You’re the owner of a transportation company and you want your fleet of vehicles running like a well-oiled machine. An efficient fleet management solution means no more wasted time, money or resources. But how do you achieve that? IoT fleet management technology is the answer.
Cutting-edge tech like GPS, sensors, and wireless connectivity revolutionize fleet management with IoT. It’s like having a crystal ball that helps you monitor and track your drivers safer on the road. But IoT isn’t just about fleet location tracking. IoT powers real-time tracking of your goods, predictive maintenance schedules, and even driver behavior monitoring. And the best part? You can start using it today for a streamlined, smoothly operating fleet.
What is fleet management?
Traditionally, fleet management refers to overseeing all aspects of fleet performance and maintenance to maximize productivity. But IoT takes it to the next level by automating that process with real-time data and analytics in the cloud. Companies can finally manage their fleet operations with true precision and insight instead of operating blind.
The market reflects the immense potential here. IoT fleet management solutions are projected to grow from 20 billion in 2023 to a staggering 44.21 billion worldwide by 2030 at a CAGR of 12%. As vehicle connectivity and technologies like electrification and vehicle to everything (V2X) become the norm, IoT’s role in fleet operations will only continue to expand. Any fleet operator looking to maintain a competitive edge need to capitalize on these powerful IoT technologies.
How IoT in a fleet management system works
An IoT fleet tracking system combines GPS technology with wireless connectivity methods like NB-IoT, GSM, and LoRaWAN. Small GPS trackers installed in each vehicle transmit real-time location data to a cloud server over these wireless networks. Fleet managers can then access and analyze this location tracking data through mobile apps. But the system does more than just location – it also captures and transmits vehicle speed, driver status, fuel consumption levels and other metrics. And by integrating additional technologies like cameras and sensors, the IoT fleet system provides even deeper visibility into fleet operations.
Top 7 technologies used in IoT fleet management
The advent of the IoT has ushered in a new era of fleet management. At the heart of this transformation lie technologies that seamlessly integrate vehicles, devices, and systems. Here are the top seven technologies driving innovation in IoT fleet management:
GPS (Global Positioning System)
GPS is the backbone of fleet tracking, enabling real-time monitoring of vehicle locations. This process includes putting GPS devices in vehicles, which communicate with satellites to give real-time location and tracking details.
Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth beacons and sensors play a crucial role. Bluetooth tags can be used for driver identification and emergency assistance. Various BLE sensors deployed in vehicles can monitor the status of on-board assets, door opening and closing, etc.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)
RFID is suitable for asset tracking and inventory management within fleets. RFID tags are attached to vehicles or assets, and RFID readers capture data and track their movement. However, it provides limited tracking because it relies on proximity to the reader.
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things)
NB-IoT is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology specifically designed for IoT applications. It’s ideal for tracking vehicle locations over long distances.
LoRa (Long Range)
LoRa is another LPWAN technology that offers long-range, low-power communication capabilities. It is particularly useful for fleet management in remote or rural areas, where traditional cellular networks may have limited coverage.
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
GSM provides a reliable and widely available cellular network for data transmission in IoT fleet management. It enables real-time communication between vehicles and fleet management systems. GSM offers global coverage, allowing fleet managers to monitor and manage assets across different regions.
OBD (On-Board Diagnostics)
OBD systems are built into modern vehicles, capable of self-diagnosis and reporting. Embedded within the vehicle, OBD monitors engine performance and identifies any necessary repairs to maintain optimal vehicle health.
