The IoT has the potential to change the world, much like the Internet did, or perhaps even more so. In today’s digital age, the IoT has completely transformed the way businesses manage their warehouses. Mistakes in warehouse operations can often create a significant hole in a company’s pocket. In traditional setups, warehouse managers faced the biggest challenge of having limited data available to make informed decisions, while inaccurate operations required additional labor to rectify. With the advancements and progress of wireless technologies such as RFID, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC, and LoRa, connectivity has become energy-efficient and cost-effective, making warehouses “smarter” by integrating IoT wireless technologies into their infrastructure.
This article aims to conduct a thorough analysis and comparison of the five mentioned IoT warehouse management technologies. By examining their characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks, we intend to empower businesses with the knowledge necessary to make well-informed decisions regarding the most appropriate technology for their unique warehouse management requirements. Additionally, we will discuss the factors to consider when choosing between these technologies and explore the trends in warehouse management.
A Comparison Table of the 5 Types of Warehouse Management Technologies
To provide a quick overview, let’s compare the five technologies based on their key features:
| TECHNOLOGY | RANGE | TRANSFER RATE | POWER CONSUMPTION | COST | APPLICATIONS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFID | Short (up to several meters) | Low | Low | Moderate | Inventory tracking, asset management |
| Bluetooth | Short (up to 100 meters) | Medium | Low | Low | Real-time tracking, device connectivity |
| Wi-Fi | Medium (up to several hundred meters) | High | Medium | High | High-speed data transmission, real-time monitoring |
| NFC | Very Short (within a few centimeters) | Low | Low | Low | Contactless payments, access control |
| LoRa | Long (several kilometers) | Low | Low | High | Large-scale asset tracking, remote monitoring |
Detailed Information on the 5 Types of Warehouse Management Technologies
RFID Warehouse Management: RFID warehouse management refers to the use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology for tracking and managing inventory and assets within a warehouse. It involves the deployment of RFID tags on objects or products, which can be wirelessly identified and tracked using RFID readers. Compared to Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, RFID has a shorter range and is typically used for localized tracking within a specific area or zone in the warehouse.
Bluetooth Warehouse Management: Bluetooth warehouse management utilizes Bluetooth technology to manage and track assets and devices within a warehouse environment. Bluetooth facilitates wireless communication over short distances, enabling real-time tracking, seamless connectivity, and efficient data exchange between devices. It is commonly used for device-to-device communication, such as connecting handheld scanners, mobile devices, and tracking tags, facilitating efficient warehouse operations and inventory management. Compared with RFID, Bluetooth has a longer range and a faster transmission rate, but the Bluetooth signal is more susceptible to interference from obstacles.
Wi-Fi Warehouse Management: Wi-Fi warehouse management refers to the use of Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) technology for managing and controlling warehouse operations. Wi-Fi facilitates wireless internet connection and offers rapid data transfer capabilities within the confines of a LAN or warehouse premises. Wi-Fi offers a wider coverage range and high-speed data transfer compared to RFID and Bluetooth. It allows for real-time monitoring, data exchange, and connectivity across various devices and systems, facilitating efficient inventory management and warehouse operations. However, due to its higher transmission rate, Wi-Fi also consumes more power than RFID and Bluetooth technologies.
NFC Warehouse Management: NFC warehouse management involves the application of NFC (Near Field Communication) technology in warehouse operations. NFC facilitates wireless communication between devices that are nearby, allowing for short-range data exchange. It is primarily used for contactless payments and identification, but in warehouse management, NFC can be utilized for tasks like quick item scanning, employee identification, and access control. It offers secure and efficient data exchange in a close-range environment. Compared to RFID and Bluetooth, NFC has a lower data transfer rate but is suitable for small-scale inventory tracking and access control.
LoRa Warehouse Management: LoRa warehouse management involves the use of LoRa (Long Range) technology for managing and monitoring warehouse operations, particularly in large-scale environments. Compared to Wi-Fi and other higher bandwidth technologies, LoRa technology simultaneously has longer coverage and lower data transfer rates. It provides extended coverage over long distances, making it suitable for asset tracking, remote monitoring, and management of large warehouses or facilities. LoRa technology offers low power consumption and enables cost-effective deployment for wide-area coverage and connectivity.
