven world, smart wearable has emerged as one of the most exciting and innovative advancements in the field of Internet of Things. These intelligent devices seamlessly integrate with our daily lives, offering a wide range of functionalities and enhancing our overall experience. Smart wearable technology refers to the combination of hardware and software that enables users to monitor and control various aspects of their lives. From fitness trackers to smartwatches, the possibilities are endless. MOKOSmart, a leading provider of IoT solutions, offers diverse types of smart wearable products that cater to almost all IoT industries, including construction sites, military operations, and the fashion industry.
In this blog, we will classify and compare smart wearable devices based on different wireless technology. We will explore their applications in various industries and their impact on our lives. Together, we will discover their past advancements and future potential, and assist you in selecting a wearable device that can benefit you in your work or daily life.
What is Smart Wearable?
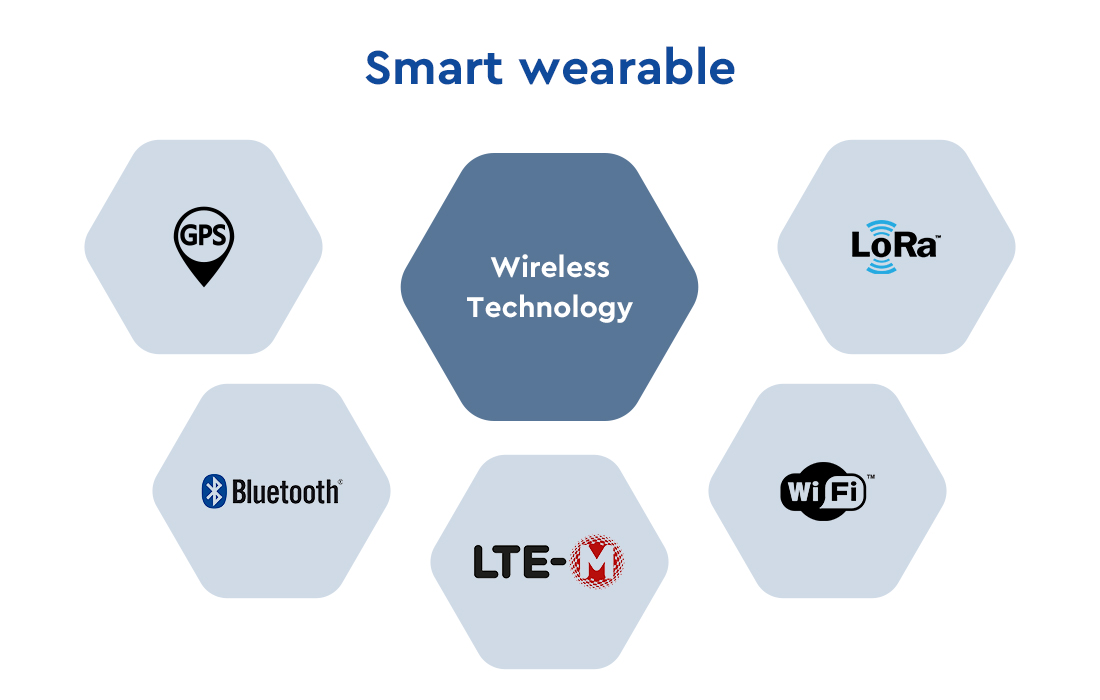
A smart wearable is an electronic device designed to be worn on the body, typically as an accessory or integrated into clothing. They are equipped with sensors, processors, and wireless connectivity, enabling them to collect and transmit data, interact with other devices, and provide users with valuable insights. These devices work by leveraging various technologies such as GPS, Bluetooth, LTE, Wi-Fi, and LoRa. By harnessing these wireless technologies, smart wearables can seamlessly connect to other devices, such as smartphones or laptops, and transmit data for analysis or display.
Key Differences of 5 Types of Smart Wearables with Different Wireless Technology
5 Types of Smart Wearables with Different Wireless Technologies
Five types of smart wearables employ different wireless technologies: GPS wearable, Bluetooth wearable, LTE wearable, Wi-Fi wearable, and LoRa wearable.
