With the rapid rise of the IoT, a rapid transformation of economic systems and social relations has been noticed globally. In this transformation, China plays a critical role thanks to its digitalizing industries and ambitions to lead and embrace new technologies. China is committed to adopting IoT developments using a sustained state policy to influence its diverse markets and its central position in global manufacturing. Initially, IoT had little influence in China, but now it is a major player in transforming and shaping international trade globally.
It is possible to make devices Smart. IoT in China is made possible by its applications. At MOKOSmart, we have various applications of Internet of Things solutions. We enable you to know more about the fantastic works of IoT applications and how the technology can be used. For instance, we not only enable you to know how you can keep fresh products cool in a refrigerator, but we also enlighten you on how you can remotely control your home through various IoT solutions.
Some of the applications of IoT solutions available at MOKOSmart are;
• Asset tracking solutions
• Cold chain logistics solutions
• Smart office and home solutions
• Indoor GPS solutions
• IoT healthcare solutions
• IoT farming solutions
• IoT industry 4.0 solutions
• IoT wearable and sensors
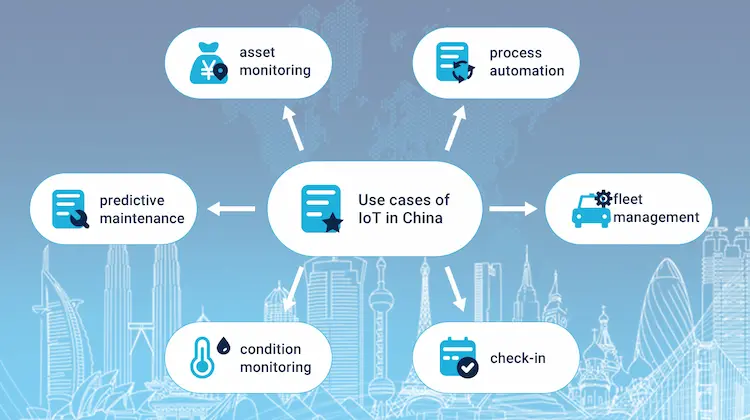
Use cases of IoT in China
Below are the top 6 most adopted use cases of IoT in China;
Smart Check-in
IoT introduces new possibilities by making the process of check-in more seamless. Most hotels in China are using IoT to automatically send electronic keys to their expected visitors an hour before the check-in time.
IoT-based process automation
Over 33 per cent of IoT companies in China have already rolled out the process of IoT-based automation. The process involves automating manual technologies that rely on old-fashioned setups by upgrading them with state-of-the-art hardware and software.
Vehicle fleet management
This is the leading IoT supply chain application in China right now. Its complexity is higher when the management of the transportation means is higher. The management of cross-border fleets is at times overwhelming. That is why most companies have opted to collect real-time data using professional vehicle fleet management solutions.
Location tracking
When developing a successful IoT business model, it is essential to consider location tracking. Tracking the location of an asset enables the users to find their lost items easily and is beneficial to vendors. It allows them to have a clear understanding of the usage patterns.
IoT-based goods condition monitoring in transit
It is essential to monitor goods in transit, especially pharmaceutical or food and beverage products. This is an effective way of tackling the issue of food shortage. The most significant sensor value is the temperature sensor data in this use case. It assures that the product in transit is safe throughout the delivery process. This is achieved by closely monitoring the transit and storage stages and the entire supply chain.
Predictive maintenance
Most companies in China have invested mainly in linking predictive maintenance and artificial intelligence. This allows them to quickly estimate the remaining beneficial life of assets and make sure that before they fail, they are repaired.
The IoT market in China
The Chinese IoT market is anticipated to experience a noteworthy development with a CAGR of about 23 per cent throughout the period forecasted. China is proposed to be the top IoT market in the Asia Pacific. Its IoT market size is estimated to be more than $65.4billion in 2022.
IoT appearance of “Internet Plus”, a section of the plan “Made in China 2025”, is considered a massive potential in making the country’s economy a big deal. One significant factor driving the growth of the IoT in China is the rapid increase of smartphone users in the country. The IoT market in China is categorized based on infrastructure, application and vertical.