Which Warehouse Management Technology is the Most Suitable One?
RFID vs Bluetooth vs WIFI vs NFC vs LoRa: Pros and Cons
RFID Warehouse Management
Pros
- Non-line-of-sight data capture
- Fast and efficient inventory tracking
- Improved accuracy and reduced manual errors
- Real-time visibility of stock levels
- Enables automated processes such as automated check-in/check-out
Cons
- Limited range and coverage
- Relatively higher implementation costs
- Requires infrastructure setup with RFID readers and tags
- Interference from other RFID devices in the vicinity
Bluetooth Warehouse Management
Pros
- Real-time tracking and monitoring of devices or assets
- Easy integration with various devices (e.g., handheld scanners, mobile devices)
- Cost-effective solution
Cons
- Limited range compared to other technologies
- Interference from other Bluetooth devices in the vicinity
- Device compatibility issues may arise
Wi-Fi Warehouse Management
Pros
- Real-time tracking and monitoring of inventory and assets.
- Seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure.
- Enables centralized control and management.
Cons
- Higher power consumption compared to other technologies.
- Requires sufficient Wi-Fi coverage throughout the warehouse.
- Potential interference from other Wi-Fi devices or physical obstacles.
NFC Warehouse Management
Pros
- Quick and secure identification/authentication of items or personnel.
- Efficient for small-scale inventory tracking and access control.
- Low implementation costs.
Cons
- Very short communication range.
- Necessitates devices to be within a close range for effective communication.
- Limited data transfer rate.
LoRa Warehouse Management
Pros
- Extended range coverage.
- Low-power consumption for long battery life.
- Cost-effective for large-scale deployments.
Cons
- Lower data transfer rate compared to other technologies.
- Requires LoRa gateways and network infrastructure setup.
- Longer setup and implementation process compared to other technologies.
RFID vs Bluetooth vs WIFI vs NFC vs LoRa: Factor Consideration
When choosing the most suitable warehouse management technology from RFID, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC, and LoRa, several factors should be considered:
Range and Coverage: Evaluate the range requirements of your warehouse operations. Determine whether you need short-range, medium-range, or long-range coverage. RFID and NFC are suitable for short-range applications within a specific area or zone. Bluetooth offers short-range coverage, while Wi-Fi provides broader coverage within the range of access points. LoRa is designed for long-range communication, making it suitable for large-scale operations.
Data Transfer Rate: Consider the speed of data transfer required for your warehouse management needs, as Wi-Fi offers high-speed transfer, while RFID, Bluetooth, and NFC have lower rates but are often sufficient for inventory tracking.
Power Consumption: Evaluate the power requirements and battery life expectations for your devices. LoRa and Bluetooth are known for their low power consumption, providing longer battery life for connected devices. Wi-Fi and RFID consume relatively more power compared to Bluetooth and LoRa.
Implementation Costs: Assess the budgetary constraints and cost-effectiveness of each technology. RFID and NFC often require an upfront investment in infrastructure setup, including readers and tags. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are more cost-effective options as they leverage existing devices and infrastructure. LoRa may require initial setup costs for gateways and network infrastructure, but it offers cost-effectiveness for large-scale deployments.
Compatibility and Integration: It is essential to assess how well the technology aligns with your warehouse’s existing systems and devices. Bluetooth demonstrates a broad range of device compatibility and offers effortless integration with various devices. On the other hand, Wi-Fi offers a seamless integration experience by effortlessly merging with your warehouse’s current IT infrastructure.
Application Specifics: Lastly, evaluate the specific application requirements, such as RFID for inventory management, Bluetooth for real-time tracking, Wi-Fi for high-speed data transfer and centralized control, NFC for identification/authentication, and LoRa for extended coverage in large-scale tracking and monitoring.
Where Needs Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management technology has numerous applications that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity in various aspects of warehouse operations. Some key applications include:
Inventory Management: Warehouse management technologies facilitate instant tracking and surveillance of inventory quantities, whereabouts, and movements in real time. This ensures accurate inventory control, minimizes stockouts, reduces excess stock, and streamlines order fulfillment.
Asset Tracking: Warehouse management systems play a vital role in monitoring and controlling various assets, including equipment, tools, and vehicles, within the warehouse environment. Moreover, they help mitigate the risks of loss, theft, or damage, ensuring that assets are managed in an organized and productive manner.