GPS Wearable: A GPS wearable refers to a type of smart wearable device equipped with GPS technology. It integrates GPS receivers and sensors into a wearable form factor. GPS technology enables these devices to receive signals from multiple satellites in orbit and determine the precise location, speed, and direction of the wearer.
Bluetooth Wearable: Bluetooth wearable device refers to a wearable device that uses Bluetooth technology for wireless communication and connection, which can transmit data between devices in close range. They are popular for tasks like music streaming, call handling, and receiving notifications.
LTE Wearable: An LTE wearable typically incorporates a built-in LTE modem or module, allowing it to connect to cellular networks and access the internet without relying on a paired smartphone or Wi-Fi connection. It utilizes LTE bands and protocols to establish a stable and fast wireless connection, enabling various functionalities.
Wi-Fi Wearable: Wi-Fi wearable utilizes Wi-Fi technology for wireless connectivity. It incorporates Wi-Fi modules or chips that enable the device to connect to Wi-Fi networks, providing internet access and allowing for data transfer and communication with other devices or the cloud.
LoRa Wearable: LoRa wearables leverage low-power, wide-area network technology to provide long-range communication capabilities. They typically incorporate LoRa modules or chips to connect to LoRaWAN gateways, allowing for communication over a wide area.
A Detailed Comparison Table of the 5 Smart Wearables
| WEARABLE TYPE | RANGE | BATTERY LIFE | TRANSFER RATE | INDEPENDENCE | APPLICATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Wearable | Global coverage | Moderate to short-term | N/A (Primarily location) |
Dependent on connected devices | Outdoor Activities, Geolocation and Tracking |
| Bluetooth Wearable | Short-range (up to 100m) |
Moderate | Moderate | Dependent on connected devices | Health Monitoring, Hands-Free Communication |
| LTE Wearable | Wide coverage | Moderate to short-term | Fast | Independent (cellular connectivity) |
Mobile Payments, Emergency Services |
| Wi-Fi Wearable | Within Wi-Fi range | Moderate to short-term | Fast | Independent (Wi-Fi connectivity) |
Smart Home Integration, Internet Access and Web Services |
| LoRa Wearable | Long-range | Long-lasting | Low | Independent (long-range connectivity) |
Asset Tracking, Environmental Monitoring |
Compare Types of Smart Wearables: GPS vs. Bluetooth vs. LTE vs. WIFI vs. LoRa
When comparing these types of smart wearables, several factors come into play:
Connectivity Range of Smart Wearable
GPS wearables provide location information, regardless of proximity to other devices. Bluetooth wearables have a limited range, generally up to 100m, and require proximity to connected devices. LTE and Wi-Fi wearables provide broader coverage areas, depending on the availability of cellular networks or Wi-Fi hotspots. LoRa wearables offer long-range connectivity for applications that require extended coverage, typically a few kilometers to tens of kilometers.
Battery Life of Smart Wearable
GPS wearables tend to have shorter battery life due to constant location tracking. Bluetooth wearables have moderate battery life depending on the usage frequency. LTE and Wi-Fi wearables may have shorter battery life due to the higher power consumption associated with cellular or Wi-Fi connectivity. LoRa wearables typically have long battery life as they are designed for low power consumption.
Data Transfer Speed of Smart Wearable
GPS wearables do not require high-speed data transfer as their primary function is location tracking. Bluetooth wearables offer moderate data transfer speeds suitable for tasks like music streaming and notifications. LTE and Wi-Fi wearables provide faster data transfer rates for activities that require Internet access. LoRa wearables have lower data transfer rates.
Independence of Smart Wearable
GPS and Bluetooth wearables rely on connected devices for certain functions, such as map displays or notifications. LTE and Wi-Fi wearables offer more independence as they have their own cellular or Wi-Fi connectivity. LoRa wearables operate independently with their long-range connectivity.
Application of Smart Wearable
GPS wearables are commonly used in fitness trackers and navigation devices. Bluetooth wearables are popular for tasks such as call handling and receiving notifications. LTE wearables provide functionalities like phone calls and internet access, allowing users to stay connected on the go. Smartwatches and similar devices that necessitate a consistent connection to receive features such as updates often incorporate Wi-Fi wearables. LoRa wearables are suitable for applications that require remote connectivity, such as asset tracking and environmental monitoring.