The market is divided into platforms, analytics, access technologies and mobile networks, security, and storage and cloud solutions based on infrastructure. The vertical market is segmented into transport, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, energy, public, services, and many more sections.
Furthermore, the application market is divided into smart cities, smart homes, smart grids, smart wearable, smart sensors, smart cities, smart grid, connected healthcare, connected cars, industrial internet, and many others.
Internet plus Roadmap
The new strategy of Internet plus in China has a vast influence on businesses across all industries, especially with the growth of the big data and data centres roles. It is essential for any business aiming to enter the Chinese IoT market to understand Internet Plus better, as it is an essential component needed to achieve success.
The motive of building the Internet Plus initiative was to link the developing economy of China to the power of connected services. China has so many traditional industries, ranging from agricultural to manufacturing sectors.
According to its 2015 work report, the government has already stated that it will introduce critical projects to develop networks, equipment, energy, biomedicines, circuits, and materials to enable the upcoming industries to become leading ones. The quest for this push comes due to the success of the manufacturing industry that has enabled China to grow at astonishing rates. More new sources of growth are required. In 2019, China recorded a gross domestic product of 4.4, higher than the GDP of the United States and Germany. This represented a potential opportunity for significant developments.
The Growth of China’s footprint in Global IoT
The expansion of the electronics manufacturing industry in China has offered a base for the rapid growth of IoT products and services. Immense consumer demands for domestic products have further roused this. By the end of 2020, China contributed to around three-quarters of cellular IoT connections globally. Cisco projects that by 2023, China will be the leading provider of the 5G connection in the world.
Private digital technology industries in China have embraced IoT as a new stream of generating revenue, providing saturation for the market of present products and services. For instance, Xiaomi in 2020 generated more than 30 per cent of its revenue from the IoT and articulates that over 50 per cent of its total revenue comes from markets outside the country. Xiaomi stated that it aims to connect over 350 million smart home appliances by the end of the year 2022. Moreover, companies like Huawei and China have already established IoT platforms for large-scale consumers.
These industries control the entering strengths of new sectors in networking and artificial intelligence (AI), especially the smart connected vehicles. On the other hand, demands on the performance of these developing IoT ecosystems enable most Chinese companies to become world leaders in enabling technologies.
Moreover, the development of IoT in China primarily benefits from the vast spending of the state in enabling infrastructure. By mid-2022, the Chinese government claims it will have installed over 800,000 5G base stations. The telecom operators owned by the Chinese government are anticipated to invest over 200 billion USD in network infrastructure before 2025. Most European actors have developed an interest in collaborating with Chinese entities due to their rising profiles in IoT technologies.
How the Chinese state is helping to drive IoT developments
IoT in China was a step in the pervasive application of ICT that the top government leadership identified as a universal trend over 20 years ago. It was recognized as a tool that should be mastered for a company’s success in this competitive world. Both national and regional state agencies have promptly churned the stimulation of IoT developments.
Besides, the partnership between public and private companies has contributed to developing the IoT ecosystem in China, including enabling technologies like the 5G infrastructure. In 2013, the IMT-2020 5G Promotion Group was established by the alliance of three national ministries. The group aimed at coordinating efforts by the government, enterprises owned by the state, research institutes and private companies. For Chinese companies to move up the technological ladder, they must play a significant role in influencing the guiding standards of ICT development.
The aim of China in Shaping IoT standards
IoT in China related to standardization happens under the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) and MIIT. The technical standardization committees do much of the work. Although these committees are technically independent, they are, in reality, closely allied with the Chinese state agencies.
The prominent technological firms in china are among the most influential players that have had a noticeable responsibility in developing IoT-linked standards. Nevertheless, the unopened nature of the technical standardization processes in China has contributed to a substantial discrepancy with standards abroad. It is estimated that only 15 per cent of TC-260 standards are presently affiliated with international standards.
The government recognizes that most Chinese firms are at a competitive shortcoming abroad if they are subjected to similar local and foreign standards. This has steered the attempts of rationalizing local standards and blending them with universal ones. Simultaneously, the Chinese government is pursuing internationalizing its local standards by promoting them out of the country.