Order Fulfillment: Warehouse management technologies that are optimized for efficiency enable expedited order processing, picking, and packing activities. They provide real-time information on order status, stock availability, and optimal picking routes, resulting in improved order accuracy and faster shipment processing.
Labor Management: Warehouse management systems help optimize labor utilization and productivity. They provide insights into worker performance, task allocation, and workflow optimization, enabling better resource planning and efficient labor utilization.
Quality Control: Warehouse management technologies support quality control processes by enabling systematic inspection, sampling, and tracking of products throughout the warehouse. This guarantees compliance with quality standards, minimizes product flaws, and boosts customer satisfaction.
Returns Management: Effective handling of product returns is vital for the success of businesses. Warehouse management systems facilitate the handling, inspection, and processing of returned items, ensuring timely restocking or appropriate disposition, and improving the overall returns management process.
Compliance and Security: Warehouse management technologies aid in maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and security protocols. They enable tracking of goods, personnel identification/authentication, and monitoring access to restricted areas, ensuring compliance and enhancing overall warehouse security.
Analytics and Reporting: Warehouse management systems provide valuable data and analytics capabilities. They generate comprehensive reports and provide valuable insights regarding KPIs such as the accuracy of inventory, rates of order fulfillment, labor productivity, and overall efficiency of operations. This enables businesses to make informed decisions based on data analysis and identify opportunities for ongoing enhancements and optimization.