GPS vs. Bluetooth vs. LTE vs. WIFI vs. LoRa: Which Smart Wearable is Better?
Features of the 5 Smart Wearables
Determining which smart wearable is better depends on individual needs, preferences, and the specific use case. Here are the features of each type of smart wearable:
GPS Wearable
– Accurate location tracking and navigation capabilities
– Limited battery life due to constant GPS usage
– Relies on GPS satellite signals for positioning
Bluetooth Wearable
– Seamless connectivity with other devices nearby
– Moderate battery life depending on usage
– Requires a connected device for certain functionalities
LTE Wearable
– Offers greater independence from a smartphone
– Battery life may be shorter due to cellular data usage
– Works with a compatible cellular network for coverage
Wi-Fi Wearable
– Provides internet access and data transfer through Wi-Fi networks
– May have shorter battery life due to Wi-Fi data consumption
LoRa Wearable
– Long-range communication capabilities with low power consumption
– Long-lasting battery life
Things to Consider in the Selection of Smart Wearable
- Purpose and Use Case: Determine the specific purpose you have in mind for the smart wearable. Are you looking for fitness tracking, navigation, communication, or specialized industry applications? Different wearables excel in different areas, so aligning the purpose with the intended use case is crucial.
- Connectivity Range: Consider the range of connectivity required for your use case. GPS wearables can offer global coverage, while Bluetooth wearables have a limited range of up to 100 meters.
- Battery Life: Evaluate the expected battery life of the wearable. GPS wearables tend to have shorter battery life due to continuous location tracking. Bluetooth wearables and LTE wearables have moderate battery life, while Wi-Fi wearables may have shorter battery life due to Wi-Fi data consumption. LoRa wearables are known for their long-lasting battery life.
- Data Transfer Speed: Consider the required data transfer speed for your use case. LTE and Wi-Fi wearables provide faster data transfer rates for activities that require internet access, while wearables have lower data transfer rates.
- Cost: Consider the cost implications, including the upfront price of the wearable device, any ongoing service fees, and additional data plan expenses. The cost of smart wearables can vary greatly based on factors such as the type of device, its features, and the brand offering it.
By conducting a thorough evaluation of these factors and aligning them with your individual needs and preferences, you can select the smart wearable that best matches your specific requirements.
Benefits of Using Smart Wearable
Real-time health and fitness monitoring: Fitness trackers and smartwatches can track metrics like heart rate, sleep patterns, step count, and calories burned, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being.
Enhanced communication and connectivity: With features like notifications, calls, and messaging, users can stay connected without needing to constantly check their phones.
Improved safety: Through smart wearable devices, children, adults, or elderly family members can call for emergency help in the event of an accident, matching GPS positioning function, can ensure that their location information is always known.
Better sleep quality: Many wearable devices track and analyze your sleep and can help you wake up more refreshed in the morning by using gentle vibrations to wake you up at the right time.
Personalization Settings: Smart wearables offer personalized experiences, with the ability to customize settings, display options, and app integration to suit individual preferences.
What Industries Benefit from Smart Wearable?
Smart wearables have indeed become increasingly prevalent in various industries and everyday life, offering a wide range of applications. Some common applications of smart wearables include:
Fitness and Health Tracking: Smartwatches, fitness bands, and activity trackers are popular for monitoring physical activities, tracking steps, calories burned, heart rate, and sleep patterns, and providing insights for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Medical and Healthcare: Wearable devices are used for remote patient monitoring, vital signs tracking, medication reminders, fall detection, and managing chronic conditions. They allow healthcare providers to remotely monitor the health of patients and deliver timely interventions.
Personal Safety and Security: Smart wearables like panic buttons, personal alarms, and safety bracelets provide a sense of security by allowing users to send distress signals, share location information, or call for help in emergencies.
Location and Navigation: GPS-enabled smartwatches and trackers assist in precise location tracking, navigation, and outdoor activities like hiking, cycling, and running. They provide real-time location information, mapping, and route guidance.
Smart Home Integration: Certain wearables can connect with smart home devices, enabling users to conveniently control various aspects of their home environment. This includes managing lights, adjusting thermostats, locking and unlocking doors, and operating other appliances directly from their wearable devices.