The following table provides a brief comparison of several popular IoT fleet tracking technologies:
| TECHNOLOGY | GPS | LoRa | NB-IoT | GSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tracking | Real-time | Limited | Limited | Real-time |
| Coverage Range | Global | Long | Long | Global |
| Accuracy | High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Data Transmission | N/A | Low | Low | High |
| Battery Life | Moderate | Long | Moderate | Moderate |
| Applications | Vehicle Tracking, equipment tracking | warehouse tracking | Smart city, smart agriculture | Autonomous vehicles, telematics |
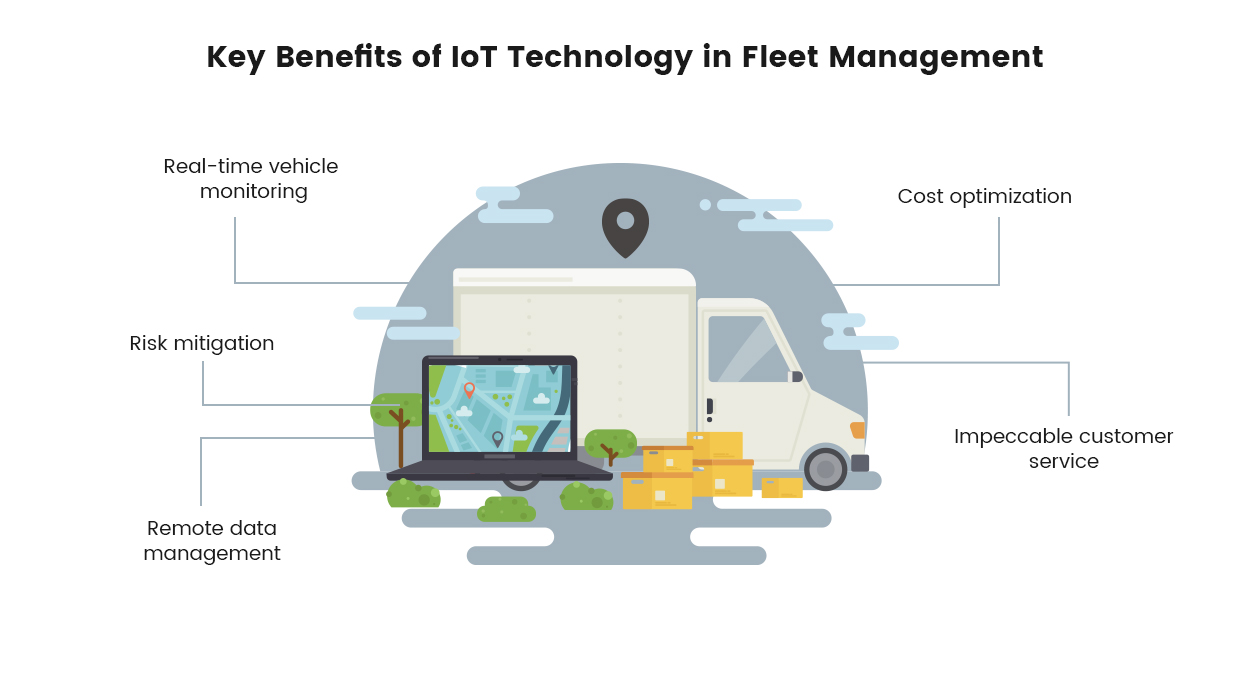
Key benefits of IoT technology in fleet management
Internet of Things (IoT) tech has completely shaken up how fleets are managed these days. Here are the major benefits that IoT brings to the table for fleet operations:
- Real-time vehicle monitoring: The implementation of IoT fleet management technologies enable the efficient monitoring of vehicles and associated assets. Through a two-way communication system, essential data is recorded, allowing for remote monitoring.
- Risk mitigation: The application of wireless technology sensors and intelligent transportation systems aids in risk mitigation within fleet management.
- Remote data management: IoT-based solutions empower fleet operators to access vehicle performance data remotely, facilitating quick and informed decision-making.
- Cost optimization: Wireless technology aids freight and transportation businesses in operating more efficiently.
- Impeccable customer service: Fleet management centers have the ability to incorporate intelligent solutions into their current ERP systems, thereby optimizing performance in every facet of their operations.
Use cases of IoT in fleet management technologies
IoT fleet management encompasses a wide range of industries and applications. Here are some common use cases of fleet management:
Vehicle Tracking: Fleet management systems allow real-time tracking of vehicles, enabling fleet operators to monitor their location, speed, and route.
Asset Tracking: Fleet management systems can track not only vehicles but also other assets, such as equipment, trailers, or containers.
Route Optimization: Fleet management solutions help optimize routes for vehicles, taking into account factors like traffic, road conditions, and customer locations.
Maintenance and Diagnostics: These systems give you full insights into vehicle health. They track maintenance needs, monitor engines, and alert you when something needs fixing.