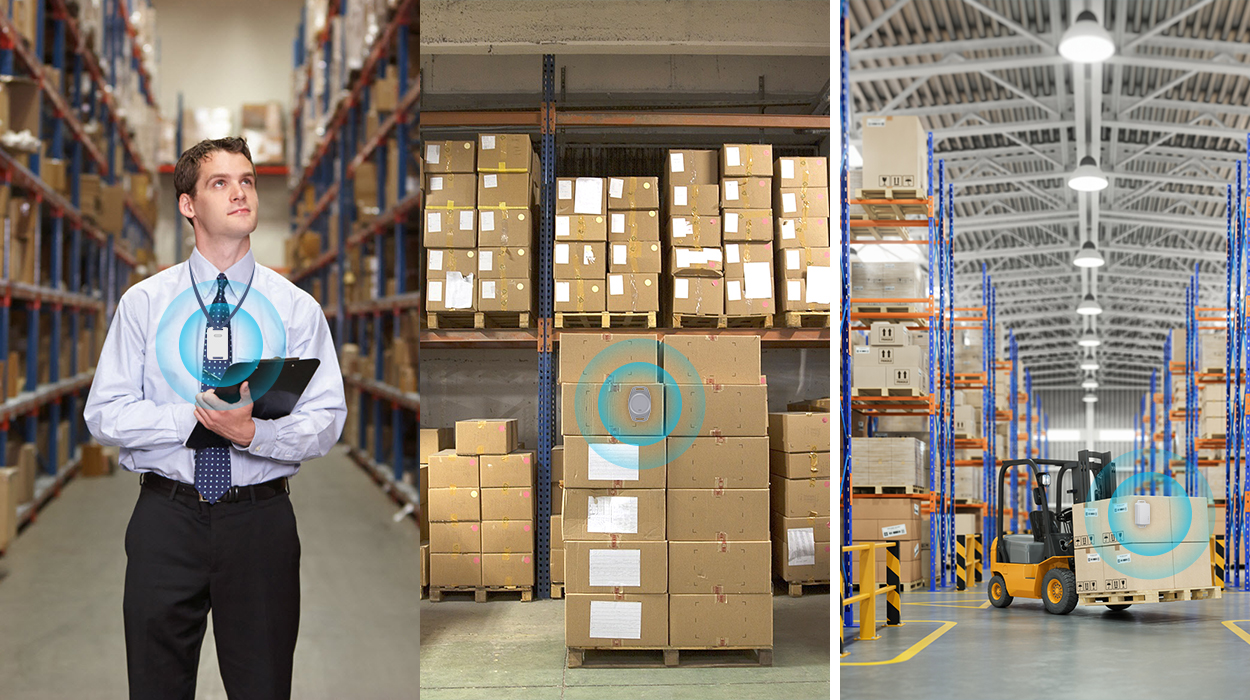

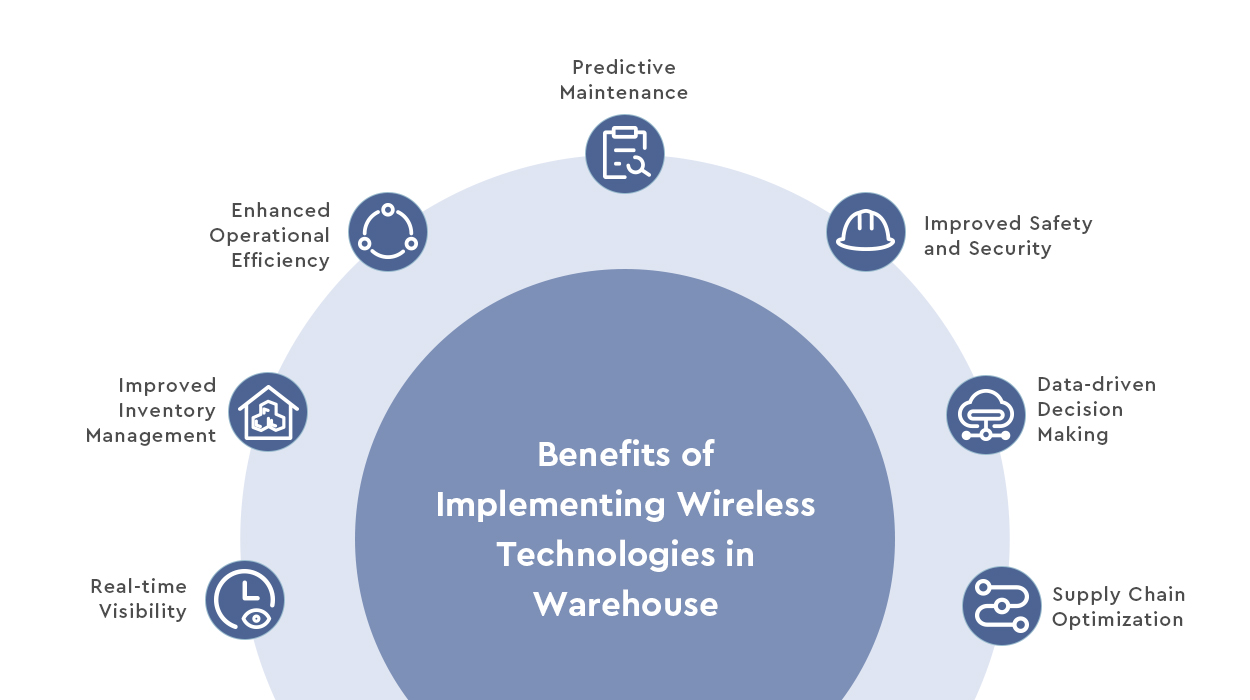
Benefits of Implementing IoT Technologies in Warehouse Management
Real-time Visibility: Warehouse management technologies provide real-time visibility of inventory and assets within the warehouse. Sensors, RFID tags, and connected devices collect and transmit data, allowing warehouse managers to have accurate, up-to-date information on stock levels, locations, and conditions.
Improved Inventory Management: With IoT, inventory management becomes more accurate and efficient. Automated tracking and monitoring systems enable real-time updates on stock levels, reducing manual errors and the risk of stockouts or overstocking. This leads to optimized inventory control and reduced carrying costs.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Warehouse management technologies enable automation and process optimization in warehouse operations. Automating the collection and analysis of data eliminates the need for manual data entry and simplifies workflows, resulting in time savings and a reduction in human errors. IoT-powered devices, such as autonomous robots and drones, can also be utilized for tasks like picking, sorting, and inventory inspection, increasing operational efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors and connectivity allow for proactive maintenance of warehouse equipment and machinery. By consistently monitoring the performance of equipment, identifying deviations from normal functioning, and forecasting potential malfunctions, maintenance can be arranged proactively before breakdowns occur. This proactive approach minimizes periods of inactivity, prolongs the lifespan of equipment, and reduces overall maintenance expenses.