Entertainment and Media: Smart glasses, VR headsets, and headphones offer immersive entertainment experiences, allowing users to enjoy virtual reality games, videos, and music.
Fashion and Style: Wearable technology has also entered the fashion industry, with intelligent jewelry, smart clothing, and accessories that combine style with functionality, such as fitness tracking or notification alerts.
Gaming and Augmented Reality (AR): Wearable devices like AR glasses and motion-tracking wearables provide immersive gaming experiences, blending the real world with virtual elements.

Advancements in the Smart Wearables Market
According to a report by Market.us, the smart wearables market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the rising interest in health, fitness, and technology. The market is projected to exceed USD 383.5 billion by 2032, showing substantial growth from USD 95.7 billion in 2022. The market is expected to maintain a CAGR of 15.3% from 2023 to 2032.
The smart wearables market has witnessed significant advancements in the past and continues to evolve in exciting ways for the future. In the past, we have seen miniaturization, making wearables smaller and more comfortable to wear. Enhanced sensors and tracking capabilities have improved health and fitness monitoring, while integration with smartphones and apps has expanded its functionalities. The market has also seen a diverse range of form factors, offering consumers more options for their preferences and needs.
Looking ahead, future advancements in smart wearables will focus on health monitoring and medical applications, with wearables providing real-time insights, early detection of medical conditions, and remote patient monitoring. AI integration will personalize wearables, offering customized suggestions and predictive insights. Battery life will be extended through improved efficiency and charging technologies. Connectivity and interoperability will improve, allowing wearables to seamlessly integrate into smart homes and larger digital ecosystems.
MOKOSmart Solutions for Smart Wearable
LoRaWAN Based Wearable
MOKOSmart’s LoRaWAN wearable devices include the LW001-BG Pro LoRaWAN Tracker and the LW004-PB Panic Button. These devices can be applied in scenarios such as contact tracing, asset management, and logistics processes. Among them, LW001-BG and LW004-PB are equipped with GPS high-precision outdoor positioning functions and Bluetooth and WiFi indoor positioning functions. This compact and user-friendly equipment effectively scans data from nearby BLE beacons. Once the data is collected, it is subsequently transmitted to the nearest LoRaWAN gateway. Subsequently, the gateway sends the data to a cloud server, enabling worldwide access at any time. This capability allows for continuous monitoring of contact tracing, asset management, logistics, and other related information.
Feature
- Detect and record close interactions with other individuals.
- with Bluetooth Low Energy, advertising, and scanning roles.
- Support BLE indoor geolocation.
- Utilizing the LoRaWAN-based protocol can transmit the scanned data to the cloud via LoRaWAN connectivity.
- Built-in vibration motor for the alert.
- Built-in 3-axis accelerometer for motion detection.
BLE Based Wearable
MOKOSmart’s BLE wearables like the H4 Sensor Beacon, H7 Helmet Beacon, W5 Beacon Tracker, and H3 Card Beacon can assist both staff and visitors in case they encounter a dangerous situation or require assistance. By pressing a button on the beacon tracker, it will send emergency alerts anytime, anywhere. The real-time alarm and location information will be transmitted to the platform using a wireless Bluetooth network. This information will then be received by the emergency control room or security personnel. As such, it will ensure the safety of all employees in the workplace.
Feature
- Wearable bracelet shape with Bluetooth Low Energy, advertising and scanning roles
- Built-in vibration motor for alert, the safety distance can be set
- 3-axis accelerometer sensor with a motion trigger
- SOS button for Alarm
- Rechargeable Li battery, USB direct charging
- All parameters can be modified via the Contact Tracker APP
Conclusion
Smart wearables have revolutionized our lives, offering us a glimpse into a connected and intelligent future. These devices empower individuals with real-time information, personalized experiences, and improved convenience. With a diverse range of options available, it is crucial to understand the different types of smart wearables, their wireless technologies, and their unique features to make an informed decision. Whether it’s for fitness tracking, communication, or specialized industries, smart wearables are here to stay, providing endless possibilities for a smarter and more connected world.
With the multitude of smart wearable options available and the rapid advancements in the field, it can be overwhelming to select the right device that aligns with your desired technical specifications, application requirements, and budget. Check out the great list of products at MOKOSmart and let our team of experts help you explore the best smart wearable solutions.