Driver Behavior Monitoring: These solutions monitor how your drivers are doing – speeding, harsh braking, aggressive driving, etc. With that data, you can promote safer driving habits, prevent accidents, and save on insurance.
Cold Chain Monitoring: For perishable goods like fruits and pharma, the systems monitor and control temperatures and humidities in refrigerated vehicles, keeping cargo fresh throughout the supply chain.

Where do fleet management technologies apply
Fleet management applies to various industries and sectors where efficient management, tracking, and optimization of vehicles and assets are vital. Here are some common applications of fleet management and the technologies suitable for each:
Transportation and Logistics: GPS fleet management for real-time vehicle tracking, RFID and BLE for asset identification and inventory, NB-IoT for remote data and cost optimization – used by shipping, delivery, and logistics companies.
Construction and Heavy Equipment: GPS/LoRaWAN tracking monitors the location and utilization of construction vehicles/heavy equipment. BLE aids in equipment identification and maintenance tracking.
Public Transportation: GPS tracking and real-time data communication (WiFi, NB-IoT) optimize bus/train schedules, routes, and enhance passenger experience. BLE helps driver identification and emergency response.
Emergency Services: GPS/GSM enables real-time tracking and routing for quick emergency response – ambulances, fire trucks, police cars. LoRaWAN/NB-IoT solutions assist remote diagnostics and patient monitoring.
Field Services: GPS/LoRaWAN aids efficient dispatching and route planning for utility, telecom, and maintenance service providers. RFID/BLE helps with asset tracking, inventory management, and access control.
Waste Management: GPS trackers help track waste collection vehicles and optimize routes. LoRaWAN monitors container fill levels remotely for efficient collection scheduling.
School Transportation: GPS tracking ensures safety and efficient transportation for school buses. Integrated with student safety monitoring systems.
Considerations for choosing IoT fleet management technologies
With numerous IoT options available, selecting the right technologies for fleet management is critical. This section covers key considerations:
- Coverage Range: Evaluate the coverage range required for your fleet operations. GPS, NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, and GSM offer global or widespread coverage, suitable for operations spanning large geographical areas. RFID, and BLE have more limited coverage ranges and are better suited for localized or regional operations.
- Data Transmission Speed: Consider the speed at which data needs to be transmitted for effective fleet management. GSM provides relatively high data transmission speeds. LoRa and NB-IoT have lower data transmission rates but are still suitable for applications where real-time data is not critical.
- Power Consumption: Assess the power consumption requirements of the fleet management technology. LoRa and NB-IoT are designed for low-power, battery-operated devices, suitable for applications where power efficiency is crucial. GPS, RFID, and GSM typically consume more power.
- Cost: Consider the cost implications of implementing and maintaining the fleet management technology. GPS and GSM technologies may have higher costs due to their infrastructure requirements and service subscriptions. RFID, LoRa, and NB-IoT technologies often offer more cost-effective options.
- Scalability: Determine whether the fleet management technology can scale to accommodate future growth or changing operational needs. GPS, NB-IoT, and GSM have established infrastructures and are readily scalable. LoRaWAN and BLE may have limitations in scalability due to their specific use cases and coverage range.
- Application Specificity: Evaluate the specific requirements of your fleet management application. Different technologies have strengths and weaknesses depending on the application. For example, GPS is well-suited for real-time tracking and global positioning, while BLE and RFID excel in asset identification and inventory management.
MOKOSmart’s featured IoT devices for fleet management
MOKOSmart offers BLE, NB-IoT, and LoRaWAN solutions for comprehensive IoT fleet management. Our LoRaWAN portfolio includes GPS trackers for indoor/outdoor tracking and temperature/humidity sensors for cargo monitoring. The NB-IoT GPS trackers provide global real-time location tracking and monitoring for vehicles/assets with customizable alarms. Additionally, we offer BLE tags for driver identification, multiple sensors for monitoring door status, and panic alarms.
Our IoT devices can assist you in better real-time tracking of vehicles and efficient fleet management. If you still have doubts about selecting fleet management technologies, at MOKOSmart, we can help you find the most suitable solution for you. Contact us now!
Continue Reading About fleet management