Improved Safety and Security: Warehouse management technologies contribute to the enhancement of safety and security within the warehouse premises. Connected sensors and cameras can monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, IoT-based surveillance systems and access control enable real-time monitoring, unauthorized access detection, and incident response.
Data-driven Decision Making: Data generated by IoT devices offers valuable information and analysis opportunities for warehouse managers. Advanced analytics and data visualization tools enable the interpretation and analysis of vast amounts of data, facilitating informed decision-making. Managers can recognize trends, streamline operations, and implement data-informed enhancements to warehouse activities.
Supply Chain Optimization: Warehouse management technologies facilitate improved integration and collaboration throughout the supply chain. Real-time data sharing between suppliers, manufacturers, and warehouses allows for improved demand forecasting, efficient inventory replenishment, and synchronized logistics operations. This leads to a supply chain that is more adaptable and quick to respond.
How MOKOSmart Can Help You Revolutionize Warehouse Management?
The Internet of Things has completely transformed warehouse management, and MOKOSmart is dedicated to helping business owners automate their workflow to accelerate processes, implement better security measures to save costs, and effectively meet customer demands. Leveraging their extensive experience, MOKOSmart has been exploring the undeniable advantages of technologies such as RFID, Bluetooth, and LoRa. Here are some featured products from MOKOSmart used for warehouse management.
MOKOSmart’s RFID Products
MOKOSmart offers a range of RFID products that can be used for warehouse management, including the H5 RFID beacon. The H5 Beacon is an RFID beacon tag equipped with a three-axis accelerometer, which facilitates accurate monitoring of object locations. It can also be used for recording employee attendance, setting access control, identity recognition, and remote cloud data management.
MOKOSmart’s Bluetooth Products
For Bluetooth products in warehouse management, MOKOSmart provides the M2 Asset Tracking Beacon, H2 Indoor Navigation Beacon, H2A Location Beacon, and more. These beacons utilize Bluetooth low-energy asset tracking technology. These technologies have versatile applications both indoors and outdoors, enabling warehouse inventory monitoring with a range that extends up to 160 meters. They are portable and easy to install, capable of being hung, screwed, or attached with adhesive stickers. They assist employees in easily locating items within the warehouse.
MOKOSmart’s LoRaWAN Products
In terms of LoRaWAN products for warehouse management, MOKOSmart offers the LW008-MT Small LoRaWAN Tracker and LW001-BG PRO LoRaWAN Tracker. These devices provide remote and low-power connectivity for large-scale tracking and monitoring in warehouses. They can provide real-time tracking of assets, inventory, and equipment. These products are designed to withstand harsh operating environments with features like impact resistance, durability, and waterproofing.
Warehouse Management Trends
Several emerging trends and future developments are shaping the future of warehouse management:
AR and VR: AR and VR technologies are finding applications in warehouse management, particularly in training and order-picking processes. AR glasses and VR simulations can provide interactive training experiences, guide employees in picking operations, and offer virtual walkthroughs of warehouse layouts. These technologies improve worker efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance safety.
Automation and Robotics: The use of automation and robotics is projected to witness a sustained increase in the field of warehouse management. AGVs, robotic picking systems, and self-governing drones are being employed to enhance various aspects of warehouse operations, including inventory transportation, order selection, and facility upkeep, to achieve operational optimization.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is gaining traction in warehouse management, offering secure and transparent transactions, enhanced traceability, and improved supply chain visibility. Blockchain can be used to track and authenticate goods, optimize inventory management, and ensure compliance with regulations and standards.
Conclusion
In this rapidly evolving warehouse management landscape, businesses must embrace IoT technologies and stay updated with emerging trends to remain agile, efficient, and competitive in the global market. RFID, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC, and LoRa all offer unique functionalities and benefits, suitable for different warehouse management applications. Considering factors such as range, data transmission rate, power consumption, and cost can help you make better choices in selecting the appropriate IoT warehouse management technology.
At MOKOSmart, our primary objective is to assist warehouse managers in optimizing their operations by providing a streamlined platform that simplifies processes and keeps them ahead of their competitors. Therefore, instead of relying on outdated operational systems, embrace our cutting-edge warehouse management solution and take a proactive step towards staying ahead in the industry.
Continue Reading About WAREHOUSE management