In China, the Standards development organizations (SDOs) have also pursued the industrial growth of standards in cycles with real-life applications. Hence, the pace of standardization related to IoT responds to different market forces. Generally, Chinese actors are mainly contributing to a notable influence on the IoT standardization processes in the world.
Can IoT accelerate the world’s digital division into a ‘splinter net’?
With China influencing the growth of IoT, most countries are being forced to evaluate the connection risks to networks in China. In most open-minded democracies, many concerns are being raised regarding CPP’s political values and methods.
These are replicated in debates over the contribution of Chinese companies in the development of 5G networks and the responsibility of Chinese players in technical standardization. Concerns regarding the purported cyber-espionage sponsored by the Chinese state and alleged the control of companies like Huawei has trickled over into IoT debates.
Regardless of the talks of bringing together technologies and industrial policies in China, there is little appetite for widespread ‘decoupling’ in other countries. To this point, most governments cannot offer sufficient resources that can substitute the prospects provided by the emerging IoT ecosystem in China.
Simultaneously, there is increased competition between all advanced economies to control markets and technologies in the future. This has been noted in the growing outbreaks of policies by the European Union to attain ‘digital sovereignty at the cost of the United States’ business interests. It is unlikely to have an outlook of the international internet ‘splintering’ simply into a “liberal independent” internet on one side and the other cyberspace dominated by China. Instead, the world can probably achieve sustained growth towards a ‘federation’ of united networks.
The United States is at an edge of pursuing technological ‘decoupling’ with China, which strive to reduce the reliance on the US for core technologies. Most third parties will likely continue to choose elements and connections that suit them by following their paths.
China’s IoT Ecosystem
Various reports and studies indicate that China is prowess growing to become an IoT sector. According to the Morgan Stanley report, it is estimated that between 2020 and 2030, the IoT investment in China will be up to $27 billion. In 2015, China launched an initiative dubbed “Made in China 2025”. It was exhibited on the Industrie 4.0 in Germany. The primary goal of introducing this initiative was to improve IoT manufacturing in China.
Moreover, the Made in China 2025 initiative had a significant component dabbed the ‘Internet Plus’. It offers a comprehensive tactic that integrates big data, cloud computing, mobile internet, and IoT initiatives, thus promoting IT and smart technologies in the country. More importantly, this initiative aimed to reduce the rate at which China depends on foreign technology, much to the alarm of Trump’s management.
China is rapidly accelerating its governance position in leading technologies like IoT. It has been reported that the Chinese government aims to invest over a trillion dollars to roll out technologies, from IoT to wireless networks to AI. The IoT ecosystem in China comprises key hardware providers like Huawei, Xiaomi, MediaTek, and Qualcomm. The IoT suppliers of China network providers include China Unicom, China Mobile Limited, and China Telecom Corporation. Software providers are Microsoft, IBM, and Alibaba.
According to a report, the leading areas of IoT applications in China include the industrial, automation, healthcare, consumer electronics, and transportation sectors. Based on the use cases, the largest markets are held by the automotive and transportation applications in speed monitoring and navigation areas.
Trends of IoT in China
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) is rapidly evolving as a top IoT technological trend, especially in China. The NB-IoT technology dramatically improves the device’s power consumption rate, spectrum efficiency and system capabilities.
Moreover, a substantial part of the NB-IoT modules was exported outside China, specifically to help fight the COVID-19 pandemic in applications like contactless body temperature sensors and door status trackers. Some of the uses of the NB-IoT technology already in use include;
• Intelligent road management
• Asset tracking
• Smart home appliances
• Smart locks.
NB-IoT is becoming as significant as LTE since it is easily deployable in industries, households, utilities, and even GSM connections. It is predicted that by the end of 2022, NB-IoT will have reached over 26 per cent of the cellular IoT connections. The China Unicom network provider has attracted more than 20,000 industrial IoT companies, whereas the China Telecom network provider has attracted over 50 million customers.
Advantages of Manufacturing IoT Devices in China
Below are the pros and cons of manufacturing IoT devices in China.
1. Low manufacturing costs – Manufacturing IoT gadgets in China is less costly than in most countries. China has a vast difference in labour cost and has numerous factories manufacturing all IoT essential parts such as cables, sensors, batteries, gateways, etc.
2. Faster production – As there are many Chinese IoT companies and cheap labour in the country, it is now easy to acquire IoT devices in a shorter time.
3. Market expansion opportunities – Manufacturing IoT devices in China is an excellent way to go if you intend to triumph over the global IoT market. All devices manufactured in China quickly enter the Asian market, and the shipping cost is also low.
4. Better service – Although we cannot guarantee that all IoT companies offer excellent services, most companies manufacture fantastic devices. Moreover, China hosts so many factories, and the competition rate is also very high in the country.
Disadvantages of Manufacturing IoT Devices in China
1. Difficulties with finding a factory – Although there are numerous manufacturing companies in China, it is challenging to find the right one. Most important, when finding a factory, it is essential to find one that can manufacture your desired product.
2. Language barrier – Only 10 million people in China can fluently speak English. That is virtually nothing when compared with the whole population. Hence, you may face some hard times trying to explain what you intend to produce, its cost, and more.
3. Costly and time-consuming shipping – A gadget must be shipped after being manufactured. If you are to sell them in China, everything is fine. But you will have to pay a lot if you ship your devices to European countries or the United States. Moreover, you will have to wait for a long time before your product arrives at your desired location.
4. Quality problems – It is deplorable that China is not allied with an exceptional quality of products. This does not mean that everything produced in China is faulty – no, the stereotype only exists and is well-founded. Therefore, you may encounter difficulties regarding the quality of materials and work when you choose the wrong factory to manufacture your IoT devices.
5. Copyright issues – In China, it is unfortunate that the protection of Intellectual Property is more risky and expensive. Although things are becoming better as we progress, you may still encounter some issues regarding trademarks and copyrights.
How does China Cope with the Current IoT Challenges
IoT is currently facing numerous challenges. Below is a brief description of how China is coping with these challenges.
Connectivity
No system can link IoT to many gadgets on the internet. Hence, China has introduced a decentralized architecture to reduce the load from the servers. They are implementing blockchain technology as a perfect solution to this connectivity issue.
Security
IoT is encountering severe issues related to security. Security proves to be a disastrous and disturbing issue for the public and administration who have embraced the IoT technology. Hackers are accessing smart devices and changing their instructions, thereby endangering the future of IoT. As this is a big challenge, IoT companies should implement strategies of overcoming this issue for the technology to grow. Before focusing on functionality, most IoT companies in China first address the issue of security before releasing the technology to the market for use.
Standards
Standard is a significant IoT issue as most companies are not implanting approaches when planning their processes. This is because they disapprove of a precise standard, thus making the devices unreliable. The Chinese government plays a vital role in encouraging IoT companies to adopt a certain standard when planning and executing their IoT systems.
Lack of intelligent analysis
Some of the algorithms produced by IoT devices are at times inaccurate. For instance, it is possible for a sensor sometimes to give incorrect data, in turn giving wrong results and inaccurate analysis. China is developing strategies that will offer proper analytical tools to help overcome these inaccuracies.
Compatibility
Multiple IoT companies are developing different technologies hence posing a question to the issue of a specific standard. China has noticed that this is a significant issue and is already establishing ways to approve a specific standard for IoT technology.
Why you should Consider MOKOSmart when Choosing IoT in China
When choosing your IoT in China, consider MOKOSmart. We are the top IoT supplier in China. Our company provides an excellent performance referent, advanced infrastructure algorithms and industrial equipment to its customers. Our products are developed to help both the world and engineering communities. The company is fully dedicated to implementing IoT technologies in China. Besides, our LoRa device-to-cloud platform offers low power solutions for IoT use cases. More specifically, we allow the fast growth and positioning of ultra-low power, cheap and long-range IoT networks, modules, gateways, sensors, and IoT services globally. Furthermore, MOKOSmart is a member of the LoRa Alliance.